上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 46_Diesel cycle and dual cycle

上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 46 Chapter 9 Gas Power Cycles Spring,5/15/2018 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG 强 LA http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html SHANG 1日 ERSITY
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 46 Spring, 5/15/2018 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG Chapter 9 Gas Power Cycles http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html
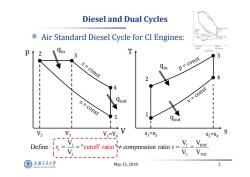
Diesel and Dual Cycles Air Standard Diesel Cycle for CI Engines: k p 3 s=const Qin p=const 4 v=const s=const Qout 1 V1=V4 ---。。-1 S1=S2 S3=S4 Define:ir ="cutoff ratio"compression ratio r= V2 上游充通大率 May15,2018 2 SHANGHA BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 15, 2018 2 Diesel and Dual Cycles Air Standard Diesel Cycle for CI Engines: qout s T 1 2 4 3 s 1=s 2 s 3=s 4 qin qout V p 1 2 4 3 V 1=V 4 qin V 2 V 3 3 1 BDC c 2 2 TDC V V V Define : r " " compression ratio r V V cutoff ratio V
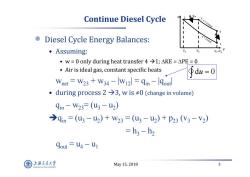
Continue Diesel Cycle qin s=const Diesel Cycle Energy Balances: const ·Assuming: V, V3 ·w=0 only during heat transfer4→1;AKE=APE=0 Air is ideal gas,constant specific heats du=0 Wnet W23 W34-W12=qin -lqoutl . during process2→3,wist0(change in volume) qin-W23=(u3-u2) 今qin=(u3-u2)+W23=(u3-u2)+p23(V3-V2) =h3-h2 dout u4 -u1 上游充通大 May15,2018 3 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 15, 2018 3 Continue Diesel Cycle Diesel Cycle Energy Balances: • Assuming: • w = 0 only during heat transfer 4 1; KE = PE = 0 • Air is ideal gas, constant specific heats wnet = w23 + w34 – |w12| = qin – |qout| • during process 2 3, w is ≠0 (change in volume) qin – w23= (u 3 – u 2) qin = (u 3 – u 2) + w23 = (u 3 – u 2) + p23 (v 3 – v 2) = h 3 – h 2 qout = u 4 – u 1 d 0 u V p 1 2 4 3 V1=V4 qin V2 V3
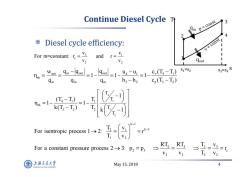
Continue Diesel Cycle Tt p=const 3 Diesel cycle efficiency: v=const For m-constant:=V3 and r=VL V2 V2 Qout n%-w-99-19-1-u=u=1-cc,-p S1=S2 3S4S Qin Qin Qin h3-h2 c(T3-T2) or1→2是-() =rk-l For a constant pressure process2-→3:p2=P3→ → V2 V3 T V2 上游充通大率 May15,2018 4 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 15, 2018 4 Continue Diesel Cycle Diesel cycle efficiency: 3 1 c 2 2 v v For m=constant: r and r v v s T 1 2 4 3 s1=s2 s3=s 4 qin qout net v 4 1 in out out 4 1 th in in in 3 2 p 3 2 w c (T T ) qq q u u 11 1 q q q h h c (T T ) 4 1 3 2 41 1 th 32 2 T T T T 1 (T T ) T 1 1 k(T T ) T k 1 k 1 2 1 k 1 1 2 T v For isentropic process 1 2: r T v 2 3 33 23 c 2 3 22 RT RT T v For a constant pressure process 2 3: p p r v v Tv
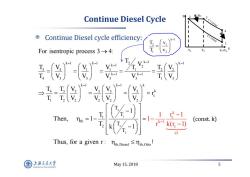
Continue Diesel Cycle s=const Continue Diesel cycle efficiency: s=const For isentropic process3-→4: 1V2 V3 Vi=V,V k- Then, 1-1 =1- k。-) (const.k) ≥1 Thus,for a given r:nth.Diesel snth.ot! 上游充通大率 May15,2018 5 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 15, 2018 5 Continue Diesel Cycle Continue Diesel cycle efficiency: k 1 k1 k1 k1 2 k 1 2 3 4 1 1 1 22 k1 k1 4 3 3 3 3 13 k1 k1 k 4 33 33 3 k c 1 22 22 2 For isentropic process 3 4: T V T V V V T TV T V V V V TV T TV VV V r T TV VV V k 1 2 1 1 2 T v T v (const. k) 4 1 3 2 k c k 1 th 2 1 c 1 T T T T 1 T Then, 1 T k 1 1 r 1 1 r k(r 1) V p 1 2 4 3 V1=V4 qin V2 V3 Thus, for a given r : ! th,Diesel th,Otto
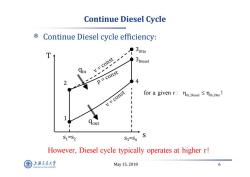
