北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 10 Chemical Reaction Kinetics

Chemical Reaction Kinetics PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建m,fineprint.com,cn
Chemical Reaction Kinetics PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 _www.fineprint.com.cn

Introduction This chapter introduces the principles of chemical kinetics,the study of reaction rates,by showing how the rates of reactions may be measured and interpreted. The rate of a chemical reaction might depend on variables under our control,such as the pressure,the temperature,and the presence of a catalyst,and we may be able to optimize the rate by the appropriate choice of conditions. The study of reaction rates also leads to an understanding of the mechanisms of reactions,their analysis into a sequence of elementary steps PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建w.fineprint.com.cn
Introduction This chapter introduces the principles of chemical kinetics, the study of reaction rates, by showing how the rates of reactions may be measured and interpreted. The rate of a chemical reaction might depend on variables under our control, such as the pressure, the temperature, and the presence of a catalyst, and we may be able to optimize the rate by the appropriate choice of conditions. The study of reaction rates also leads to an understanding of the mechanisms of reactions, their analysis into a sequence of elementary steps. PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 f www.fineprint.com.cn ÿ

Why do some reactions take place very rapidly (less than millionths of a second)while some reactions take years to occur? Why can changing the concentration(s)of reactants often change the rate with which they react? Why does temperature have such a dramatic effect on chemical reactions? Why do catalysts speed up some reactions but have little or no effect on other reactions? PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建m,fineprint.com,cn
Why do some reactions take place very rapidly (less than millionths of a second) while some reactions take years to occur? Why does temperature have such a dramatic effect on chemical reactions? Why do catalysts speed up some reactions but have little or no effect on other reactions? Why can changing the concentration(s) of reactants often change the rate with which they react? PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 _www.fineprint.com.cn

Heterogeneous Reactions:Reactants and/or products are in different phases (ie.,mixture of gases and liquids or solids. Homogeneous Reactions:Reactants and products are all in the same phase.ie.,all gases or all liquids. PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建wm,fineprint.com,cn
Heterogeneous Reactions: Reactants and/or products are in different phases (ie., mixture of gases and liquids or solids. Homogeneous Reactions: Reactants and products are all in the same phase. ie., all gases or all liquids. PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 _www.fineprint.com.cn

How fast a reaction occurs Reactions are not instantaneous-they take a finite time. Demonstration: Reaction: PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建ww.fineprint.com,cn
How fast a reaction occurs Reactions are not instantaneous - they take a finite time. Demonstration: PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 èwww.fineprint.com.cn
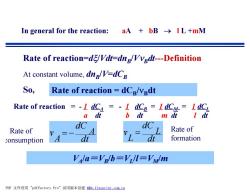
In general for the reaction: aA+bB→IL+mM Rate of reaction=dg/Vdt=dng/Vvgdt---Definition At constant volume,dng/V=dCg S0, Rate of reaction dCg/vedt Rate of reaction =-I dC=-I dCB=I dCM=I dC a dt b dt m正ldi dC dc Rate of Rate of consumption dt dt formation Vala=VB/b=Vil=VMlm PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建m,fineprint,com,cn
In general for the reaction: aA + bB ® l L +mM Rate of reaction=dx/Vdt=dnB /VnBdt---Definition At constant volume, dnB /V=dCB So, Rate of reaction = - 1 dCA = - 1 dCB = 1 dCM = 1 dCL a dt b dt m dt l dt Rate of reaction = dCB /nBdt dt A dC A v = - dt L dC L v = VA /a=VB /b=VL /l=VM/m Rate of consumption Rate of formation PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 f www.fineprint.com.cn ÿ

For Example 2Ht+3+H202→2H20+L3 rate -0-⅓ etc dt ● rates go as 1/(stoichiometric coefficient) Learn reactants products have opposite sign PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建m,fineprint.com,cn
2H+ + 3I– + H2O2 ® 2H2O + I3 – etc. dt d[I ] dt d[H ] dt d[H O] dt d[I ] rate 3 1 2 2 1 2 3 1 - + - = = = - = - • rates go as 1/(stoichiometric coefficient) • reactants & products have opposite sign Learn For Example PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 f www.fineprint.com.cn ÿ

