电子科技大学:《现代数字信号处理理论与算法 Modern theory and algorithm of digital signal processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)08 盲信号处理 BSS
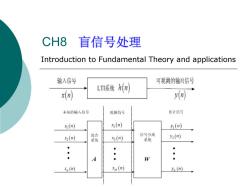
CH8 盲信号处理 Introduction to Fundamental Theory and applications 输入信号 可观测的输出信号 LT系绕h) x(n) 未知的输入信号 观测倍号 估计信号 s(n) (n) 3(n) 信号分离 5(n 混合 系统 (n) 系统 2(m A V s.(n) x (n) y(n)
CH8 Introduction to Fundamental Theory and applications

Contents 盲系统辨识 盲源分离(BSS, Blind Source Separation) 独立分量分析 (ICA, Independent Component Analysis) 信道盲均衡 盲波束形成 2020-01-18 2
2020-01-18 2 Contents
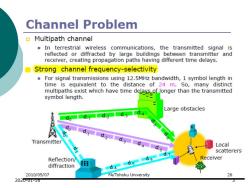
Channel Problem Multipath channel ■ In terrestrial wireless communications,the transmitted signal is reflected or diffracted by large buildings between transmitter and receiver,creating propagation paths having different time delays. 回 Strong channel frequency-selectivity For signal transmissions using 12.5MHz bandwidth,1 symbol length in time is equivalent to the distance of 24 m.So,many distinct multipaths exist which have time delays of longer than the transmitted symbol length. Large obstacles d Transmitter Local scatterers Reflection/ Receiver diffraction 进 d.4d.s 2010/05/07 FA/Tohoku University 26 2020-U1-18 5】
2020-01-18 3

Blind system identification o Time-varying radio channel ●( Channel identification has to be repeated continuously o Training bits constitute a significant portion (roughly 18%)of the transmitted sequence GSM system is based on burst mode communication, where bursts of 148 bits each are transmitted.Each burst has a 26 bit training sequence,which is used to update the channel model. o Fewer training bits,or even without them blind identification/estimation 2020-01-18 4
2020-01-18 4 Blind system identification Time-varying radio channel Channel identification has to be repeated continuously Training bits constitute a significant portion (roughly 18%) of the transmitted sequence GSM system is based on burst mode communication, where bursts of 148 bits each are transmitted. Each burst has a 26 bit training sequence, which is used to update the channel model. Fewer training bits, or even without them blind identification/estimation
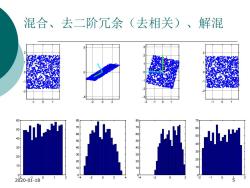
混合、去二阶冗余(去相关)、解混 0 -2 0 -2 -1 0 -1 0 60 50 00000000 000000010 50 40 n 0 30 30 20 20 10 10 0 2020-01-18 0 2 -2 0 0 0 15
混合、去二阶冗余(去相关)、解混 2020-01-18 5 - 1 0 1 - 2 - 1 0 1 2 - 2 - 1 0 1 2 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 - 2 0 2 - 5 0 5 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 - 2 - 1 0 1 - 3 - 2 - 1 0 1 2 3 - 4 - 2 0 2 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 - 1 0 1 - 2 - 1 0 1 2 - 2 - 1 0 1 2 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
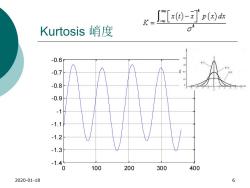
[x)-x灯p(x) Kurtosis峭度 -0.6 -3 -0.7 -0.8 -0.9 -1 -1.1 -1.2 -1.3 -1.4 0 100 200 300 400 2020-01-18 6
Kurtosis 峭度 2020-01-18 6 0 100 200 300 400 -1.4 -1.3 -1.2 -1.1 - 1 -0.9 -0.8 -0.7 -0.6
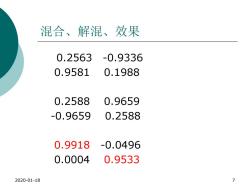
混合、解混、效果 0.2563 -0.9336 0.9581 0.1988 0.2588 0.9659 -0.9659 0.2588 0.9918 -0.0496 0.0004 0.9533 2020-01-18 7
混合、解混、效果 0.2563 -0.9336 0.9581 0.1988 0.2588 0.9659 -0.9659 0.2588 0.9918 -0.0496 0.0004 0.9533 2020-01-18 7
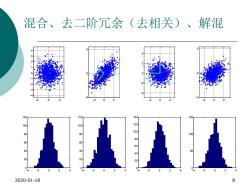
混合、去二阶冗余(去相关)、解混 5 2 .2 2 0 120 120 150 100 o 00 80 100 60 60 40 10 440000000 50 20 20 0 0 -2 0 4 .2 .2 0 2020-01-18 8
混合、去二阶冗余(去相关)、解混 2020-01-18 8 - 2 0 2 - 4 - 3 - 2 - 1 0 1 2 3 4 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 - 2 0 2 - 5 0 5 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 - 2 0 2 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 - 2 0 2 - 5 0 5 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 0 50 100 150
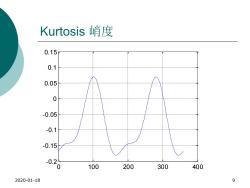
Kurtosis峭度 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 -0.05 -0.1 -0.15 -0. 0 100 200 300 400 2020-01-18 9
Kurtosis 峭度 2020-01-18 9 0 100 200 300 400 -0.2 -0.15 -0.1 -0.05 0 0.05 0.1 0.15