Continue Diesel Cycle Continue Diesel cycle efficiency: T v=const 3piesel Qin 2 p=const 4 v=const for a given r:mth.Diesel t.o! I S1=S2 S3=S4 However,Diesel cycle typically operates at higher r! 上游充通大率 May15,2018 6 SHANGHA BAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 15, 2018 6 Continue Diesel Cycle Continue Diesel cycle efficiency: s T 1 2 4 s 1=s 2 s 3=s 4 qin qout 3Diesel 3Otto th,Diesel th,Otto for a given r : ! However, Diesel cycle typically operates at higher r!
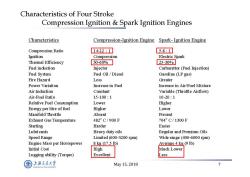
Characteristics of Four Stroke Compression Ignition Spark Ignition Engines Characteristics Compression-Ignition Engine Spark-Ignition Engine Compression Ratio 14-22:1 5-8:1 Ignition Compression Electric Spark Thermal Efficiency 30-60% 25-30% Fuel induction Injector Carburettor (Fuel Injection) Fuel System Fuel Oil/Diesel Gasoline (LP gas) Fire Hazard Less Greater Power Variation Increase in Fuel Increase in Air/Fuel Mixture Air Induction Constant Variable (Throttle Airflow) Air-Fuel Ratio 15-100:1 10-20:1 Relative Fuel Consumption Lower Higher Energy per litre of fuel Higher Lower Manifold Throttle Absent Present Exhaust Gas Temperature 482°C/900F 704°C/1300F Starting Harder Easier Lubricants Heavy duty oils Regular and Premium Oils Speed Range Limited (600-3200 rpm) Wide range (400-6000 rpm) Engine Mass per Horsepower 8kg(17.51b) Average 4 kg (9 1b) Initial Cost 五igh Much Lower Lugging ability (Torque) Excellent ess 上游充通大粤 May15,2018 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 15, 2018 7 Characteristics of Four Stroke Compression Ignition & Spark Ignition Engines

Example 46.1 for Diesel Cycle Given: ·Ideal Diesel cycle: r=18,re=2,p1=0.1MPa,T1=300K ④Find: ● Pressures,temperatures and specific volumes at all state points Heat input,net work output and thermal efficiency ·MEP Assumption: (1)air-standard assumptions (2)△KE=0,△PE=0 上游充通大 May15,2018 8 HANGHAI HAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 15, 2018 8 Example 46.1 for Diesel Cycle Given: • Ideal Diesel cycle: r = 18, r c = 2, p 1 = 0.1 MPa, T1 = 300 K Find: • Pressures, temperatures and specific volumes at all state points • Heat input, net work output and thermal efficiency • MEP Assumption: (1) air‐standard assumptions (2) KE=0, PE=0
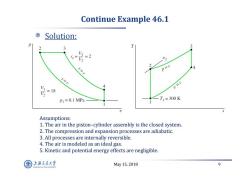
Continue Example 46.1 Solution: P 3 3 V3-2 Io= 0 S=c p=c S=C =18 U=C P1=0.1 MPa T1=300K U Assumptions: 1.The air in the piston-cylinder assembly is the closed system. 2.The compression and expansion processes are adiabatic. 3.All processes are internally reversible. 4.The air is modeled as an ideal gas. 5.Kinetic and potential energy effects are negligible. 上游充通大¥ May15,2018 9 SHANGHA BAO TONG LINIERSITY
May 15, 2018 9 Continue Example 46.1 Solution: Assumptions: 1. The air in the piston–cylinder assembly is the closed system. 2. The compression and expansion processes are adiabatic. 3. All processes are internally reversible. 4. The air is modeled as an ideal gas. 5. Kinetic and potential energy effects are negligible

Continue Example 46.1 Tab.A-17 ©T1=300K,p1=1atm→u1=214.07k/kg,Vr1=621.2 T=300K ©Process1-2: 621.2 v2二V,n =34.51 18 T2=898.3K h2=930.98k/kg Tab.A-17 Ty=0.) EoS P2=PIT]V: 898.3 300 (18)=5.39MPa ©Process2-3: T3= ,=3=2898.3)=1766K V2 h3=1999.1k/kg Tab.A-17 Vr3=3.97 Process 3-4: (S U3= V2V- 3u4=664.3k/kg Tab.A-17 T4=887.7 Process 4-1: EoS T(0.1 MPa) 887.7K 300K/ =0.3 MPa 上游充通大率 May15,2018 10 SHANGHAI BAO TONG LINIVERSITY
May 15, 2018 10 Continue Example 46.1 T 1 = 300 K, p 1=1atm u 1= 214.07kJ/kg, vr1=621.2 Process 1‐2: Process 2‐3: Process 3‐4: Process 4‐1: Tab. A‐17 S Tab. A‐17 T 2=898.3 K h 2 = 930.98 kJ/kg EoS p Tab. A‐17 h 3=1999.1 kJ/kg vr3 = 3.97 S u 4=664.3 kJ/kg T 4 = 887.7 Tab. A‐17 EoS
