南京大学:单相多铁性物理与材料的理论与实验研究(讲稿)Multiferroicity - Our experiences beyond manganites,主讲:刘俊明)
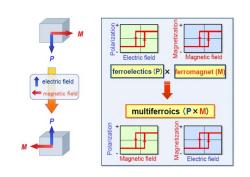
+ M onezuelo Electric field Magnetic field ferroelectics(P) ferromagnet(M) ↑ electric field ◆magnetic field multiferroics (Px M) Magnetic field Electric field

國 Multiferroicity: Our experiences beyond manganites J.-M.Liu(刘俊明) Nanjing University Email:liujm@nju.edu.cn Group page http://pld.nju.edu.cn/
J. –M. Liu ( M. Liu (刘俊明) Nanjing University Nanjing University Email: liujm@nju.edu.cn liujm@nju.edu.cn Group page Group page http://pld.nju.edu.cn/ //pld.nju.edu.cn/ Multiferroicity: Our experiences beyond manganites
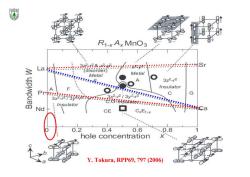
R1-xAx MnO3 多ma8ogo (disorder Metal Metal A 3z2-2 Insulator A ● C G 3x2.213y2-2 Insulator Nd CE ■ CxE1-x 0.2 0.4 0.6 ….0.8 hole concentration X Y.Tokura,RPP69,797 (2006)
Y. Tokura, RPP69, 797 (2006)

Content >Background motivations Origin of spiral spin order in manganites >Predictions of novel multiferroics >Phase competition and beyond Exchange bias in multiferroic heterostructure Summary perspectives
Content Background & motivations Origin of spiral spin order in manganites Predictions of novel multiferroics Phase competition and beyond Exchange bias in multiferroic heterostructure Summary & perspectives
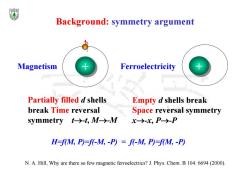
Background:symmetry argument Magnetism Ferroelectricity Partially filled d shells Empty d shells break break Time reversal Space reversal symmetry symmetry t-→-t,M→-M x→-x,P→-P H-f(M,P)=f(-M,-P)=f(-M,P)=f(M,-P) N.A.Hill,Why are there so few magnetic ferroelectrics?J.Phys.Chem.B 104:6694(2000)
Background: symmetry argument ++ - ++ Partially filled d shells break Time reversal symmetry t-t, M-M N. A. Hill, Why are there so few magnetic ferroelectrics? J. Phys. Chem. B 104: 6694 (2000). Empty d shells break Space reversal symmetry x-x, P-P Magnetism Ferroelectricity H=f(M, P)=f(-M, -P) = f(-M, P)=f(M, -P)

Background:symmetry argument Mostovoy,PRL 96,067601(06) If spin order is spatially inhomogeneous, symmetry allows for the 3rd-order coupling POM and then P may appear. Φem(P,M )= yP.[M(V·M)-(M·7)M+··], D=Φem+P2/2mE →P∝[(M·a)M-M(a.M)]
Background: symmetry argument If spin order is spatially inhomogeneous, symmetry allows for the 3rd-order coupling P∂M and then P may appear. =em+P2/2 Mostovoy, PRL 96, 067601 (06)
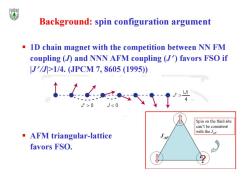
Background:spin configuration argument 1D chain magnet with the competition between NN FM coupling (J)and NNN AFM coupling (J)favors FSO if J'/J>1/4.(JPCM7,8605(1995) J'>0 J<0 Spin on the third site can't be consistent with the J AFM triangular-lattice AF favors FSO
Background: spin configuration argument AFM triangular-lattice favors FSO. 1D chain magnet with the competition between NN FM coupling (J) and NNN AFM coupling (J ) favors FSO if |J /J|>1/4. (JPCM 7, 8605 (1995))

