同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Design of P-3623 Composite Slab

Design of P-3623 Composite Slab Professor Shiming Chen College of Civil Engineering Tongji University
Design of P-3623 Composite Slab Professor : Shiming Chen College of Civil Engineering Tongji University
90 Bearing Capacity of Composite Slabs Bending resistance Ultimate limited Diagonal shear resistance state design Longitudinal shear resistance Serviceability limited Deflections state design
Bearing Capacity of Composite Slabs Ultimate limited state design Bending resistance Diagonal shear resistance Longitudinal shear resistance Serviceability limited state design Deflections

Design Example:P-3623 Composite Slab 1.Parameters of P-3623 composite slab 1000 305 140 Fig.1 Cross-section of P-3623 Steel deck: Thickness of the steel deck:t=0.76mm Steel: Area of the steel deck:A=950mm2 Yielding strength:f=230MPa Moment of inertia:/=441080mm4 Elastic modulus:Es=2.03 X 105N/mm2 Composite slab: Concrete: Span length:L=1600mm Compressive strength:f=20.7MPa Width:b=1000mm Elastic modulus:E。=2.8×104N/mm2
Design Example: P-3623 Composite Slab 1. Parameters of P-3623 composite slab Fig.1 Cross-section of P-3623 Steel deck: Thickness of the steel deck: t=0.76mm Area of the steel deck: As=950mm2 Moment of inertia: Is=441080mm4 Composite slab: Span length: L=1600mm Width: b=1000mm Steel: Yielding strength: fy=230MPa Elastic modulus: Es=2.03 × 105N/mm2 Concrete: Compressive strength: fc=20.7MPa Elastic modulus: Ec=2.8× 104N/mm2

90 Positive bending resistance Assume neutral axis lies in concrete slab above the steel deck fA,=fbx。 x-4-230x950 fb20.7×1000 =10.56mm<51mm Neutral axis does locate in concrete slab above the steel deck So,bending resistance is M,=xfbx.(h-x。/2)=0.8×20.7×1000×10.56×(84.5-10.56/2)=13.85kWm In midspan:M. The ultimate design load: qu= 8M_8x13.85=49.24kW/m2 b12 1×1.52
Positive bending resistance Assume neutral axis lies in concrete slab above the steel deck y s c c f A f bx 230 950 10.56 51 20.7 1000 y s c c f A x mm mm f b Neutral axis does locate in concrete slab above the steel deck So, bending resistance is : 0 ( / 2) 0.8 20.7 1000 10.56 (84.5 10.56/ 2) 13.85 M f bx h x kN m u c c c 1 2 8 In midspan: M q bl u u 2 2 2 8 8 13.85 49.24 / 1 1.5 u u M q kN m bl The ultimate design load:
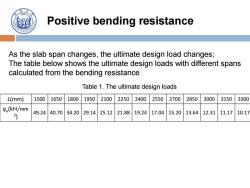