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 45_Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 43-44_Vapor-compression refrigeration, Heat pump systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 41-42_superheat and reaheat.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 39-40_vapor power cycles.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 38_Exergy of CV systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 37_Concept of exergy and apply to CM systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 36_Heat transfer and Work of internal reversible, ss flow.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 35_Isentropic processes, Isentropic efficiencies.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 34_Entropy balance to open systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 33_Entropy increase principle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 32_Internally reversible processes, Closed system entropy balance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 31_Retrieve entropy data.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 30_Clausius inequality and Entropy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 29_Carnot Cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 27-28_Applying 2nd law to thermodynamic cycles, Maximum performance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 23-24_Introducing 2nd law, concept of irreversibilities.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 22_Transient analysis of Energy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 20-21_Illustrations_3 Heat exchangers, throttling devices, System integration.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 19_Illustrations_2 Compressors, pumps.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 18_Illustrations_1 Nozzles, diffusers, turbines.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 47_Compressor, compression with intercooling.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 48_Review and Final Exam.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 01-02_Course Introduction-web.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 03-04_Concepts.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 05-06_Energy, work, heat transfer.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 07-08_Energy balance for close system and cycles.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 09-10_Substance, property and phase.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 11_Retrieving pvt properties.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 12_Evaluating u, h, cp, cv properties.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 13_Equation of state and ideal gas model.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 14_cv, cp, Δu, Δh of ideal gas and applied to close system.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 15_Polytropic process.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 16_Control volume analysis - mass conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 17_Control volume analysis - energy conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 18_Illustrations_1 Nozzles, diffusers, turbines.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 19_Illustrations_2 Compressors, pumps.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 20-21_Illustrations_3 Heat exchangers, throttling devices, System integration.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 22_Transient analysis of Energy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 23-24_Introducing 2nd law, concept of irreversibilities.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 25-26_Applying 2nd law to thermodynamic cycles, Maximum performance.pdf
