南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)18-Scheme

Lecture 19 -Scheme
Lecture 19 - Scheme

Scheme Scheme is a dialect of Lisp. It uses a lot of parentheses. LISP IS OVER HALFA I WONDER IF THE CYCLES THESE ARE YOUR CENTURY OLD AND IT WILL CONTINUE FOREVER. FATHER'S PARENTHESES STILL HAS THIS PERFECT, TIMELESS AIR ABOUT IT. ELEGANT A FEW CODERS FROMEACH WEAPONS NEW GENERATION RE- DISCOVERING THE LISP ARTS. FOR A MORE...CIVIUZED AGE 'The greatest single programming language ever designed." -Alan Kay,co-inventor of Smalltalk and OOP "The only computer language that is beautiful." -Neal Stephenson,John DeNero's favorite sci-fi author
Scheme Scheme is a dialect of Lisp. It uses a lot of parentheses. "The greatest single programming language ever designed." -Alan Kay, co-inventor of Smalltalk and OOP "The only computer language that is beautiful." -Neal Stephenson, John DeNero's favorite sci-fi author
Why another language? The goal of this class is not to teach Python,but rather to teach a variety of programming techniques and core concepts. How does learning another language help us? To see some key components across many programming languages. To see what paradigms certain languages prioritize. To learn how interpreters are implemented!
Why another language? The goal of this class is not to teach Python, but rather to teach a variety of programming techniques and core concepts. How does learning another language help us? ● To see some key components across many programming languages. ● To see what paradigms certain languages prioritize. ● To learn how interpretersare implemented!

Scheme Expressions
Scheme Expressions

Scheme expressions Scheme programs consist entirely of two types of expressions. Atomic expressions Self-evaluating:numbers,booleans 3,5.5,-10,#t,#f Symbols:names bound to values +modulo,list,x,foo,hello-world Combinations (
Scheme programs consist entirely of two types of expressions. Atomic expressions ● Self-evaluating: numbers, booleans 3, 5.5, -10, #t, #f ● Symbols: names bound to values +, modulo, list, x, foo, hello-world Combinations ( …) Scheme expressions
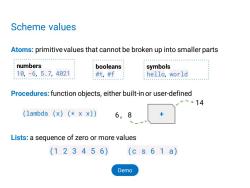
Scheme values Atoms:primitive values that cannot be broken up into smaller parts numbers booleans symbols :10,-6,5.7,4021 #t,#f hello,world Procedures:function objects,either built-in or user-defined 2-14 (1ambda (x)(xx)) 6, 8 Lists:a sequence of zero or more values (123456) (c s 6 1 a) Demo
Scheme values Atoms: primitive values that cannot be broken up into smaller parts Procedures:function objects, either built-in or user-defined Lists: a sequence of zero or more values numbers 10, -6, 5.7, 4021 symbols hello, world booleans #t, #f (1 2 3 4 5 6) (c s 6 1 a) 6, 8 + 14 (lambda (x) (* x x)) Demo

Combinations All non-primitive expressions in Scheme have the following syntax: (.. A combination is either a call expression or a special form expression. The operator of a call expression evaluates to a procedure. (+23) (abs(/285)) (<48.5) The operator of a special form expression is a special form. (define x 5) (1f#t1020) (1ambda (x)(xx))
Combinations All non-primitive expressions in Scheme have the following syntax: ( …) A combination is either a call expression or a special form expression. The operator of a call expression evaluates to a procedure. (+ 2 3) (abs (/ 20 5)) (< 4 8.5) The operator of a special form expression is a special form. (define x 5) (if #t 10 20) (lambda (x) (* x x))
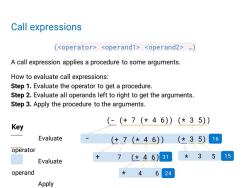
Call expressions () A call expression applies a procedure to some arguments. How to evaluate call expressions: Step 1.Evaluate the operator to get a procedure. Step 2.Evaluate all operands left to right to get the arguments. Step 3.Apply the procedure to the arguments. (-(+7(*46)(*35) Key Evaluate (+7(*46)) (*35) 16 operator 7(*46)31 大3 5 15 Evaluate operand 4 6 24 Apply
(* 4 6) Call expressions ( …) A call expression applies a procedure to some arguments. How to evaluate call expressions: Step 1. Evaluate the operator to get a procedure. Step 2. Evaluate all operands left to right to get the arguments. Step 3. Apply the procedure to the arguments. (- (+ 7 (* 4 6)) (* 3 5)) - (+ 7 (* 4 6)) + 7 * 4 6 * 3 (* 3 5) 5 24 31 15 16 Key Evaluate operator Evaluate operand Apply

Special form expressions () Special forms have special behaviors that allow us to write complex programs. How to evaluate special form expressions: Each special form has its own rules! ● Some operands may not be evaluated. scm> (define x (/10 2)) X scm> (if(>18)(-34)(/10)) -1 scm> (1 ambda(xy)(+xy)) (lambda(xy)(+xy))
Special form expressions ( …) Special forms have special behaviors that allow us to write complex programs. How to evaluate special form expressions: ● Each special form has its own rules! ● Some operands may not be evaluated. scm> (define x (/ 10 2)) x scm> (if (> 1 0) (- 3 4) (/ 1 0)) -1 scm> (lambda (x y) (+ x y)) (lambda (x y) (+ x y))

Special Forms
Special Forms
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)17-Interfaces.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)16-Linked Lists & Mutable Trees.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)15-Inheritance.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)14-Object-Oriented Programming.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)13-Iterators & Generators.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)13-Iterators.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)12-Mutable Functions & Growth.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)11-Mutable-Values.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)10-Trees.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)09-Data-Abstractions.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)08-Containers.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)07-Recursion Examples.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)06-Recursion.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)05-Higher-Order Functions.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)04-Environment Diagrams.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)03-Control.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)02-Names & Functions.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)01-Introduction(主讲:冯新宇).pptx
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Modular Verification of Concurrent Assembly Code with Dynamic Thread Creation and Termination.ppt
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Modular Verification of Assembly Code with Stack-Based Control Abstractions.ppt
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)19-More-Scheme.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)20-Interpreters.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)21-Macros.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)22-Streams.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)23-SQL-I.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)24-SQL-II.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)25-Conclusion, and Final Exam Review.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)01 绪论 Introduction(主讲:曹洋).pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)02 傅里叶分析与卷积 Fourier Analysis and Convolution.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)03 数字图像处理基础 Basics of Digital Image Processing.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)04 图像模型 Basics of Image.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)05 空域滤波 Spatial Filtering.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)06 小波变换 Wavelet Analysis.pptx
- CodeIgniter 中国开发者社区:CodeIgniter4 中文手册(版本 4.0.0).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)07 图像复原 Image Restoration.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)08 自适应滤波 Adaptive Filter.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)要点复习 Review(主讲:曹洋).pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)09 图像压缩 Image Compression.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算机视觉》课程教学资源(参考论文)Tour Into the Picture_Using a Spidery Mesh Interface to Make Animation from a Single Image.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算机视觉》课程教学资源(参考论文)3D photography on your desk.pdf