Positive bending resistance As the slab span changes,the ultimate design load changes; The table below shows the ultimate design loads with different spans calculated from the bending resistance Table 1.The ultimate design loads L(mm) 1500 1650 1800 1950 2100 2250 2400 2550 2700 2850 3000 3150 3300 qu(kN/mm 49.24 40.70 34.20 29.14 2) 25.12 21.88 19.24 17.04 15.20 13.64 12.31 11.17 10.17
Positive bending resistance As the slab span changes, the ultimate design load changes; The table below shows the ultimate design loads with different spans calculated from the bending resistance L(mm) 1500 1650 1800 1950 2100 2250 2400 2550 2700 2850 3000 3150 3300 qu (kN/mm 2 ) 49.24 40.70 34.20 29.14 25.12 21.88 19.24 17.04 15.20 13.64 12.31 11.17 10.17 Table 1. The ultimate design loads
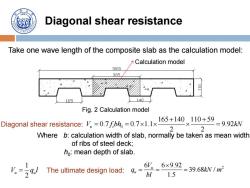
190 Diagonal shear resistance Take one wave length of the composite slab as the calculation model: Calculation model 1000 305 140 Fig.2 Calculation model Diagonal shear resistance:.7.7xx10059 2 2 2=9.92kW Where b:calculation width of slab,normally be taken as mean width of ribs of steel deck; ho:mean depth of slab. The ultimate design load: 6-6×9.92 =39.68kW/m2 bl 1.5
Diagonal shear resistance Take one wave length of the composite slab as the calculation model: 0 165 140 110 59 0.7 0.7 1.1 9.92 2 2 V f bh kN u t Calculation model Where b: calculation width of slab, normally be taken as mean width of ribs of steel deck; h0 : mean depth of slab. Fig. 2 Calculation model 1 2 V q l u u 6 6 9.92 2 39.68 / 1.5 u u V q kN m bl Diagonal shear resistance: The ultimate design load:
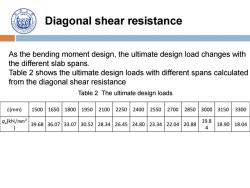
Diagonal shear resistance As the bending moment design,the ultimate design load changes with the different slab spans Table 2 shows the ultimate design loads with different spans calculated from the diagonal shear resistance Table 2 The ultimate design loads L(mm) 1500 1650 1800 1950 2100 2250 2400 2550 2700 2850 3000 3150 3300 qu(kN/mm2 39.68 36.07 33.07 30.52 28.34 26.45 24.80 23.34 22.04 20.88 19.8 18.90 18.04 4
Diagonal shear resistance As the bending moment design, the ultimate design load changes with the different slab spans. Table 2 shows the ultimate design loads with different spans calculated from the diagonal shear resistance L(mm) 1500 1650 1800 1950 2100 2250 2400 2550 2700 2850 3000 3150 3300 qu (kN/mm2 ) 39.68 36.07 33.07 30.52 28.34 26.45 24.80 23.34 22.04 20.88 19.8 4 18.90 18.04 Table 2 The ultimate design loads

