电子科技大学:《高级数字信号处理》研究生课程(PPT课件)Chapter 9 Adaptive Filters

CHAPTER 9 Adaptive Filters Goal of an adaptive filter: To "find and track"the optimum filter obtained by using the knowledge of signal statistics. Why to find?How to track?
CHAPTER 9 Adaptive Filters Goal of an adaptive filter: To “find and track” the optimum filter obtained by using the knowledge of signal statistics. Why to find? How to track?

Contents 9.1 Typical Applications of Adaptive Filters 9.2 Principles of Adaptive Filters 9.3 Method of Steepest Descent 9.4 Least-Mean-Square Adaptive Filters 9.5 Recursive Least-Squares Adaptive Filters 9.6 Fast RLS Algorithms for FIR Filtering 9.7 Tracking Performance of Adaptive Algorithms 9.8 Summary
9.1 Typical Applications of Adaptive Filters 9.2 Principles of Adaptive Filters 9.3 Method of Steepest Descent 9.4 Least-Mean-Square Adaptive Filters 9.5 Recursive Least-Squares Adaptive Filters 9.6 Fast RLS Algorithms for FIR Filtering 9.7 Tracking Performance of Adaptive Algorithms 9.8 Summary Contents

9.1 Typical Applications of Adaptive Filters 9.1.1 Echo Cancelation in Communications (1)electrical or line echoes (2)acoustic echoes
(1) electrical or line echoes (2) acoustic echoes 9.1.1 Echo Cancelation in Communications 9.1 Typical Applications of Adaptive Filters

9.1.1 Echo Cancelation in Communications Four-wire connection Two-wire connection Speech from Hybrid Hybrid A B Talker Echo of 4's Talker A speech Speech B from B FIGURE 9.1 Echo generation in a long-distance telephone network
FIGURE 9.1 Echo generation in a long-distance telephone network 9.1.1 Echo Cancelation in Communications

9.1.1 Echo Cancellation in Communications The switch remains off when talker B is silent! Echo suppressor 声控开关 Control Hybrid Talker Speech B from B What if talkers A and B quarrel with each other? Voice clipping will happen! FIGURE 9.2 Principle of echo suppression
FIGURE 9.2 Principle of echo suppression 9.1.1 Echo Cancellation in Communications 声控开关 The switch remains off when talker B is silent! What if talkers A and B quarrel with each other? Voice clipping will happen!

9.1.1 Echo Cancelation in Communications Two Possible Ways 1.Design a compromise fired echo canceler based on some “average'”echo path(平均的抵消回声). 2.Design an adaptive echo canceler that can "learn"the echo path when it is first turned on and afterward "tracks"its variations without any intervention from the designer 应的抵消回声)·
Two Possible Ways 1. Design a compromise fixed echo canceler based on some “average” echo path(平均的抵消回声). 2. Design an adaptive echo canceler that can “learn” the echo path when it is first turned on and afterward “tracks” its variations without any intervention from the designer(自适 应的抵消回声). 9.1.1 Echo Cancelation in Communications

9.1.1 Echo Cancelation in Communications Echo canceler From talker A Hybrid B Speech Talker Echo from B B To talker A replica D Echo from 4 The adaptive filter attempts to estimate the path from C to D and then generate an echo replica for noise cancellation. In this way,the talkers can quarrel if they want t0. FIGURE 9.3 Principle of echo cancelation
9.1.1 Echo Cancelation in Communications FIGURE 9.3 Principle of echo cancelation The adaptive filter attempts to estimate the path from C to D and then generate an echo replica for noise cancellation. In this way, the talkers can quarrel if they want to

9.1.3 Noise Cancelation What is the practical scenario for such a noise cancellation paradigm? 1)KARAOKE Bar. 2)Noise-cancellation Headphone Signal s(n)+(n) e(n) source Primary input Noise 2物 Filter source Reference input FIGURE9.6 Principle of adaptive noise cancellation using a reference input
FIGURE 9.6 Principle of adaptive noise cancellation using a reference input. 9.1.3 Noise Cancelation What is the practical scenario for such a noise cancellation paradigm? 1) KARAOKE Bar. 2) Noise-cancellation Headphone

9.1.3 Noise Cancelation Signal s(n)+(n) e(n source Primary input Noise (倒 Filter source Reference input The signals s(n),v(n),and v2(n)are jointly wide-sense stationary with zero mean values.The"clean"signal is given by the error e(n)=s(n)+[y(n)-n)] where (n)depends on the filter structure and parameters
The signals and are jointly wide-sense stationary with zero mean values. The “clean” signal is given by the error s n v n ( ) ( ) 1 v n 2 ( ) where depends on the filter structure and parameters. y n ˆ( ) 9.1.3 Noise Cancelation
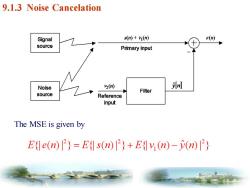
9.1.3 Noise Cancelation Signal (m)+y1(m) e(n) source Primary input Noise 2(例 Filter source Reference input The MSE is given by Ede(n)=Es(n)+Ev(n)-(n
The MSE is given by 9.1.3 Noise Cancelation
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《高级数字信号处理》研究生课程(PPT课件)Chapter 8 Parametric Spectrum Estimation.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(作业习题)课后习题(无答案).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 二端口电路.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 电路的频率响应和谐振现象(2/4)5.2 一阶电路和二阶电路的频率响应 5.3 串联谐振电路.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 电路的频率响应和谐振现象(3/4)5.4 并联谐振电路.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 电路的频率响应和谐振现象(1/4)5.1 网络函数与频率特性 5.2 一阶电路和二阶电路的频率响应.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 电路的频率响应和谐振现象(4/4)5.4 并联谐振电路.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 正弦稳态分析(8/8)4.7 变压器.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 正弦稳态分析(5/8)4.5 正弦稳态电路的功率.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 正弦稳态分析(4/8)4.4 阻抗与导纳、正弦稳态电路的计算.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 正弦稳态分析(6/8)4.5 正弦稳态电路的功率 4.6 互感耦合电路.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 正弦稳态分析(2/8)4.2 相量法的基本概念 4.3 电路定律的相量形式.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 正弦稳态分析(3/8)4.3 电路定律的相量形式 4.4 阻抗与导纳、正孩稳态电路的计算.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 正弦稳态分析(7/8)4.6 互感耦合电路 4.7 变压器.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 正弦稳态分析(1/8)4.1 正弦量 4.2 相量法的基本概念.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 动态电路(2/4)3.2 动态电路的方程及其解 3.3 电路的初始值 3.4 一阶动态电路的响应.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 动态电路(3/4)3.4 一阶动态电路的响应 3.5 一阶电路的三要素公式.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 动态电路(4/4)3.5 一阶电路的三要素公式 3.6 阶跃函数和阶跃响应.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 动态电路(1/4)3.1 动态元件.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 电阻电路分析(4/5).pptx
- 《MIMO多进多出多天线》课程教学资源(文献资料)Wireless Communications - Present and Future.pdf
- 《MIMO多进多出多天线》课程教学资源(文献资料)6G——Massive MIMO is a Reality—What is Next? Five Promising Research Directions for Antenna Arrays.pdf
- 《MIMO多进多出多天线》课程教学资源(文献资料)Massive MIMO for Next Generation Wireless Systems.pdf
- 《MIMO多进多出多天线》课程教学资源(文献资料)A Simple Transmit Diversity Technique for Wireless Communications.pdf
- 《MIMO多进多出多天线》课程教学资源(文献资料)Capacity of Multi-antenna Gaussian Channels.pdf
- 《MIMO多进多出多天线》课程教学资源(文献资料)An Overview of MIMO Communications—A Key to Gigabit Wireless.pdf
- 《MIMO多进多出多天线》课程教学资源(文献资料)Polarization Diversity in Mobile Communications.pdf
- 《MIMO多进多出多天线》课程教学资源(文献资料)Radiowave Propagation——GEOMETRIC MODELS FOR ANGLE AND TIME OF ARRIVAL.pdf
- 《MIMO多进多出多天线》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)MIMO系统中的多天线设计(西安电子科技大学:赵鲁豫).pdf
- 《MIMO多进多出多天线》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Antennas for Base Stations in Wireless Communications,Zhi Ning Chen Kwai-Man Luk.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(课件讲义)绪论、电路模型与变量(主讲老师:赵鲁豫).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字通信理论与系统》课程教学课件(研究生)第1章 绪论(主讲:孙永军).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字通信理论与系统》课程教学课件(研究生)第2章 数字通信的数学基础.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字通信理论与系统》课程教学课件(研究生)第3章 通信信源与信源编码.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字通信理论与系统》课程教学课件(研究生)第4章 数字调制与基带传输技术.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字通信理论与系统》课程教学课件(研究生)第5章 AWGN信道下的数字解调.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字通信理论与系统》课程教学课件(研究生)第6章 载波跟踪与符号同步.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字通信理论与系统》课程教学课件(研究生)第7章 通信信道与无线链路.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字通信理论与系统》课程教学课件(研究生)第8章 信道编码.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字通信理论与系统》课程教学课件(研究生)第9章 扩频通信概述.pdf
