北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 4 The thermodynamics of mixtures

The thermodynaminixtures PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建wm,fineprint..com,c四
1 The thermodynamics of mixtures PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 www.fineprint.com.cn

Introduction Chemistry deals with mixtures,including mixtures of substances that can react together. Therefore,we need to generalize the concepts introduced so far to deal with substances that are mixed together. As a first step towards dealing with chemical reactions, here we consider mixtures of substances that do not react together.At this stage we deal mainly with binary mixtures (mixtures of two components,A and B). Another restriction of this chapter is that we consider mainly non-electrolyte solutions,in which the solute is not present as ions PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建織ifineprint..com,cn
2 Introduction Chemistry deals with mixtures, including mixtures of substances that can react together. Therefore , we need to generalize the concepts introduced so far to deal with substances that are mixed together. As a first step towards dealing with chemical reactions, here we consider mixtures of substances that do not react together. At this stage we deal mainly with binary mixtures (mixtures of two components, A and B). Another restriction of this chapter is that we consider mainly non-electrolyte solutions, in which the solute is not present as ions . PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 ÿ駌ÿ www.fineprint.com.cn

The solute dissolves in the solveni The solubility of a substance is the maximum amount that can dissolve in a fixed amount of a particular solvent. When the components of a mixture are homogeneous/y intermingled it is called a solution. PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建m,fineprint.com,c四
3 n The solute dissolves in the solvent. n The solubility of a substance is the maximum amount that can dissolve in a fixed amount of a particular solvent. n When the components of a mixture are homogeneously intermingled it is called a solution. PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 ÿÿwww.fineprint.com.cn

Molarity,Molality and Mole Fraction → Molarity Ca the number of moles of solute per m3 of solution (mol m3) Molality o the moles of solute dissolved in 1000 g (1kg)of solvent.(mol kg-1) Mole fraction is the ratio of the number of moles of a given component to the total number of moles of solution. XB=nBl∑nB The relation between Cs and xB: C> C。+ P-MC M方 PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建m,fineprint.com,c四
4 Molarity, Molality and Mole Fraction ð MolarityCB : the number of moles of solute per m3 of solution (mol m-3 ) ð Molality bB : the moles of solute dissolved in 1000 g (1kg) of solvent. (mol kg-1 ) ð Mole fraction xB: is the ratio of the number of moles of a given component to the total number of moles of solution. xB=nB /ånB ð The relation between CB and xB: A B B B B B M M C C C x - + = r PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 ÿwww.fineprint.com.cn
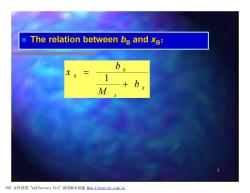
The relation between bB and xB: b B +b M PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建fm,fineprint.com,cn
5 n The relation between bB and xB: B A B B b M b x + = 1 PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 fwww.fineprint.com.cn

The Vapour Pressure Of Solutions A solutions vapour pressure is affected by the concentration of solute and the interactions of solute and solvent. salt to melt ice on a footpath-causes the freezing point of the water to decrease thus ice melts if T=0C add a to the water in the radiator of a car to lower the freezing point of the water. The presence of a non-volatile solute lowers the vapour pressure of a solvent. PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建m,fineprint.com,cn
6 The Vapour Pressure Of Solutions n A solutions vapour pressure is affected by the concentration of solute and the interactions of solute and solvent. n salt to melt ice on a footpath- causes the freezing point of the water to decrease - n thus ice melts if T = 0oC n add antifreeze to the water in the radiator of a car to lower the freezing point of the water. n The presence of a non-volatile solute lowers the vapour pressure of a solvent. PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 ÿwww.fineprint.com.cn