90 Longitudinal shear resistance m-k method: Take two groups of data from the profiled steel manufacturers:L=1650mm and L=1950mm 1=1650mm,q=12.51kW/m2 1=1950m,q=9.39kN/m2 +利 V=bd (mL 59x=125,4= 950 +k)× Using the two groups of data,then 2×12.51x1650=1000x51xm 000×1/4×1650 1.25 950 ×9.39×1950=1000×51×( 1000x174x1950+)×125 The solution is: m=80.63 k=0.06727
Longitudinal shear resistance m-k method: Take two groups of data from the profiled steel manufacturers: L=1650mm and L=1950mm 2 l mm q kN m 1650 , 12.51 / 2 l mm q kN m 1950 , 9.39 / , 1 ( ) p L Rd p s s A V bd m k bL , 1 1 , 1.25, 2 4 V ql L l L Rd s s Using the two groups of data, then 1 950 1 12.51 1650 1000 51 ( ) 2 1000 1/ 4 1650 1.25 m k 1 950 1 9.39 1950 1000 51 ( ) 2 1000 1/ 4 1950 1.25 m k The solution is: 80.63 0.06727 m k

Longitudinal shear resistance S0,上则=bd,(80.63是+0.06727) bL Y When the slab span is taken as L=1500mm. The ultimate design load: bd,m子+月 950 bL. 1000×51×(80.63× +0.06727)× 9m= 1000×1/4×1500 125=14.77kW1m2 1/21 1/2×1500 Table 3 shows the ultimate design loads with different spans calculated from the longitudinal shear resistance Table 3 The ultimate design loads L(mm) 1500 1650 1800 1950 2100 2250 2400 2550 2700 2850 3000 3150 3300 q(kN/mm2) 14.77 12.51 10.77 9.39 8.28 7.38 6.63 6.00 5.46 5.00 4.61 4.26 3.96
Longitudinal shear resistance So, , 1 (80.63 0.06727) p L Rd p s s A V bd bL When the slab span is taken as L=1500mm, 1 1 (80.63 0.06727) 2 p u p s s A q l bd bL 2 1 950 1 ( ) 1000 51 (80.63 0.06727) 1000 1/ 4 1500 1.25 14.77 / 1/ 2 1/ 2 1500 p p s s u A bd m k bL q kN m l L(mm) 1500 1650 1800 1950 2100 2250 2400 2550 2700 2850 3000 3150 3300 qu (kN/mm2 ) 14.77 12.51 10.77 9.39 8.28 7.38 6.63 6.00 5.46 5.00 4.61 4.26 3.96 Table 3 shows the ultimate design loads with different spans calculated from the longitudinal shear resistance Table 3 The ultimate design loads The ultimate design load:
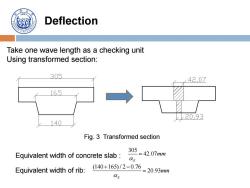
4907 Deflection Take one wave length as a checking unit Using transformed section: 305 4207 165 上20,93 140 Fig.3 Transformed section Equivalent width of concrete slab 305=42.07mm E Equivalent width of rib: (140+165)/2-0.76 =20.93mm CE
Deflection Take one wave length as a checking unit Using transformed section: Equivalent width of concrete slab : 305 42.07 E mm Equivalent width of rib: (140 165) / 2 0.76 20.93 E mm Fig. 3 Transformed section
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Design of Composite Floors.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Flexural behavior of shallow cellular composite floor beams.pptx
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Course Report - Composite Structures 组合结构.pdf
- 《高等混凝土结构理论》课程教学资源(学习资料)高等混凝土结构试验资料.docx
- 同济大学:《高等混凝土结构理论》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 5 Shearing Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Structural Members.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等混凝土结构理论》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 2 Mechanical Behavior and Constitutive Relationships of Concrete and Steel Materials.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等混凝土结构理论》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 1 Introduction(负责人:顾祥林).ppt
- 同济大学:《高等混凝土结构理论》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 4 Bending and Compression Behavior of RC Structural Members.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等混凝土结构理论》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 3 Bond and Anchorage.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第8章 建筑施工图(房屋施工图).ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第6章 组合体的投影图.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第1章 制图基础.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第9章 结构施工图.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第7章 工程形体的表达方法.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第2章 点、线、面的投影 2.1 三视图与点的投影.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第2章 点、线、面的投影 2.2 直线的投影.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(建筑制图)透视投影 perspective projection.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(建筑制图)建筑施工图.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(建筑制图)建筑形体的表达方法.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(建筑制图)组合体的投影图.ppt
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)DESIGN OF COMPOSITE BEAMS FOR DIFFERENT DEGREE OF SHEAR CONNECTION.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)A comparative study between concrete filled composite columns and steel reinforced concrete columns.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)A comparative study of concrete filled composite columns and steel reinforced concrete columns.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 1 Composite Construction - General(负责人:陈世鸣).pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 2 Design Principles and Fundamentals of Composite Action 设计原理和组合作用.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 4 Steel and concrete composite beams Simply supported composite beams 钢-混凝土组合梁——简支组合梁.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 5 Shear Connection 组合梁的抗剪连接.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 6 Continuous composite Beams 连续组合梁.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 7 Composite Columns.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 8 Composite Frames and Joints.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Lecture - advanced composite floor.pptx
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)lecture-Composite Steel-Concrete Shear Walls.pptx
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)lecture-Introduction to Structural Fire Engineering.ppt
- 上海市工程建设规范:轻型钢结构技术规程(DG/TJ08—2089—2012)Technical specification for light weight steeI building structures.pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Seismic design of building structures(负责人:熊海贝)Introduction.pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 Earthquake and Ground motions(1/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 Earthquake and Ground motions(2/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Site, Subsoil and Foundation.pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Seismic Responses of SDOF and MDOF(1/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Seismic Responses of SDOF and MDOF(2/2).pdf
