南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)21-Macros

Lecture 22 Macros Chris Allsman
Lecture 22 - Macros Chris Allsman

Macrosns ⊙
Mac OS Macros Macron Macarons Macaroni

Announcements ●HW6out,due Tues8/6 ●Proj4,Scheme out o Phase I/ll due Mon 8/5 o Whole project due Fri 8/9 o 1 EC point by submitting Thurs 8/8 11:59 PM PDT Midterm Regrades due 8/1
Announcements ● HW6 out, due Tues 8/6 ● Proj4, Scheme out ○ Phase I/II due Mon 8/5 ○ Whole project due Fri 8/9 ○ 1 EC point by submitting Thurs 8/8 11:59 PM PDT ● Midterm Regrades due 8/1

Review:Interpreters Representing Expressions
Review: Interpreters & Representing Expressions

Read-Eval-Print Loop (REPL) Read Lexer ..expression... value output Eval Print ,,。… input representation string string …tokens: Parser 。..年gg年。。。。。。 “(+12)” +12N 3 ["(",,“+”,1,2,“)",]Pair("+”,Pair(1,Pair(2,ni1))
input string value expression representation Read-Eval-Print Loop (REPL) Read Eval Print output string Lexer Parser tokens “(+ 1 2)” + 1 2 3 [“(“, “+”, 1, 2, “)”, ] Pair(“+”, Pair(1, Pair(2, nil)))

Demo Representing Expressions o In Scheme,we can create lists that "look like"combinations o In fact,in Scheme,expressions are lists (or primitive values) Quoting prevents evaluation of an expression Calling eval on an unevaluated expression will evaluate that value scm>‘(+12) scm>(list quotient 10 2) (+12) (quotient 10 2) scm>(eva1'(+12)) scm>(eval (list quotient 10 2)) 3 5
Representing Expressions ● In Scheme, we can create lists that “look like” combinations ○ In fact, in Scheme, expressions are lists (or primitive values) ● Quoting prevents evaluation of an expression ● Calling eval on an unevaluated expression will evaluate that value Demo scm> ‘(+ 1 2) (+ 1 2) scm> (eval ‘(+ 1 2)) 3 scm> (list 'quotient 10 2) (quotient 10 2) scm> (eval (list 'quotient 10 2)) 5

Expressions In Scheme
Expressions In Scheme

Demo Expressions As Data Recall:programs are composed of expressions,but manipulate values or data In Scheme,expressions are either primitive expressions or lists which means they're also a form of data! This means we can: Assign expressions to variables ● Pass expressions into functions Create return new expressions within functions
Expressions As Data Recall: programs are composed of expressions, but manipulate values or data In Scheme, expressions are either primitive expressions or lists - which means they’re also a form of data! This means we can: ● Assign expressions to variables ● Pass expressions into functions ● Create & return new expressions within functions Demo

Begin Demo begin is a special form takes in any number of expressions, evaluates them in order,and evaluates to the value of the final expression (begin 3 2 1) scm>(begin (define x 2)(define x (x 1))x) 3
Begin begin is a special form takes in any number of expressions, evaluates them in order, and evaluates to the value of the final expression Demo (begin 3 2 1) 1 scm> (begin (define x 2) (define x (+ x 1)) x) 3
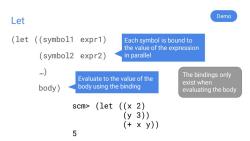
Let Demo (let ((symbol1 expr1) Each symbol is bound to the value of the expression (symbo12 expr2) in parallel …) Evaluate to the value of the The bindings only exist when body body using the binding evaluating the body scm>(1et((x2) (y3) (+xy)) 5
Let (let ((symbol1 expr1) (symbol2 expr2) …) body) Demo scm> (let ((x 2) (y 3)) (+ x y)) 5 Each symbol is bound to the value of the expression in parallel Evaluate to the value of the body using the binding The bindings only exist when evaluating the body
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)20-Interpreters.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)19-More-Scheme.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)18-Scheme.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)17-Interfaces.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)16-Linked Lists & Mutable Trees.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)15-Inheritance.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)14-Object-Oriented Programming.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)13-Iterators & Generators.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)13-Iterators.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)12-Mutable Functions & Growth.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)11-Mutable-Values.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)10-Trees.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)09-Data-Abstractions.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)08-Containers.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)07-Recursion Examples.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)06-Recursion.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)05-Higher-Order Functions.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)04-Environment Diagrams.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)03-Control.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)02-Names & Functions.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)22-Streams.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)23-SQL-I.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)24-SQL-II.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)25-Conclusion, and Final Exam Review.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)01 绪论 Introduction(主讲:曹洋).pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)02 傅里叶分析与卷积 Fourier Analysis and Convolution.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)03 数字图像处理基础 Basics of Digital Image Processing.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)04 图像模型 Basics of Image.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)05 空域滤波 Spatial Filtering.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)06 小波变换 Wavelet Analysis.pptx
- CodeIgniter 中国开发者社区:CodeIgniter4 中文手册(版本 4.0.0).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)07 图像复原 Image Restoration.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)08 自适应滤波 Adaptive Filter.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)要点复习 Review(主讲:曹洋).pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《信号与图像处理基础 Signal and Image Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)09 图像压缩 Image Compression.pptx
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算机视觉》课程教学资源(参考论文)Tour Into the Picture_Using a Spidery Mesh Interface to Make Animation from a Single Image.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算机视觉》课程教学资源(参考论文)3D photography on your desk.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算机视觉》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第一章 绪论 Computer Vison(主讲:曹洋).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算机视觉》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二章 视觉的基本知识 第一节 人类生理视觉系统.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算机视觉》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二章 视觉的基本知识 第二节 视觉物理学特性.pptx
