同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Lecture - advanced composite floor

Advanced Floor Structures By Professor Chen Shiming 2015
By Professor Chen Shiming 2015 Advanced Floor Structures

Introduction >In modern building constructions,the increasing demands of long span floors but with shallow floor depth have led to the development of various composite floor systems. >In conventional composite floor systems,the depth of beam section normally increases with the length that the floor spans over and it results in the steel sections of the ordinary down stand composite beams being heavier and deeper than expected. The height of the floor is usually about 400mm and the composite beam is at least 600mm
Introduction ➢ In modern building constructions, the increasing demands of long span floors but with shallow floor depth have led to the development of various composite floor systems. ➢ In conventional composite floor systems, the depth of beam section normally increases with the length that the floor spans over and it results in the steel sections of the ordinary down stand composite beams being heavier and deeper than expected. ➢ The height of the floor is usually about 400mm and the composite beam is at least 600mm

> Composite slim floor systems were developed in the 1990s in the UK to provide floor systems with a minimum constructional depth.The feature is the steel beam contained within the slab depth,resulting in a flat appearance. >Several arrangements of beams and slabs can be used to obtain the structural floor system;however the beam always is contained within the slab depth They have several advantages ①shallow floor depth; ② inherent fire resistance; 3 benefits in terms of cost
➢ Composite slim floor systems were developed in the 1990s in the UK to provide floor systems with a minimum constructional depth. The feature is the steel beam contained within the slab depth, resulting in a flat appearance. ➢ Several arrangements of beams and slabs can be used to obtain the structural floor system; however the beam always is contained within the slab depth . They have several advantages : ① shallow floor depth; ② inherent fire resistance; ③ benefits in terms of cost
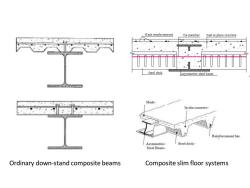
Mesh reinforcement Tie member Cast in place concrete Steel deck Asymmetric steel beam Mesh In situ concrete Reinforcement bar Asymmetric Steel deck. Steel Beam. Ordinary down-stand composite beams Composite slim floor systems
Ordinary down-stand composite beams Composite slim floor systems
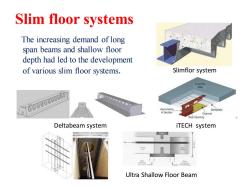
Slim floor systems The increasing demand of long span beams and shallow floor depth had led to the development of various slim floor systems. Slimflor system 月0000000000 Deltabeam system iTECH system Ultra Shallow Floor Beam
Slim floor systems The increasing demand of long span beams and shallow floor depth had led to the development of various slim floor systems. Slimflor system Deltabeam system iTECH system Ultra Shallow Floor Beam

Research on composite slim beams Experimental studies have been conducted by many researchers.The key technical problems are: Effective width of concrete slab Equivalent elastic stiffness Shear connection design ·Vibration comfort
Research on composite slim beams Experimental studies have been conducted by many researchers. The key technical problems are: • Effective width of concrete slab • Equivalent elastic stiffness • Shear connection design • Vibration comfort

Shallow Cellular Slim Floor Beam A composite Shallow Cellular Slim Floor Beam (SCSFB )system with the steel beam embedded within the depth of the floor with regularly spaced openings along the steel web filled with concrete is a new type of Slim Floor system Shallow cellular floor Shallow cellular floor using steel decking and using precast floor units cast in place concrete
Shallow Cellular Slim Floor Beam A composite Shallow Cellular Slim Floor Beam (SCSFB ) system with the steel beam embedded within the depth of the floor with regularly spaced openings along the steel web filled with concrete is a new type of Slim Floor system. Shallow cellular floor using steel decking and cast in place concrete Shallow cellular floor using precast floor units

Shallow Cellular Slim Floor Beam:It offers important benefits in terms of cost (long spanning capabilities without or with fewer secondary beams, shallow floor depth,inherent fire resistance,etc...),as well as others advantages offered by conventional composite beams construction. >Compared to others trade mark of slim floor systems,the SCSFB presents some important advantages such as: The service integration:The web openings provide the structural depth,minimizing the overall floor depth.Full service integration can be achieved when the deep profile decking is employed for the ducting passing between the ribs of the decking
➢ Shallow Cellular Slim Floor Beam: It offers important benefits in terms of cost (long spanning capabilities without or with fewer secondary beams, shallow floor depth, inherent fire resistance, etc…), as well as others advantages offered by conventional composite beams construction. ➢ Compared to others trade mark of slim floor systems, the SCSFB presents some important advantages such as: ✓ The service integration: The web openings provide the structural depth, minimizing the overall floor depth. Full service integration can be achieved when the deep profile decking is employed for the ducting passing between the ribs of the decking

