上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 03-04_Concepts

上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Engineering Thermodynamics I Lectures 3-4 Spring,2019 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG 强 A月是 http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html AN 1日G
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lectures 3-4 Spring, 2019 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html

Chapter 1 Concepts,Systems Units ④Objective fundamental concepts:including closed system,control volume,boundary and surroundings,property,state, process,the distinction between extensive and intensive properties,and equilibrium. apply SI Engineering units. Kelvin,Rankine,Celsius,and Fahrenheit temperature scales. apply the problem-solving methodology. 上游气通大粤 February 28,2019 2 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
February 28, 2019 2 Chapter 1 Concepts, Systems & Units Objective • fundamental concepts: including closed system, control volume, boundary and surroundings, property, state, process, the distinction between extensive and intensive properties, and equilibrium. • apply SI Engineering units. • Kelvin, Rankine, Celsius, and Fahrenheit temperature scales. • apply the problem-solving methodology

1.1 System and Surroundings Thermodynamic system -Any three-dimensional region of space bounded by one or more arbitrary geometric surfaces SURROUNDINGS Surroundings SYSTEM -The region of space outside the arbitrary boundaries BOUNDARY Abstraction of system Air Air actuating shaft gasoline gasoline Automobile engine actuating shaft Boundary > exhaust gas (a) (h) 上游充通大学 February 28,2019 3 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
February 28, 2019 3 1.1 System and Surroundings Thermodynamic system –Any three-dimensional region of space bounded by one or more arbitrary geometric surfaces Surroundings –The region of space outside the arbitrary boundaries Abstraction of system Automobile engine
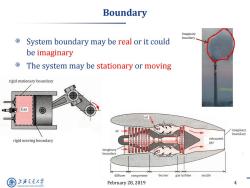
Boundary Imaginary boundary System boundary may be real or it could be imaginary The system may be stationary or moving rigid stationary boundary chimney Gas air imaginary boundary exhausted rigid moving boundary gas imaginary boundary diffuser compressor burner gas turbine nozzle 上游充通大学 February 28,2019 4 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
February 28, 2019 4 Boundary System boundary may be real or it could be imaginary The system may be stationary or moving Imaginary boundary chimney

Types of Systems System interaction with its surroundings: Mass No Closed ·mass/energy system Closed System m=constant allows transfer of energy only across its boundaries; Energy Yes no mass transfer 。 Chemical composition within the system may change;but mass remains constant (volume may change) boundary Closed System Control Mass [CM] mass YES Open System Open allows both transfer of energy and mass system Open system=Control volume [CVI energyYES Simple compressible system:consists of compressible fluids,only volume change work (reversible)exchanged 上游充通大 February 28,2019 5 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
February 28, 2019 5 Types of Systems System interaction with its surroundings: • mass /energy Closed System allows transfer of energy only across its boundaries; no mass transfer • Chemical composition within the system may change; but mass remains constant (volume may change) • Closed System = Control Mass [CM] Open System allows both transfer of energy and mass • Open system= Control volume [CV] Simple compressible system: consists of compressible fluids, only volume change work (reversible) exchanged Open system

Adiabatic system,Isolated system heat insulation material Q=0 adiabatic system Adiabatic system:No heat exchange Isolated system:No energy and mass exchange 上游气通大粤 February 28,2019 6 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
February 28, 2019 6 Adiabatic system: No heat exchange Isolated system: No energy and mass exchange Adiabatic system, Isolated system

Examples for understanding system (1).Rigid adiabatic cylinder-piston system.Electrical heater in room B Red line closed,adiabatic system Yellow line without heater -closed system Yellow line with heater A B 庋 -closed,adiabatic system Blue line -isolated system 上游充通大 February 28,2019 7 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
February 28, 2019 7 (1).Rigid adiabatic cylinder-piston system. Electrical heater in room B Red line ——closed, adiabatic system Yellow line without heater ——closed system Yellow line with heater ——closed, adiabatic system Blue line ——isolated system Examples for understanding system

(2).Water heater at steady state boundarv mout outlet hot water water heater nlet min II 10L cold water mout=mn? Close system or open system? 上游充通大 February 28,2019 8 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
February 28, 2019 8 mout mout = min ? min Close system or open system? (2).Water heater at steady state

(3).Chemical reaction:Calcium carbonate System? CaCO3 上游充通大学 February 28,2019 9 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
February 28, 2019 9 System? (3).Chemical reaction: Calcium carbonate

(4).Rigid adiabatic nozzle P P. m2-r i t P2Cf c-velocity i-mass flow rate Red line system(gas)-Closed system Nozzle as system- Open,adiabatic system 上游充通大 February 28,2019 10 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
February 28, 2019 10 Closed system (4).Rigid adiabatic nozzle Red line system (gas) — Nozzle as system— Open, adiabatic system c – velocity m –mass flow rate
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 01-02_Course Introduction-web.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 48_Review and Final Exam.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 47_Compressor, compression with intercooling.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 46_Diesel cycle and dual cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 45_Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 43-44_Vapor-compression refrigeration, Heat pump systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 41-42_superheat and reaheat.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 39-40_vapor power cycles.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 38_Exergy of CV systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 37_Concept of exergy and apply to CM systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 36_Heat transfer and Work of internal reversible, ss flow.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 35_Isentropic processes, Isentropic efficiencies.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 34_Entropy balance to open systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 33_Entropy increase principle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 32_Internally reversible processes, Closed system entropy balance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 31_Retrieve entropy data.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 30_Clausius inequality and Entropy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 29_Carnot Cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 27-28_Applying 2nd law to thermodynamic cycles, Maximum performance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 23-24_Introducing 2nd law, concept of irreversibilities.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 05-06_Energy, work, heat transfer.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 07-08_Energy balance for close system and cycles.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 09-10_Substance, property and phase.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 11_Retrieving pvt properties.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 12_Evaluating u, h, cp, cv properties.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 13_Equation of state and ideal gas model.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 14_cv, cp, Δu, Δh of ideal gas and applied to close system.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 15_Polytropic process.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 16_Control volume analysis - mass conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 17_Control volume analysis - energy conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 18_Illustrations_1 Nozzles, diffusers, turbines.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 19_Illustrations_2 Compressors, pumps.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 20-21_Illustrations_3 Heat exchangers, throttling devices, System integration.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 22_Transient analysis of Energy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 23-24_Introducing 2nd law, concept of irreversibilities.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 25-26_Applying 2nd law to thermodynamic cycles, Maximum performance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 27_Carnot Cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 28_Clausius inequality and Entropy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 31_Retrieve entropy data.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 32_Internally reversible processes, Closed system entropy balance.pdf
