南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)02-Names & Functions

Lecture 2 Names Functions 09/25 Slides adapted from Berkeley CS61a
Lecture 2 - Names & Functions 09/25 Slides adapted from Berkeley CS61a

Program Structure
Program Structure

Review-Expressions Primitive Expressions: 2 “he11o!" add numbers strings names Arithmetic Expressions: 1+2 15//3 add(3,4) Call Expressions: max(add(2,3),5*min(-1,4))
Review - Expressions Primitive Expressions: Call Expressions: 2 “hello!” add add(3, 4) max(add(2, 3), 5 * min(-1, 4)) Arithmetic Expressions: 1 + 2 15 // 3 numbers strings names
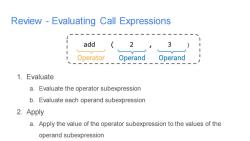
Review-Evaluating Call Expressions add (2 ,3 Operator Operand Operand 1.Evaluate a.Evaluate the operator subexpression b.Evaluate each operand subexpression 2.Apply a.Apply the value of the operator subexpression to the values of the operand subexpression
Review - Evaluating Call Expressions 1. Evaluate a. Evaluate the operator subexpression b. Evaluate each operand subexpression 2. Apply a. Apply the value of the operator subexpression to the values of the operand subexpression add ( 2 , 3 ) Operator Operand Operand

Nested Call Expression Evaluate operator Evaluate operands 3 Apply! 45 add(add(6,mu1(4,6),mu1(3,5)) add 30 15 add(6,mu1(4,6)) mu1(3,5) 24 add 6 mu1(4,6) mul 3 5 mul 4 6 Expression Tree
Nested Call Expression Evaluate operator Evaluate operands Apply! add(add(6, mul(4, 6)), mul(3, 5)) add 1 2 3 add(6, mul(4, 6)) add 6 mul(4, 6) mul 4 6 24 30 mul(3, 5) 15 mul 3 5 45 Expression Tree

Values Programs manipulate values Values represent different types of data Integers:2 44-3 Strings:“hello!”“cs61a” Floats:3.144.5-2.0 Booleans:True False
Values Programs manipulate values Values represent different types of data Floats: Integers: Strings: Booleans: 2 44 -3 3.14 4.5 -2.0 “hello!” “cs61a” True False

Expressions Values Expressions evaluate to values in one or more steps Expression: Value: he11o!' 'hello!' 7/2 3.5 add(1,max(2,3)) 4
Expressions & Values Expressions evaluate to values in one or more steps ‘hello!’ 7 / 2 3.5 add(1, max(2, 3)) 4 Expression: ‘hello!’ Value:
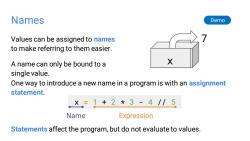
Names Demo Values can be assigned to names to make referring to them easier. A name can only be bound to a X single value. One way to introduce a new name in a program is with an assignment statement. ×=1+2*3-4//5 Name Expression Statements affect the program,but do not evaluate to values
Names Values can be assigned to names to make referring to them easier. A name can only be bound to a single value. Demo One way to introduce a new name in a program is with an assignment statement. x = 1 + 2 * 3 - 4 // 5 Name Expression 7 x Statements affect the program, but do not evaluate to values

Check Your Understanding >>f min >>>f= max >>g,h min, max >>> max g >>>max(f(2,g(h(1,5),3)),4) ???
Check Your Understanding >>> f = min >>> f = max >>> g, h = min, max >>> max = g >>> max(f(2, g(h(1, 5), 3)), 4) ???
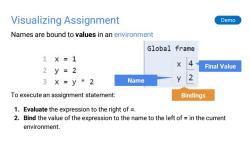
Visualizing Assignment Demo Names are bound to values in an environment Global frame 1X=1 X 2y=2 Final Value 3X=y*2 Name To execute an assignment statement: Bindings 1.Evaluate the expression to the right of = 2.Bind the value of the expression to the name to the left of in the current environment
Visualizing Assignment Names are bound to values in an environment To execute an assignment statement: 1. Evaluate the expression to the right of =. 2. Bind the value of the expression to the name to the left of = in the current environment. Final Value Bindings Name Demo
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)01-Introduction(主讲:冯新宇).pptx
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Modular Verification of Concurrent Assembly Code with Dynamic Thread Creation and Termination.ppt
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Modular Verification of Assembly Code with Stack-Based Control Abstractions.ppt
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)An Open Framework for Foundational Proof-Carrying Code.ppt
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Certifying Low-Level Programs with Hardware Interrupts and Preemptive Threads.ppt
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)On the Relationship between Concurrent Separation Logic and Assume-Guarantee Reasoning.ppt
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Technical Report TTIC-TR-2008-1(Local Rely-Guarantee Reasoning).pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Deny-Guarantee Reasoning.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)A Rely-Guarantee-Based Simulation for Verifying Concurrent Program Transformations.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Modular Verification of Linearizability with Non-Fixed Linearization Points.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Characterizing Progress Properties of Concurrent Objects via Contextual Refinements.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Rely-Guarantee-Based Simulation for Compositional Verification of Concurrent Program Transformations.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Compositional Verification of Termination-Preserving Refinement of Concurrent Programs.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)A Program Logic for Concurrent Objects under Fair Scheduling.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)A Practical Verification Framework for Preemptive OS Kernels.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Progress of Concurrent Objects with Partial Methods.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)POMP:Protocol Oblivious SDN Programming with Automatic Multi-Table Pipelining.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Decay of Correlation in Spin Systems.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Counting with Bounded Treewidth.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源:The Magical Wild Animals(神奇的动物).pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)03-Control.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)04-Environment Diagrams.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)05-Higher-Order Functions.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)06-Recursion.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)07-Recursion Examples.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)08-Containers.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)09-Data-Abstractions.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)10-Trees.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)11-Mutable-Values.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)12-Mutable Functions & Growth.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)13-Iterators.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)13-Iterators & Generators.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)14-Object-Oriented Programming.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)15-Inheritance.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)16-Linked Lists & Mutable Trees.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)17-Interfaces.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)18-Scheme.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)19-More-Scheme.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)20-Interpreters.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)21-Macros.pptx