The Effect of Solute on the Vapour Pressure of a Solution A.Equilibrium occurs between a pure liquid and its vapour when the numbers of molecules vaporising and condensing in a given time are equal. Rate of vaporisation Rate of condensation B.With a non-volatile solute present,fewer solvent molecules vaporise in a given time,so fewer molecules need to condense to balance them.Thus equilibrium is reached at a lower vapour pressure. PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建www.fineprint.com.cn
7 The Effect of Solute on the Vapour Pressure of a Solution n A. Equilibrium occurs between a pure liquid and its vapour when the numbers of molecules vaporising and condens condensing in a given time are equal. n Rate of vaporisation = Rate of condensation n B. With a non-volatile solute present, fewer solvent molecules vaporise in a given time, so fewer molecules need to condense condense to balance them. Thus equilibrium is reached at a lower vapour pressure. PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 www.fineprint.com.cn
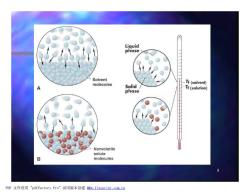
Liquid phase Solvent molecules Solid/ Tf(solvent) Tf(solution) phase Nonvolatile solute B molecules PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建fw.fineprint.com,cn
8 PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 ÿwww.fineprint.com.cn f

The Effect of solute on the vapour pressure A.Equilibrium occurs B.With a nonvolatile between pure liquid solute present,fewer and its vapour when molecules vaporise the number of in a given time,so molecules vaporising fewer molecules and condensing in a molecules need to given time are equal. condense to balance them.Thus the equilibrium is reached at a lower vapour pressure PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建wm,fineprint..com,c里
9 The Effect of solute on the vapour pressure n A. Equilibrium occurs between pure liquid and its vapour when the number of molecules vaporising and condensing in a given time are equal. n B. With a nonvolatile solute present, fewer molecules vaporise in a given time, so fewer molecules molecules need to condense to balance them. Thus the equilibrium is reached at a lower vapour pressure PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 ÿwww.fineprint.com.cn

Raoult's Law ▣ Psoln=Xsolvents so is the observed vapour pressure of the solution,xsolvent is the mole fraction of solvent and P"soent is the vapour pressure of the pure solvent. For a solution of half solvent and solute the mole fraction is 0.5 and thus the vapour pressure is decreased by half. The non-volatile solute simply s the solvent. Psoln=Xsolvent solvent --for the solvent of dilute solution 10 PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建w,fineprint.com,c四
10 Raoult’s Law Psoln= csolventP* solvent n Psoln is the observed vapour pressure of the solution, csolvent is the mole fraction of solvent and P*solvent is the vapour pressure of the pure solvent. n For a solution of half solvent and solute the mole fraction is 0.5 and thus the vapour pressure is decreased by half. n The non-volatile solute simply dilutes the solvent. n Psoln= csolventP* solvent --- for the solvent of dilute solution PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 www.fineprint.com.cn
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 3 The Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 2 First Law Of Thermodynamics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 1 The properties of gases.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 0 PYHSICAL CHEMISTRY(Introduction).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题化学动力学(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题表面胶体化学(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题统计热力学(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题相平衡(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题电化学(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题多组分热力学(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题热力学第二定律(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题热力学第一定律(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)计算题气体pVT关系(含参考答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)物理化学(下册)提高题及参考答案(第7-11章).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)物理化学(上册)提高题及参考答案(第1-6章).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)2010-2011年第一学期物理化学(上册)期末试题.doc
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(作业习题)2009-2010年第一学期物理化学(上册)期末试题.doc
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)治理工业含苯废气Cu-Mn-O复合氧化物催化剂的活性评价.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)用差热分析方法测定催化剂的还原度及还原活化能.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)镁铝水滑石清洁合成组成分析及其晶体结构表征.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 5 Chemical Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 6 Phase Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 7 Electrochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 8 Elementary Statistical Thermodynamics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 9 Surfaces(Interfacial Chemistry).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 10 Chemical Reaction Kinetics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(理科双语)Chapter 11 Colloid Chemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第一章 绪论与气体pVT关系(性质)Physical Chemistry.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第三章 热力学第二定律 The second law of thermodynamics.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第二章 热力学第一定律 The first law of thermodynamics.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第四章 多组分系统热力学 Thermodynamics for open systems.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第九章 电化学 Electrochemistry.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第十章 界面化学 Surface Chemistry.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第五章 化学平衡 Chemical equilibrium.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第七章 统计热力学初步 Statistical Thermodynamics.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第六章 相平衡 Phase equilibrium.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第十一章 胶体化学 Colloid Chemistry.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科化工专业)第八章 化学反应动力学 Chemical reaction dynamics.pps
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科非化工专业)第一章 绪论及气体的PVT性质 Physical Chemistry(主讲:张丽丹).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《物理化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,工科非化工专业)第三章 热力学热二定律 The Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf
