上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 07-08_Energy balance for close system and cycles

上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Engineering Thermodynamics I Lectures 7-8 Spring,2019 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG 强 月n是n http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html 1日G
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lectures 7-8 Spring, 2019 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html
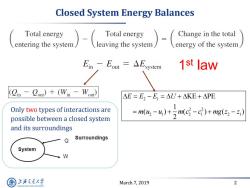
Closed System Energy Balances Total energy Total energy Change in the total entering the system energy of the system En-Eout=△Esystem 1st law (Qin-Cou)+(Win -Wou) AE=E2-E,=△U+AKE+APE Only two types of interactions are =m(4-4)+与m(c-c)+mg(2-21) possible between a closed system and its surroundings Surroundings System W 上降文通大学 March 7,2019 2 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 7, 2019 2 Closed System Energy Balances 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 KE PE 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 E E E U m u u m c c mg z z Only two types of interactions are possible between a closed system and its surroundings 1 st law
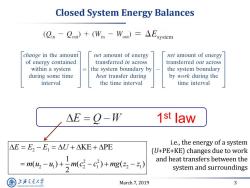
Closed System Energy Balances (gn-Qo)+(Wn-Wou)=△Fsystem change in the amount net amount of energy net amount of energy of energy contained transferred in across transferred out across within a system the system boundary by the system boundary during some time heat transfer during by work during the interval the time interval time interval △E=Q-W 1st law AE=E2-E,=△U+AKE+APE i.e.,the energy of a system (U+PE+KE)changes due to work =m(4,-4)+5m(c-c2)+mg(32-z) and heat transfers between the system and surroundings 上降文通大学 March 7,2019 3 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 7, 2019 3 Closed System Energy Balances i.e., the energy of a system (U+PE+KE) changes due to work and heat transfers between the system and surroundings 1 st law 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 KE PE 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 E E E U m u u m c c mg z z

Important Notes on 1st Law 1.E is always measured relative to reference point! ··Reference plane for PE 。·Reference frame for KE .Reference state for U (i.e.U=0@reference state) 2.Changes in E are important,not total values of E 3.AE depends only on beginning and end states (property) 4.Q and W depend on process path (could get to the same end state with different combinations of Q and W) 国 5.Energy balance for a particular problem will depend on the system that you select >YOU MUST ALWAYS SPECIFY YOUR SYSTEM IN ORDER TO APPLY THE 1ST LAW 6.Total heat transfer is the summation of all heat transfers across the system boundary Q-∑Q, 7.Total work is the summation of all work transfers across the system boundary W=∑W 上游充通大学 March 7,2019 4 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 7, 2019 4 Important Notes on 1st Law 1. E is always measured relative to reference point! • • Reference plane for PE • • Reference frame for KE • • Reference state for U (i.e. U = 0 @ reference state) 2. Changes in E are important, not total values of E 3. ΔE depends only on beginning and end states (property) 4. Q and W depend on process path (could get to the same end state with different combinations of Q and W) 5. Energy balance for a particular problem will depend on the system that you select YOU MUST ALWAYS SPECIFY YOUR SYSTEM IN ORDER TO APPLY THE 1ST LAW 6. Total heat transfer is the summation of all heat transfers across the system boundary 7. Total work is the summation of all work transfers across the system boundary
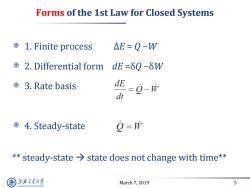
Forms of the 1st Law for Closed Systems 1.Finite process △E=Q-W 2.Differential form dE=δQ-δW ©3.Rate basis dE =9-W dt 国4.Steady-state o-w *steady-state>state does not change with time** 上游充通大学 March 7,2019 5 HANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 7, 2019 5 Forms of the 1st Law for Closed Systems 1. Finite process ΔE = Q −W 2. Differential form dE =δQ −δW 3. Rate basis 4. Steady-state ** steady-state state does not change with time**
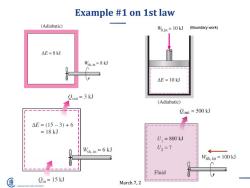
Example #1 on 1st law (Adiabatic) W.in=10 kJ (Boundary work) △E=8kJ Wsh.in=8 kJ △E=10kJ Cout=3 kJ (Adiabatic) 1 Cout =500 kJ △E=(15-3)+6 =18kJ U =800 kJ Wsh.in=6 kJ U2=? Wsh,in=100 kJ Fluid Cin =15 kJ March 7,2 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 7, 2019 6 Example #1 on 1st law (Boundary work)

Example #2 on 1st Law What if you rolled a window AC into a well-insulated room that has no other air conditioner,put it on a table and plugged it in?Would you expect the room temperature to increase,decrease,or remain the same? AC System 上游充通大学 March 7,2019 7 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 7, 2019 7 Example #2 on 1st Law What if you rolled a window AC into a well-insulated room that has no other air conditioner, put it on a table and plugged it in? Would you expect the room temperature to increase, decrease, or remain the same? System