Elementary Reactions Elementary reaction---process which occurs in a single collision or molecular event Most reactions occur in a sequence of steps called elementary reactions,each of which involves only a small number of molecules or ions. For example:H+Br2 HBr Br This equation signifies that an H atom attacks a Br2 molecule to produce an HBr molecule and a Br atom. PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建ffm,fineprint.com,cn
Elementary Reactions Elementary reaction---process which occurs in a single collision or molecular event Most reactions occur in a sequence of steps called elementary reactions, each of which involves only a small number of molecules or ions. For example: H +Br2 HBr + Br This equation signifies that an H atom attacks a Br2 molecule to produce an HBr molecule and a Br atom. PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 fwww.fineprint.com.cn f

Example:H2+Cl2→2HCl Four elementary reactions occurring simultaneously: Cl2→2Cl CI+H2→HCI+H H+CL2→HCI+CI 2Cl→Cl2 A H2 molecule and a Cl2 molecule never react by colliding together to form two HCI molecules! Instead: isolated Cl2 molecule falls apart to form two Cl atoms a CI atom can collide with a H2 molecule to form a HCI molecule and a H atom. PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建m,fineprint.com,cn
Example: H2 + Cl2 ® 2HCl Four elementary reactions occurring simultaneously: Cl2 ® 2Cl Cl + H2 ® HCl + H H + Cl2 ® HCl + Cl 2Cl ® Cl2 * A H2 molecule and a Cl2 molecule never react by colliding together to form two HCl molecules! Instead: - isolated Cl2 molecule falls apart to form two Cl atoms - a Cl atom can collide with a H2 molecule to form a HCl molecule and a H atom. PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 fwww.fineprint.com.cn f
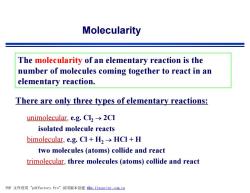
Molecularity The molecularity of an elementary reaction is the number of molecules coming together to react in an elementary reaction. There are only three types of elementary reactions: unimolecular,e.g.Cl>2CI isolated molecule reacts bimolecular,e.g.CI+H2>HCI +H two molecules(atoms)collide and react trimolecular,three molecules (atoms)collide and react PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建m,fineprint..com,cn
Molecularity The molecularity of an elementary reaction is the number of molecules coming together to react in an elementary reaction. There are only three types of elementary reactions: unimolecular, e.g. Cl2 ® 2Cl isolated molecule reacts bimolecular, e.g. Cl + H2 ® HCl + H two molecules (atoms) collide and react trimolecular, three molecules (atoms) collide and react PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 fwww.fineprint.com.cn Ì
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 9 Surfaces(Interfacial Chemistry).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 8 Elementary Statistical Thermodynamics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 7 Electrochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 6 Phase Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 5 Chemical Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 4 The thermodynamics of mixtures.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 3 The Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 2 First Law Of Thermodynamics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 1 The properties of gases.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 0 PYHSICAL CHEMISTRY(Introduction).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题化学动力学(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题表面胶体化学(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题统计热力学(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题相平衡(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题电化学(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题多组分热力学(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题热力学第二定律(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题热力学第一定律(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题气体pVT关系(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)物理化学(下册)提高题及参考答案(第7-11章).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 11 Colloid Chemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第一章 绪论与气体pVT关系(性质)Physical Chemistry.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第三章 热力学第二定律 The second law of thermodynamics.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第二章 热力学第一定律 The first law of thermodynamics.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第四章 多组分系统热力学 Thermodynamics for open systems.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第九章 电化学 Electrochemistry.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第十章 界面化学 Surface Chemistry.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第五章 化学平衡 Chemical equilibrium.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第七章 统计热力学初步 Statistical Thermodynamics.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第六章 相平衡 Phase equilibrium.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第十一章 胶体化学 Colloid Chemistry.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第八章 化学反应动力学 Chemical reaction dynamics.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科非化工专业)第一章 绪论及气体的PVT性质 Physical Chemistry(主讲:张丽丹).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科非化工专业)第三章 热力学热二定律 The Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科非化工专业)第二章 热力学热一定律 The First Law of Thermodynamics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科非化工专业)第七章 化学反应动力学 Chemical Reaction Dynamics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科非化工专业)第五章 化学平衡 Chemical equilibrium(主讲教师:张丽丹).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科非化工专业)第六章 相平衡.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科非化工专业)第四章 多组分系统热力学.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)When did Louis Pasteur present his memoir on the discovery of molecular chirality to the Académie des sciences Analysis of a discrepancy.pdf
