同济大学:《中国社会经济》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Education Development in China

Social Economic Development China Today "当代中国"豪列课程 Education Development in China
Understanding a Development Miracle Education Development in China Social Economic Development

Educationin China Imperial Examination in Ancient China Background ● The imperial examination system was applied in the feudal society to select officials from intellectuals.The Imperial Examination System in China lasted for 1300 years,from its founding during the Sui Dynasty in 605 to its abolition near the end of the Qing Dynasty in 1905
Background The imperial examination system was applied in the feudal society to select officials from intellectuals. The Imperial Examination System in China lasted for 1300 years, from its founding during the Sui Dynasty in 605 to its abolition near the end of the Qing Dynasty in 1905. Imperial Examination in Ancient China Education in China

Education in China 。 Degree types: ● Shengyuan(生员),also called xiucai(秀才),licentiate; administered at exams held in the county level each year. :●Juren(¥人)or"recommended man'",a provincial graduate, administered at the provincial level every three years ● Gongshi(贡士),a national degree"tribute personnel" Jinshi (or"presented scholar",a metropolitan graduate, administered in the capital every three years Zhuangyuan(狀元),lit.jinshi who ranked#1 first class . Bangyan(榜眼),lit.jinshi who ranked#2 first class. Tanhua(探花),lit.jinshi who ranked#3 first class
Degree types: ⚫ Shēngyuán (生员), also called xiùcái (秀才), licentiate; administered at exams held in the county level each year. ⚫ Jǔrén (举人) or "recommended man", a provincial graduate, administered at the provincial level every three years ⚫ Gongshi (贡士), a national degree "tribute personnel" ⚫ Jìnshì(进士) or "presented scholar", a metropolitan graduate, administered in the capital every three years Zhuangyuan (狀元), lit. jìnshì who ranked #1 first class Bangyan (榜眼), lit. jìnshì who ranked #2 first class. Tanhua (探花), lit. jìnshì who ranked #3 first class Education in China

Educationin China :Eight-legged essay The eight-legged essay was a style of essay writing that had to be mastered to pass the imperial examinations .It is named so because it was divided into eight sections. (1)Opening:two sentences of prose whose function is to broach the topic (2)Amplification:five sentences of prose,elaboratingupon and clarify the : theme. (3)Preliminary exposition Prosaic writing (4)Initial argument a specified number sentences pairs written in parallel,developing the initial argument. (5)Central argument: (6)Latter argument (7)Final argument (8)Conclusion
Eight-legged essay The eight-legged essay was a style of essay writing that had to be mastered to pass the imperial examinations .It is named so because it was divided into eight sections. (1) Opening: two sentences of prose whose function is to broach the topic (2) Amplification: five sentences of prose, elaborating upon and clarify the theme. (3) Preliminary exposition : Prosaic writing (4) Initial argument : a specified number sentences pairs written in parallel, developing the initial argument. (5) Central argument: (6) Latter argument (7) Final argument (8) Conclusion Education in China

Chinese Businessmen:Characteristics and New Change Shanghai Imperial Examination Museum:
Shanghai Imperial Examination Museum: Chinese Businessmen: Characteristics and New Change

Educationin China Education Development in China Background Since the founding of the People's Republic of China in 1949,an important governmental effort has been to eliminate illiteracy and popularize compulsory education (compulsory education covering primary and junior middle schooling . : · duration)
Background Since the founding of the People‘s Republic of China in 1949, an important governmental effort has been to eliminate illiteracy and popularize compulsory education (compulsory education covering primary and junior middle schooling duration) . Education Development in China Education in China
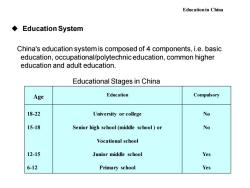
Educationin China Education System China's education system is composed of 4 components,i.e.basic education,occupational/polytechnic education,common higher education and adult education. Educational Stages in China Age Education Compulsory 18-22 University or college No 15-18 Senior high school(middle school)or No Vocational school 12-15 Junior middle school Yes 6-12 Primary school Yes
◆ Education System China's education system is composed of 4 components, i.e. basic education, occupational/polytechnic education, common higher education and adult education. Educational Stages in China Education in China Age Education Compulsory 18-22 15-18 12-15 6-12 University or college Senior high school (middle school ) or Vocational school Junior middle school Primary school No No Yes Yes

Educationin China Basic Education: Basic education in China includes pre-school education, ● primary education(6 years)and regular secondary education(6 years). 人 Pre-school education:It is an important component of education ● cause in China.In urban areas,pre-school education is mainly : kindergartens of 3 years.In rural areas,pre-school education is mainly nursery classes and seasonal kindergartens in addition. > Primary and Secondary Education:In China,primary and secondary ● education takes 12 years to complete,divided into primary,junior secondary and senior secondary stages.9-year schooling in primary and junior secondary schools pertains to compulsory education
⚫ Basic Education: Basic education in China includes pre-school education, primary education(6 years) and regular secondary education(6 years). ➢ Pre-school education: It is an important component of education cause in China. In urban areas, pre-school education is mainly kindergartens of 3 years. In rural areas, pre-school education is mainly nursery classes and seasonal kindergartens in addition. ➢ Primary and Secondary Education: In China, primary and secondary education takes 12 years to complete, divided into primary, junior secondary and senior secondary stages. 9-year schooling in primary and junior secondary schools pertains to compulsory education. Education in China

