同济大学:《货币金融学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate

9 同济大学 经济与管理学院 TONGJI UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate 年 整零存 年 存存 三年圆 息五 取 泡乔快网 xkb.com.cn
Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate

The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate 》Agenda ■ Understanding Interest and Interest Rate Determination of Interest Rates and Interest Rate Theory ● ● System of Interest Rate Regulation 2 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 2 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY Understanding Interest and Interest Rate Determination of Interest Rates and Interest Rate Theory System of Interest Rate Regulation Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate Agenda
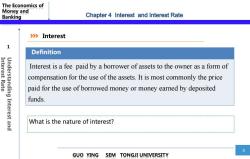
The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate >》Interest 1 Definition Interest Rate Understanding Interest is a fee paid by a borrower of assets to the owner as a form of compensation for the use of the assets.It is most commonly the price paid for the use of borrowed money or money earned by deposited funds. Interest and What is the nature of interest? 3 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 3 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 1 Interest What is the nature of interest? Definition Interest is a fee paid by a borrower of assets to the owner as a form of compensation for the use of the assets. It is most commonly the price paid for the use of borrowed money or money earned by deposited funds. Interest Rate Understanding Interest and Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate

The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate >>Western Theory of interest 1 A:Derivation of land rent Interest Rate Understanding Interest and B:Abstinence theory of interest C:Abstinence theory of interest 4 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 4 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 1 Western Theory of interest Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate Interest Rate Understanding Interest and A: Derivation of land rent B: Abstinence theory of interest C: Abstinence theory of interest

The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate D》》 Western Theory of interest 1 D:Exploitation theory Interest Rate Interest comes from surplus value Understanding Interest and Interest presents a form of price for funds Interest is converted into a general form of income Karl Marx (1818-1883) 5 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 5 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 1 Western Theory of interest Interest comes from surplus value Interest presents a form of price for funds Interest is converted into a general form of income Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate Interest Rate Understanding Interest and Karl Marx (1818-1883) D: Exploitation theory

The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate >>Interest Rate 1 Definition Interest Rate Interest rate refers to the ratio of the interest formed during the Understanding Interest and period of borrowing and lending to the principal of the granted loan. 6 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 6 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 1 Interest Rate Definition Interest rate refers to the ratio of the interest formed during the period of borrowing and lending to the principal of the granted loan. Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate Interest Rate Understanding Interest and
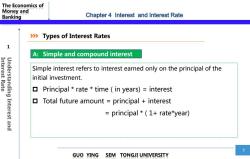
The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate >>Types of Interest Rates 1 A:Simple and compound interest Interest Rate Simple interest refers to interest earned only on the principal of the Understanding Interest and initial investment. Principal rate time(in years)=interest ▣ Total future amount principal interest principal 1+rate*year) 7 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 7 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 1 Types of Interest Rates Simple interest refers to interest earned only on the principal of the initial investment. Principal * rate * time ( in years) = interest Total future amount = principal + interest = principal * ( 1+ rate*year) Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate Interest Rate Understanding Interest and A: Simple and compound interest

The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate >>Types of Interest Rates 1 A:Simple and compound interest Interest Rate Compound interest involves earning interest in addition to the interest Understanding Interest and earned on the principal or initial investment Total future amount principal *(1+rate)n 8 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 8 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 1 Types of Interest Rates Compound interest involves earning interest in addition to the interest earned on the principal or initial investment Total future amount = principal * ( 1+ rate) n Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate Interest Rate Understanding Interest and A: Simple and compound interest

The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate >>Types of Interest Rates 1 B:Nominal and real interest rate Interest Rate Understanding Interest rate is corrected for the effects of inflation in order to make a meaningful economic comparison over time ▣r=N-INF Interest and r stands for real rate,N for nominal rate and INF for inflation rate 9 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 9 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 1 Types of Interest Rates Interest rate is corrected for the effects of inflation in order to make a meaningful economic comparison over time r = N – INF r stands for real rate, N for nominal rate and INF for inflation rate Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate Interest Rate Understanding Interest and B: Nominal and real interest rate

The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate >>Types of Interest Rates 1 C:Official,pact and market interest rates Interest Rate Official interest rate is the rate set by the central banks or monetary Understanding Interest and authorities ■ Pact interest rate is the rate set by the non-government authorities, such as trade union ■ Market interest rate is the rate wholly determined by the demand for and supply of funds in the financial markets at a certain time. 10 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 10 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 1 Types of Interest Rates Official interest rate is the rate set by the central banks or monetary authorities Pact interest rate is the rate set by the non-government authorities, such as trade union Market interest rate is the rate wholly determined by the demand for and supply of funds in the financial markets at a certain time. Chapter 4 Interest and Interest Rate Interest Rate Understanding Interest and C: Official , pact and market interest rates
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Credit and Financial Instrument.pdf
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Money and Monetary System.pdf
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 Introduction(负责人:郭英).pdf
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Answers for Test Sample(参考答案)Chapter 1-10.docx
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Chapter 9 Money and Inflation.docx
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Chapter 8 Money Supply and Money Demand.docx
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Chapter 7 Financial Markets.docx
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Chapter 6 Central Banks.docx
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Chapter 5 Commercial Banks.docx
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Chapter 4 The Economics of Financial Intermediary.docx
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Chapter 3 Interest and Interest Rate.docx
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Chapter 2 Credit and Financial Instruments.docx
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Chapter 1 Money and Monetary System.docx
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)教学大纲 The Economics of Money and Banking.pdf
- 吉林大学:《财政学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)远程教育考试样卷(无答案).doc
- 吉林大学:《经济法》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,共十三章,授课对象:远程教育,授课教师:孙凤英).ppt
- 《财务管理》课程教学资源(专项报告)南宁市宾阳县生猪现代农业产业园实施方案(简版).pdf
- 《财务管理》课程教学资源(专项报告)存栏1120头商品猪养殖小区可行性研究报告(简版).pdf
- 《财务管理》课程教学资源(专项报告)存栏2000头祖代原种猪场可行性研究报告(简版).pdf
- 《财务管理》课程教学资源(专项报告)存栏3000头曾祖代原种猪场环保生态养殖综合开发项目可研报告(简版).pdf
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 5 Financial Institutions.pdf
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Commercial Banks.pdf
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 7 Central Banks.pdf
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 8 Financial Markets.pdf
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Monetary Policy.pdf
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply.pdf
- 同济大学:《货币金融学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 Inflation and Deflation.pdf
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第一章 绪论(负责人:孙烨).ppt
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第二章 帐户与复式记帐.ppt
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第三章 分录与记帐.ppt
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第四章 试算与调整.ppt
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十章 无形资产与其他资产.ppt
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十一章 负债.ppt
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十二章 所有者权益.ppt
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第五章 结帐与编表.ppt
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 货币资金与应收帐款.ppt
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第七章 存货.ppt
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 投资.ppt
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第九章 固定资产.ppt
- 吉林大学:《会计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十三章 营业收入.ppt