The composite action The enhanced composite action due to the concrete plug passing through the web opening transfers the longitudinal shear force
The composite action The enhanced composite action due to the concrete plug passing through the web opening transfers the longitudinal shear force

The flexibility:The depth of this beam section can be designed according to the required floor depth.Typical proportion of this composite beam is 190 to 350mm for a span of 6 to 12m The inherent fire protection:The incorporation of the upper flange plates and cores of the beams in the thickness of the concrete slab provides structural protection which meet most requirements. Construction time:The beam can be used with pre-cast units and metal deck floors which eliminates the time spent for concrete hardening in the traditional beam constructions. Economic and operational:High reduction of costs can be achieved by less amount of steel used and the saving due to the stud shear connectors has to be highlighted.Another important factor is of the total life-cycle cost
The flexibility: The depth of this beam section can be designed according to the required floor depth. Typical proportion of this composite beam is 190 to 350mm for a span of 6 to 12m. The inherent fire protection: The incorporation of the upper flange plates and cores of the beams in the thickness of the concrete slab provides structural protection which meet most requirements. Construction time: The beam can be used with pre-cast units and metal deck floors which eliminates the time spent for concrete hardening in the traditional beam constructions. Economic and operational: High reduction of costs can be achieved by less amount of steel used and the saving due to the stud shear connectors has to be highlighted. Another important factor is of the total life-cycle cost
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 8 Composite Frames and Joints.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 7 Composite Columns.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 6 Continuous composite Beams 连续组合梁.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 5 Shear Connection 组合梁的抗剪连接.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 4 Steel and concrete composite beams Simply supported composite beams 钢-混凝土组合梁——简支组合梁.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 2 Design Principles and Fundamentals of Composite Action 设计原理和组合作用.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 1 Composite Construction - General(负责人:陈世鸣).pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)A comparative study of concrete filled composite columns and steel reinforced concrete columns.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)A comparative study between concrete filled composite columns and steel reinforced concrete columns.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)DESIGN OF COMPOSITE BEAMS FOR DIFFERENT DEGREE OF SHEAR CONNECTION.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Design of P-3623 Composite Slab.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Design of Composite Floors.pdf
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Flexural behavior of shallow cellular composite floor beams.pptx
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Course Report - Composite Structures 组合结构.pdf
- 《高等混凝土结构理论》课程教学资源(学习资料)高等混凝土结构试验资料.docx
- 同济大学:《高等混凝土结构理论》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 5 Shearing Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Structural Members.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等混凝土结构理论》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 2 Mechanical Behavior and Constitutive Relationships of Concrete and Steel Materials.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等混凝土结构理论》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 1 Introduction(负责人:顾祥林).ppt
- 同济大学:《高等混凝土结构理论》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 4 Bending and Compression Behavior of RC Structural Members.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等混凝土结构理论》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 3 Bond and Anchorage.ppt
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)lecture-Composite Steel-Concrete Shear Walls.pptx
- 同济大学:《钢和混凝土组合结构设计原理与应用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)lecture-Introduction to Structural Fire Engineering.ppt
- 上海市工程建设规范:轻型钢结构技术规程(DG/TJ08—2089—2012)Technical specification for light weight steeI building structures.pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Seismic design of building structures(负责人:熊海贝)Introduction.pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 Earthquake and Ground motions(1/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 Earthquake and Ground motions(2/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Site, Subsoil and Foundation.pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Seismic Responses of SDOF and MDOF(1/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Seismic Responses of SDOF and MDOF(2/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 4 Dynamic Response of MDOF System.pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 5 Earthquake Effect and Seismic Design principles(1/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 5 Earthquake Effect and Seismic Design principles(2/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Buildings(1/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Buildings(2/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 7 Seismic Design of Masonry Buildings(1/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 7 Seismic Design of Masonry Buildings(2/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 8 SEISMIC STEEL DESIGN IN CANADA and the USA(1/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 8 SEISMIC STEEL DESIGN IN CANADA and the USA(2/2).pdf
- 同济大学:《建筑结构抗震》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 9 Seismic Isolation.pdf
- 北方工业大学:城乡规划《城市Studio》课程教学大纲(2).pdf