Education in China Medium-level Occupational and Polytechnic Education Mainly composed of medium-level professional schools, ● polytechnic schools,occupational middle schools as well as short-term occupational and technical training programs of various forms. ● Common Higher Education Common higher education comprises of junior college, bachelor,master and doctoral degree programs.Junior college program usually last 2~3 years;bachelor program 4 years (medical and some engineering and technical programs,5 years);master program 2~3 years;doctoral program 3 years. 211 project,985 project
⚫ Medium-level Occupational and Polytechnic Education Mainly composed of medium-level professional schools, polytechnic schools, occupational middle schools as well as short-term occupational and technical training programs of various forms. ⚫ Common Higher Education Common higher education comprises of junior college, bachelor, master and doctoral degree programs. Junior college program usually last 2~3 years; bachelor program 4 years (medical and some engineering and technical programs, 5 years); master program 2~3 years; doctoral program 3 years. 211 project, 985 project Education in China

Educationin China 2●●●●●00●●●0●●垂● ● Adult Education Adult education comprises of schooling education,anti-illiteracy education and other programs oriented to adult groups. China's adult education has evolved rapidly since the Liberation. ●● : There are many colleges and universities destined to adult : education and some 800 correspondence-based and evening adult education programs launched by common colleges. International Cooperation
⚫ Adult Education Adult education comprises of schooling education, anti-illiteracy education and other programs oriented to adult groups. China's adult education has evolved rapidly since the Liberation. There are many colleges and universities destined to adult education and some 800 correspondence-based and evening adult education programs launched by common colleges. ⚫ International Cooperation Education in China
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《中国社会经济》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)China’s Socio-Economic Development——Understanding A Development Miracle - China.ppt
- 暨南大学:经济与社会研究院政策简报——粤港澳大湾区发展规划建议(2018年4月).pdf
- 运城学院:《日本社会与文化》课程教学资源(习题,打印版)日本政治練習問題.pdf
- 运城学院:《日本社会与文化》课程教学资源(习题,打印版)日本国土3練習問題.pdf
- 运城学院:《日本社会与文化》课程教学资源(习题,打印版)日本国土2練習問題.pdf
- 运城学院:《日本社会与文化》课程教学资源(习题,打印版)日本国土1練習問題.pdf
- 运城学院:《日本社会与文化》课程教学资源(电子教案,打印版)日本政治2.pdf
- 运城学院:《日本社会与文化》课程教学资源(电子教案,打印版)日本政治1.pdf
- 运城学院:《日本社会与文化》课程教学资源(电子教案,打印版)日本国土3.pdf
- 运城学院:《日本社会与文化》课程教学资源(电子教案,打印版)日本国土2.pdf
- 运城学院:《日本社会与文化》课程教学资源(电子教案,打印版)日本国土1.pdf
- 运城学院:《日本社会与文化》课程教学资源(教学大纲,负责人:左莉娜,打印版).pdf
- 天津开放大学:《社会保障学》课程教学资源(学习资料)社会保障与社会工作.doc
- 天津开放大学:《社会保障学》课程教学资源(学习资料)课程资源.doc
- 天津开放大学:《社会保障学》课程教学资源(学习资料)课程教学大纲.doc
- 天津开放大学:《社会保障学》课程教学资源(学习资料)补考复习.doc
- 天津开放大学:《社会保障学》课程教学资源(学习资料)考核说明.doc
- 天津开放大学:《社会保障学》课程教学资源(学习资料)第四章辅导.doc
- 天津开放大学:《社会保障学》课程教学资源(学习资料)第十章辅导.doc
- 天津开放大学:《社会保障学》课程教学资源(学习资料)第十二章辅导.doc
- 同济大学:《中国社会经济》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)The Transition of Chinese Marriage and Family System.ppt
- 同济大学:《中国社会经济》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Demographic Transition in China.ppt
- 同济大学:《中国社会经济》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Financial System in China.ppt
- 《大学图书馆学报》:大学图书馆现代化指南针报告(北京大学).pdf
- 北方工业大学:电子信息工程专业《军事技能》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 北方工业大学:电子信息工程专业《军事理论》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 北方工业大学:计算机科学与技术专业《学术与工程实践》课程教学大纲(创新实验班).pdf
- 北方工业大学:城乡规划《城市社会学》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 北方工业大学:城乡规划《文化遗产保护概论》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 华南师范大学:《中国古代婚姻史》课程教学资源(教学大纲)Acient marriage History of China.doc
- 华南师范大学:《中国古代婚姻史》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿,共六章).pptx
- 华南师范大学:《旅游文化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一讲 导论(主讲:解佳).pdf
- 《旅游文化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)《旅游者:休闲阶层的新理论》与现代性的民族志者:Dean MacCannell访谈录.pdf
- 华南师范大学:《旅游文化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二讲 旅游与认同(一).pdf
- 华南师范大学:《旅游文化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二讲 旅游与认同(二).pdf
- 华南师范大学:《旅游文化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三讲 旅游与地方.pdf
- 华南师范大学:《旅游文化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四讲 旅游与历史(文明).pdf
- 华南师范大学:《旅游文化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)美食与旅游(饮食与旅游).pdf
- 华南师范大学:《旅游文化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)互联网新媒体与旅游(影视与旅游).pdf
- 华南师范大学:《旅游文化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)文学与旅游.pdf