Background:structures and facts RMnO3 phases T.Goto et al. 100 PRL92,257201(2004) R=Nd paramagnetic g Sm Eu 50 eR兴 A-AF incommensurate-AF ↑ commen- ↑ RMnO3 surate 0 AF- 148 146 144 ↑ Mn-O-Mn bond angle(deg) ↓
Background: structures and facts T. Goto et al. RMnO3 phases PRL 92,257201 (2004) RMnO3 phases
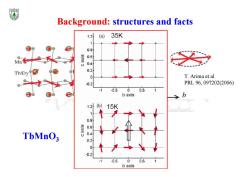
Background:structures and facts 1.2 (a)35K 0.8 0.6 Tb/D T.Arima et al. 02 PRL96,097202(2006) -0.500.5 b axis 12 (b) 5K 1 0.8 Q.cp TbMnO; Sixe 04 0.2 0 -0.2 .1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 b axis
T. Arima et al. PRL 96, 097202(2006) TbMnO3 Background: structures and facts
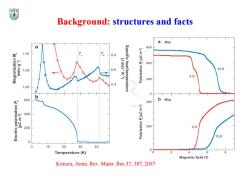
Background:structures and facts a P//c a 600 1.10 0.8 (-6 nwa) (J mol-1 K-2) Specific heat/temperature 400 1.08 0.6 15K 9K 200 0.4 1.06 0 b 600 400 400 200 200 9 15K 0 0 0 20 30 40 0 Temperature(K) 0 Magnetic field (T) Kimura,Annu.Rev.Mater.Res.37,387,2007
Background: structures and facts Kimura, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res.37, 387, 2007
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《电磁学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第四章 恒稳电流.pdf
- 南京大学:《电磁学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第六章 电磁场与电荷运动.pdf
- 南京大学:《电磁学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第八章 电磁感应.pdf
- 南京大学:《电磁学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第五章 真空中恒稳电流的磁场.pdf
- 南京大学:《电磁学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第九章 麦克斯韦方程与电磁波.pdf
- 南京大学:《电磁学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第三章 电介质.pdf
- 南京大学:《电磁学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第七章 磁介质(负责人:刘俊明).pdf
- 南京大学:《电磁学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第二章 导体周围的静电场、静电能量.pdf
- 南京大学:《电磁学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第一章 真空中固定电荷的电场.pdf
- 南京大学:《电磁学》课程电子教案(教学课件)大学电磁学绪论(负责人:刘俊明).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)静电场与物质的相互作用、电介质.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第20章 光的干涉与衍射.pdf
- 北方工业大学:《弹性力学与有限元》课程教学大纲(城市地下空间工程,智慧城市).pdf
- 北方工业大学:《大学物理》课程教学大纲Ⅶ(1)(城市地下空间工程,智慧城市).pdf
- 北方工业大学:电气工程及其自动化《物理实验》课程教学大纲Ⅰ(1).pdf
- 北方工业大学:微电子科学与工程(集成电路设计与测试)《半导体物理》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 北方工业大学:电子信息工程专业留学生《Physics for Science & Engineering I》课程教学大纲(全英语).pdf
- 北方工业大学:电子信息工程专业《物理实验》课程教学大纲Ⅰ(1).pdf
- 北方工业大学:电子信息工程专业《大学物理》课程教学大纲Ⅲ(1).pdf
- 济南大学:物理科学与技术学院本科专业人才培养方案(物理学专业、新能源科学与工程专业、光电信息科学与工程专业).pdf
- 南京大学:弛豫型铁电体中的畴形态与动力学模拟研究(讲稿)Enhanced Piezoelectricity in Enhanced Piezoelectricity in Relaxor Relaxor Ferroelectrics:Ferroelectrics - A Phenomenological Approach A Phenomenological Approach.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第1章 质点运动学 1.1 基本概念.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第1章 质点运动学 1.2 质点的位移和速度.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第1章 质点运动学 1.3 质点的加速度.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第1章 质点运动学 1.4 相对运动.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第10章 气体和凝聚态 10.1 范德瓦耳斯方程.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第10章 气体和凝聚态 10.2 气体内的输运过程.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第10章 气体和凝聚态 10.3 固体和液体的热性质.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第11章 静电场 11.1 静电学基本问题.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第11章 静电场 11.2 电场 电场强度.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第11章 静电场 11.3 高斯定理及应用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第11章 静电场 11.4 环路定理与电势.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第11章 静电场 11.5 电势与电场强度的关系.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第12章 导体电学 12.1 导体的静电平衡性质.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第12章 导体电学 12.2 空腔导体.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第12章 导体电学 12.3 电容及电容器.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第12章 导体电学 12.4 传导电流.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第12章 导体电学 12.5 电源及稳恒电流.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第13章 电介质 13.1 静电场中的电介质.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学物理教程》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第13章 电介质 13.2 介质中的高斯定理.pdf