Example #3 on 1st law Known:Data are provided for air contained in a vertical piston- cylinder fitted with an electrical resistor.Neglect friction. Find:heat transfer from the resistor to the air for (a)air alone;(b)air piston. Schematic and Given Data: -Piston Piston Patm=1 bar System System mpiston =45 kg boundary boundary Apiston=.09 m2 for part (b) for part (a) g=9.81m/s2. Air Air slowly Good mair=.27 kg V2-V1=.045m3 insulator △lair=42kJ/kg. (a)air alone (b)air piston 上游充通大 March 7,2019 8 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 7, 2019 8 Example #3 on 1st law Known: Data are provided for air contained in a vertical piston– cylinder fitted with an electrical resistor. Neglect friction. Find: heat transfer from the resistor to the air for (a) air alone; (b) air + piston. Schematic and Given Data: slowly Good insulator g =9.81 m/s2 . air alone air + piston

Energy balance analysis example_cont 国 air alone as the system,energy balance 0 0 (△KE+△PE+△U)ar=Q-W Q=W+△Uair→ Q=W+mair(△lair) 个 =4.72kJ+11.34kJ=16.06kJ Const.p =i nair(△uair) pdv=p(V2-Vi) given W=p(V2-Vi) 一Piston Force balance 10N/m2 1kJ Patm I bar =(1.049bar)(.045m2) =4.72kJ 1bar 103Nm System mpiston =45 kg boundary PApiston-mpiston PamApiston Apiston=.09 m2 for part(a) 9=9.81m/s2. Air p= Apiston 十Patm slowly (45 kg)(9.81 m/s2)1 bar mair =.27 kg Good D= 10N/m2 I bar 1.049 bar V2-1=.045m3 .09m2 insulator △4ir=42kJ/kg. (a)air alone 上游充通大 March 7,2019 9 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 7, 2019 9 Energy balance analysis example_cont. air alone as the system, energy balance Const. p Force balance given
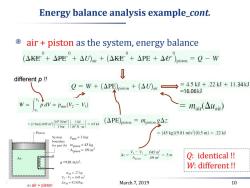
Energy balance analysis example_cont. air piston as the system,energy balance 0 (△KE+△PE+△U)air+(KE+△PE+△H)piston=Q-W different p ! Q=W+(△PE)piston+(△U)air =4.5kJ+.22kJ+11.34kJ =16.06kJ W=pdV=Pam(V2-Vi) = mair(△uair) =(1bar)(.045m 105N/m2 1kJ (APE)piston=mpiston 1bar =4.5kJ 103Nm Piston =(45kg)(9.81m/s2)(0.5m)=.22kJ System Patm =I bar boundary for part (b) mpiston =45 kg -Apiston =.09 m2 4:=上-y=045m =.5m Air Apiston .09m2 Q:identical! g=9.81m/s2. W:different!! mair =.27 kg V2-V1=.045m3 △Mai=42kJ/kg. (b)air piston March 7,2019 10
March 7, 2019 10 Energy balance analysis example_cont. air + piston as the system, energy balance Q: identical !! W: different !! different p !!
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 05-06_Energy, work, heat transfer.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 03-04_Concepts.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 01-02_Course Introduction-web.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 48_Review and Final Exam.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 47_Compressor, compression with intercooling.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 46_Diesel cycle and dual cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 45_Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 43-44_Vapor-compression refrigeration, Heat pump systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 41-42_superheat and reaheat.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 39-40_vapor power cycles.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 38_Exergy of CV systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 37_Concept of exergy and apply to CM systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 36_Heat transfer and Work of internal reversible, ss flow.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 35_Isentropic processes, Isentropic efficiencies.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 34_Entropy balance to open systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 33_Entropy increase principle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 32_Internally reversible processes, Closed system entropy balance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 31_Retrieve entropy data.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 30_Clausius inequality and Entropy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 29_Carnot Cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 09-10_Substance, property and phase.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 11_Retrieving pvt properties.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 12_Evaluating u, h, cp, cv properties.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 13_Equation of state and ideal gas model.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 14_cv, cp, Δu, Δh of ideal gas and applied to close system.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 15_Polytropic process.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 16_Control volume analysis - mass conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 17_Control volume analysis - energy conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 18_Illustrations_1 Nozzles, diffusers, turbines.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 19_Illustrations_2 Compressors, pumps.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 20-21_Illustrations_3 Heat exchangers, throttling devices, System integration.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 22_Transient analysis of Energy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 23-24_Introducing 2nd law, concept of irreversibilities.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 25-26_Applying 2nd law to thermodynamic cycles, Maximum performance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 27_Carnot Cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 28_Clausius inequality and Entropy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 31_Retrieve entropy data.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 32_Internally reversible processes, Closed system entropy balance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 33_Entropy increase principle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 34_Entropy balance to open systems.pdf
