《计算机科学》相关教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)On the Relationship between Concurrent Separation Logic and Assume-Guarantee Reasoning

On the Relationship Between Concurrent Separation Logic and Assume-Guarantee Reasoning Xinyu Feng Yale University Joint work with Rodrigo Ferreira and Zhong Shao
On the Relationship Between Concurrent Separation Logic and Assume-Guarantee Reasoning Xinyu Feng Yale University Joint work with Rodrigo Ferreira and Zhong Shao
Motivation Concurrency verification is challenging! Exponential state space caused by interleaving of execution. Memory aliasing makes it harder to ensure non-interference. Modularity is the key!
Motivation Concurrency verification is challenging! T1 T1 T1 T2 T2 T2 Exponential state space caused by interleaving of execution. Memory aliasing makes it harder to ensure non-interference. Modularity is the key!
Two kinds of modularity 。Control modularity -a.k.a.thread-modularity each thread is verified independently of others 。Data modularity -a.k.a.information hiding -each thread only cares about data it uses
Two kinds of modularity • Control modularity – a.k.a. thread-modularity – each thread is verified independently of others • Data modularity – a.k.a. information hiding – each thread only cares about data it uses

Existing work Assume-Guarantee (A-G)reasoning [Misra&Chandy'81,Jones'83] ©thread modularity general:no restriction over synchronization pattern spec of A&G requires global data invariants Concurrent Separation Logic (CSL)[o'Hearn,Brookes 20041 ©thread modularity data modularity:local reasoning restrictive synchronization pattern shared resources can be accessed only inside critical regions
Existing work • Assume-Guarantee (A-G) reasoning [Misra&Chandy’81, Jones’83] ☺ thread modularity ☺ general: no restriction over synchronization pattern spec of A&G requires global data invariants • Concurrent Separation Logic (CSL) [O’Hearn, Brookes 2004] ☺ thread modularity ☺ data modularity: local reasoning restrictive synchronization pattern shared resources can be accessed only inside critical regions

Our Contributions SAGL:combining CSL and A-G reasoning - extend A-G logic with local reasoning better data modularity (than A-G reasoning) thread modularity no restriction over synchronization pattern A formal study of the relationship between CSL and A-G reasoning
Our Contributions • SAGL: combining CSL and A-G reasoning – extend A-G logic with local reasoning ☺ better data modularity (than A-G reasoning) ☺ thread modularity ☺ no restriction over synchronization pattern • A formal study of the relationship between CSL and A-G reasoning

Outline of this talk 。Background Concurrent Separation Logic -Assume-Guarantee reasoning SAGL:combination of CSL A-G reasoning Interpretation of CSL in SAGL
Outline of this talk • Background – Concurrent Separation Logic – Assume-Guarantee reasoning • SAGL: combination of CSL & A-G reasoning • Interpretation of CSL in SAGL
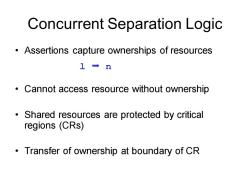
Concurrent Separation Logic Assertions capture ownerships of resources 1→n Cannot access resource without ownership ● Shared resources are protected by critical regions (CRs) Transfer of ownership at boundary of CR
Concurrent Separation Logic • Assertions capture ownerships of resources • Cannot access resource without ownership • Shared resources are protected by critical regions (CRs) • Transfer of ownership at boundary of CR l n
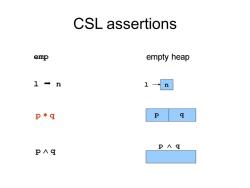
CSL assertions emp empty heap 1→1 n 1→ n p*q P g P∧g P∧g
CSL assertions l n l n p q p q emp empty heap p q p q
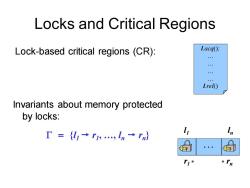
Locks and Critical Regions Lock-based critical regions (CR): Lacq(); Lrel() Invariants about memory protected by locks: Γ={化→,ln→rn} 1* *In
Locks and Critical Regions Lock-based critical regions (CR): l.acq(); … … … … l.rel() Invariants about memory protected by locks: = {l1 r1 , …, ln rn } r1 rn . . . l1 ln
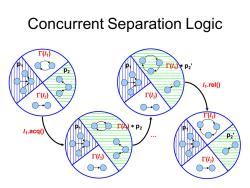
Concurrent Separation Logic T4) E()p2' P2 1.rel() T(2) *p2 1.acq() T(2)
p1 (l2 ) p2 (l1 ) p1 (l2 ) (l1 ) p2 Concurrent Separation Logic p1 (l2 ) p2 (l1 ) l1 .acq() l1 .rel() … p1 (l2 ) (l1 ) p2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Technical Report TTIC-TR-2008-1(Local Rely-Guarantee Reasoning).pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Deny-Guarantee Reasoning.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)A Rely-Guarantee-Based Simulation for Verifying Concurrent Program Transformations.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Modular Verification of Linearizability with Non-Fixed Linearization Points.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Characterizing Progress Properties of Concurrent Objects via Contextual Refinements.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Rely-Guarantee-Based Simulation for Compositional Verification of Concurrent Program Transformations.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Compositional Verification of Termination-Preserving Refinement of Concurrent Programs.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)A Program Logic for Concurrent Objects under Fair Scheduling.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)A Practical Verification Framework for Preemptive OS Kernels.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Progress of Concurrent Objects with Partial Methods.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)POMP:Protocol Oblivious SDN Programming with Automatic Multi-Table Pipelining.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Decay of Correlation in Spin Systems.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Counting with Bounded Treewidth.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源:The Magical Wild Animals(神奇的动物).pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源:Quest for Artificial Intelligence(人工智能探秘).pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源:Beautiful Journey of Theoretical Computer Science(理论计算机科学的美丽旅程).pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Phase transition of hypergraph matchings.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Correlation Decay up to Uniqueness in Spin Systems.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)What can be sampled locally?.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Sampling up to the Uniqueness Threshold.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Certifying Low-Level Programs with Hardware Interrupts and Preemptive Threads.ppt
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)An Open Framework for Foundational Proof-Carrying Code.ppt
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Modular Verification of Assembly Code with Stack-Based Control Abstractions.ppt
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Modular Verification of Concurrent Assembly Code with Dynamic Thread Creation and Termination.ppt
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)01-Introduction(主讲:冯新宇).pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)02-Names & Functions.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)03-Control.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)04-Environment Diagrams.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)05-Higher-Order Functions.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)06-Recursion.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)07-Recursion Examples.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)08-Containers.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)09-Data-Abstractions.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)10-Trees.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)11-Mutable-Values.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)12-Mutable Functions & Growth.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)13-Iterators.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)13-Iterators & Generators.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)14-Object-Oriented Programming.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机程序的构造和解释 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)15-Inheritance.pptx