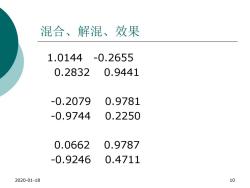
混合、解混、效果 1.0144-0.2655 0.2832 0.9441 -0.2079 0.9781 -0.9744 0.2250 0.0662 0.9787 -0.9246 0.4711 2020-01-18 10
混合、解混、效果 1.0144 -0.2655 0.2832 0.9441 -0.2079 0.9781 -0.9744 0.2250 0.0662 0.9787 -0.9246 0.4711 2020-01-18 10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《现代数字信号处理理论与算法 Modern theory and algorithm of digital signal processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)07 Array Signal Processing.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代数字信号处理理论与算法 Modern theory and algorithm of digital signal processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)06 LS Method & RLS Algorithm.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代数字信号处理理论与算法 Modern theory and algorithm of digital signal processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)05 卡尔曼滤波器 Kalman Filter.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代数字信号处理理论与算法 Modern theory and algorithm of digital signal processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 LMS Algorithm.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代数字信号处理理论与算法 Modern theory and algorithm of digital signal processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)03 Wiener Filter.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代数字信号处理理论与算法 Modern theory and algorithm of digital signal processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)02 PSD Estimation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代数字信号处理理论与算法 Modern theory and algorithm of digital signal processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)01 Introduction to ADSP - Theory, Algorithm and Application.pdf
- IC封装设计与仿真(参考资料).pdf
- 山东省中等职业学校骨干教师专业技能分级培训入学测试题:电子电器应用与维修(中级)专业训前测试题.doc
- 山东理工大学:《电力电子》课程教学资源(实验指导书).pdf
- 山东理工大学:《电工学(电工技术)》课程教学资源(实验指导书).pdf
- 山东理工大学:《直流调速和交流调速》课程教学实验指导书(共五个实验).pdf
- 山东理工大学:《传感器》课程教学资源(实验指导书).pdf
- 山东理工大学:《电磁场与电磁波》课程教学实验指导书(共四个实验).pdf
- 山东理工大学:《数字电子技术基础》课程教学资源(实验指导书).pdf
- 山东理工大学:《模拟电子技术基础》课程教学资源(实验指导书).pdf
- 山东理工大学:《可编程控制器》课程教学实验指导书(共三章).pdf
- 山东理工大学:《高频电子线路》课程教学资源(实验指导书).pdf
- 山东理工大学:《电工学(电子技术)》课程教学资源(实验指导书).pdf
- 山东理工大学:《电子工艺》课程教学资源(实验指导书).pdf
- 《数字电子技术》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 数模转换与模数转换 第二节 A/D 转换器.pdf
- 海南大学:《电路与电子技术(计算机电子电路)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 直流电路分析方法.ppt
- 海南大学:《电路与电子技术(计算机电子电路)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 放大器基础.ppt
- 海南大学:《电路与电子技术(计算机电子电路)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 三相电路及其应用.ppt
- 海南大学:《电路与电子技术(计算机电子电路)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 交流电路的基本分析方法.ppt
- 海南大学:《电路与电子技术(计算机电子电路)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 门电路和组合逻辑电路.ppt
- 海南大学:《电路与电子技术(计算机电子电路)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 集成运算放大器及其应用(集成运算放大器及其他模拟集成电路).ppt
- 海南大学:《电路与电子技术(计算机电子电路)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 触发器和时序逻辑电路.ppt
- 海南大学:《电路与电子技术(计算机电子电路)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)章节知识点复习(齐琦).ppt
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 绪论(李兴明).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 确定与随机信号分析.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 数字调制方法 3.2 无记忆调制方法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 数字调制方法 3.3 有记忆信号的传输方式.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 数字调制方法 3.4 数字调制信号的功率谱.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 AWGN信道的最佳接收机 4.2 波形与矢量AWGN信道.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 AWGN信道的最佳接收机 4.3 带限信号传输的最佳检测和错误概率.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 AWGN信道的最佳接收机 4.4 功限信号传输的最佳检测和错误概率 4.5 不确定情况下的最佳检测(非相干检测).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 AWGN信道的最佳接收机 4.5 不确定情况下的最佳检测 4.6 数字信号传输方法的比较.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 AWGN信道的最佳接收机 4.9 CPM信号的最佳接收机 4.10 有线和无线通信系统的性能分析.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 载波和符号同步 5.1 信号参数估计 5.2 载波的相位估计(1/3).pdf
