厦门大学:《海洋环境化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chap 05 Marine eutrophication and Red tide(part 3)

Contents ◼ Introduction ◼ Part One Mechanisms in marine pollution ◼ Part two Topics in marine pollution ◼ Part three Measurement of biological response toxicity and water quality assessments ◼
Contents ◼ Introduction ◼ Part One Mechanisms in marine pollution ◼ Part two Topics in marine pollution ◼ Part three Measurement of biological response toxicity and water quality assessments ◼

Part two Topics in marine pollution ◼ Chap.2 Marine oxygen-demanded organic pollution ◼ Chap.3 Eutrophication and Red tide ◼ Chap.4 Oil pollution of the sea ◼ Chap.5 Marine synthetic organic pollution ◼ Chap.6 Heavy metal contamination in the sea ◼ Chap.7 Marine radioactivity pollution ◼ Chap.8 Marine heat pollution ◼ Chap.9 Other topics of marine polltion
Part two Topics in marine pollution ◼ Chap.2 Marine oxygen-demanded organic pollution ◼ Chap.3 Eutrophication and Red tide ◼ Chap.4 Oil pollution of the sea ◼ Chap.5 Marine synthetic organic pollution ◼ Chap.6 Heavy metal contamination in the sea ◼ Chap.7 Marine radioactivity pollution ◼ Chap.8 Marine heat pollution ◼ Chap.9 Other topics of marine polltion


Chap.3 Eutrophication and Red tide 3.1 What is Eutrophication? (definition) 3.2 Why Should We Be Concerned? (harmful effect) 3.3 The nutrient in the coastal seawater 3.4 Eutrophication in the coastal seawater 3.5 HABs and Red tide
Chap.3 Eutrophication and Red tide 3.1 What is Eutrophication? (definition) 3.2 Why Should We Be Concerned? (harmful effect) 3.3 The nutrient in the coastal seawater 3.4 Eutrophication in the coastal seawater 3.5 HABs and Red tide

Eutrophication Eutrophication is the natural process by which waters (lakes, rivers etc) become excessively enriched with nutrients, typically nitrogen and phosphorus. It is one of the ways in which a water body (lake, rivers, and seas) transforms from a state where nutrients are scarce (oligotrophic), through a slightly richer phase (mesotrophic) to an enriched state (eutrophic). Human activities often enhance the rate of change due to activities such as farming, forestry, road-building, industry and waste treatment that cause nutrients to enter watercourses. This nutrient enrichment often results in a population explosion of algae and other aquatic plants
Eutrophication Eutrophication is the natural process by which waters (lakes, rivers etc) become excessively enriched with nutrients, typically nitrogen and phosphorus. It is one of the ways in which a water body (lake, rivers, and seas) transforms from a state where nutrients are scarce (oligotrophic), through a slightly richer phase (mesotrophic) to an enriched state (eutrophic). Human activities often enhance the rate of change due to activities such as farming, forestry, road-building, industry and waste treatment that cause nutrients to enter watercourses. This nutrient enrichment often results in a population explosion of algae and other aquatic plants

Eutrophication BOD and Eutrophication - rapid succession in a body of water because of an increase in biological productivity. (Oligotrophic lakes and rivers have clear water and low biological productivity)
Eutrophication BOD and Eutrophication - rapid succession in a body of water because of an increase in biological productivity. (Oligotrophic lakes and rivers have clear water and low biological productivity)
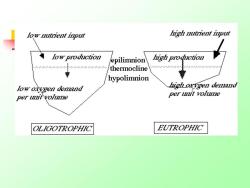
o"e2味iput high nutrient input o翔r1oGo2 epilimnion high production thermocline 5.5.5.55》 hypolimnion lowoxggen demand high osvgen deniand per unit volume per tnit volume LY⑦TRPH, EUTROPHIC

Sewage Appeared To Cause The Lake To Become Eutrophic
Sewage Appeared To Cause The Lake To Become Eutrophic

Chap.3 Eutrophication and Red tide 3.1 What is Eutrophication? (definition) 3.2 Why Should We Be Concerned? (harmful effect) 3.3 The nutrient in the coastal seawater 3.4 Eutrophication in the coastal seawater 3.5 HABs and Red tide
Chap.3 Eutrophication and Red tide 3.1 What is Eutrophication? (definition) 3.2 Why Should We Be Concerned? (harmful effect) 3.3 The nutrient in the coastal seawater 3.4 Eutrophication in the coastal seawater 3.5 HABs and Red tide

In shallow lakes and where plant production is high, deoxygenation of the sediment and water occur frequently too (black sediment, Photo 3)
In shallow lakes and where plant production is high, deoxygenation of the sediment and water occur frequently too (black sediment, Photo 3)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 厦门大学:《海洋环境化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chap 04 Marine eutrophication and Red tide(part 2).ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋环境化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chap 03 Marine eutrophication and Red tide(part 1).ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋环境化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chap 02 Marine oxygen-demanded organic pollution.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋环境化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chap 12 The protection of marine environment 海洋环境保护.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋环境化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chap 11 Marine radioactive and thermal pollution.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋环境化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chap 01 Mechanisms and problems of marine pollution.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十三章 保护海洋生物多样性.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 海洋污染和赤潮现象.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 海洋渔业资源的科学管理.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 海洋主要生态系统类型.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 海洋生态系统的分解作用与生物地化循环.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 海洋生态系统的能流及次级生产力.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 海洋初级生产力.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 生物群落的组成、结构和生态演替.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 海洋生物群落中的种间关系.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 生态系统中的生物种群.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 海洋非生物生态因子及其生态作用.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 海洋环境与海洋生物生态类群.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 生态系统概述.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)绪论(授课教师:黄凌风、郭丰).ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋环境化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chap 06 Marine eutrophication and Red tide(case study)大鹏湾环境与赤潮的研究.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋环境化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chap 07 Oil pollution of the sea 海洋石油污染(part 1/2).ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋环境化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chap 08 Oil pollution of the sea 海洋石油污染(part 2/2).ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋环境化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chap 09 海洋合成有机化合物污染 Maine Persistent Organic Pollutants(POPs)pollution(part 1/2).ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋环境化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chap 09 海洋合成有机化合物污染 Maine Persistent Organic Pollutants(POPs)pollution(part 2/2).ppt
- 福州大学:《水污染控制工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 污水水质与污水出路.ppt
- 福建船政交通职业学院:《环境监测》课程教学实验指导书(共十六个实验).doc
- 福建船政交通职业学院:《环境监测》课程电子教案(授课讲义,负责人:陈健).doc
- 福建船政交通职业学院:《环境监测》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 绪论.ppt
- 福建船政交通职业学院:《环境监测》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 大气和废气监测.ppt
- 福建船政交通职业学院:《环境监测》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 水和废水监测.ppt
- 福建船政交通职业学院:《环境监测》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七章 噪声污染监测.ppt
- 福建船政交通职业学院:《环境监测》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第九章 监测过程的质量保证.ppt
- 福建船政交通职业学院:《环境监测》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 土壤污染监测.ppt
- 福建船政交通职业学院:《环境监测》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第八章 环境放射性监测.ppt
- 福建船政交通职业学院:《环境监测》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第六章 生物污染监测.ppt
- 福建船政交通职业学院:《环境监测》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 固体废物监测.ppt
- 新疆大学:《景观生态学》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 新疆大学:《景观生态学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七章 景观生态学与土地持续利用.ppt
- 新疆大学:《景观生态学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 景观动态变化.ppt
