对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 13 The Investment Portfolio and Policy Guidelines

卧的贸易孝 1951 Chapter 13 The Investment Portfolio and Policy Guidelines
Chapter 13 Chapter 13 The Investment The Investment Portfolio and Policy Portfolio and Policy Guidelines Guidelines

The securities activities of large banks and small banks Small banks generally purchase securities and hold them until maturity. Large banks,in contrast,not only buy securities for their own portfolios,but they also frequently: manage a securities trading account manage an underwriting subsidiary that helps municipalities issue debt in the money and capital markets 蔺卧的资土号
The securities activities of The securities activities of large banks and small banks large banks and small banks Small banks generally purchase securities and hold them until maturity. Large banks, in contrast, not only buy securities for their own portfolios, but they also frequently: manage a securities trading account manage an underwriting subsidiary that helps municipalities issue debt in the money and capital markets

Dealer operations and the securities trading account Many large banks hold securities as part of a trading account. A trading account represents an inventory of securities that a bank holds for resale to other investors: In this capacity,banks operate both as primary dealers with the Federal Reserve and as market makers with other participants. 猫的资5+号
Dealer operations and the Dealer operations and the securities trading account securities trading account Many large banks hold securities as part of a trading account. A trading account represents an inventory of securities that a bank holds for resale to other investors: In this capacity, banks operate both as primary dealers with the Federal Reserve and as market makers with other participants

Banks perform three basic functions within their trading activities. 1.Offer investment advice and assistance to customers managing their own portfolios 2.Maintain an inventory of securities for possible sale to investors their willingness to buy and sell securities is called making a market 3.Traders speculate on short-term interest rate movements by taking positions in various securities 的资5土号
Banks perform three basic functions Banks perform three basic functions within their trading activities. within their trading activities. 1. Offer investment advice and assistance to customers managing their own portfolios 2. Maintain an inventory of securities for possible sale to investors their willingness to buy and sell securities is called making a market 3. Traders speculate on short-term interest rate movements by taking positions in various securities

Banks earn profits from their trading activities in several ways. When making a market,they price securities at an expected positive spread, charging a higher price (lower interest rate) Profits arise from a positive spread between the ask and the bid prices Traders can also earn profits if they correctly anticipate interest rate movements 麓封强的黄香+孝
Banks earn profits from their Banks earn profits from their trading activities in several ways. trading activities in several ways. When making a market, they price securities at an expected positive spread, charging a higher price (lower interest rate) Profits arise from a positive spread between the ask and the bid prices Traders can also earn profits if they correctly anticipate interest rate movements

Objectives of the investment portfolio A bank's investment portfolio differs markedly from a trading account as investment securities are held to meet one of six general objectives: 1.Safety or preservation of capital 2.Liquidity 3.Yield 4.Credit risk diversification 5.Help in manage interest rate risk exposure 6.Assist in meeting pledging requirements 蔺卧的资土号
Objectives of the investment Objectives of the investment portfolio portfolio A bank’s investment portfolio differs markedly from a trading account as investment securities are held to meet one of six general objectives: 1. Safety or preservation of capital 2. Liquidity 3. Yield 4. Credit risk diversification 5. Help in manage interest rate risk exposure 6. Assist in meeting pledging requirements
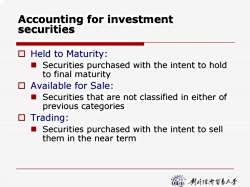
Accounting for investment securities ▣Held to Maturity: ■ Securities purchased with the intent to hold to final maturity ▣Available for Sale: ■ Securities that are not classified in either of previous categories ▣Trading Securities purchased with the intent to sell them in the near term 麓的贫香小手
Accounting for investment Accounting for investment securities securities Held to Maturity: Securities purchased with the intent to hold to final maturity Available for Sale: Securities that are not classified in either of previous categories Trading: Securities purchased with the intent to sell them in the near term

The primary impact of FASB 115 is: A bank's net income and equity capital position will be more volatile when securities are accounted for in market value terms The distinction between motives is important because of account treatment The difference between market value and par value equals the unrealized gain or loss on the security Mkt value par value unrealized gain (loss) 蔺行贺影小号
The primary impact of FASB The primary impact of FASB 115 is: 115 is: A bank’s net income and equity capital position will be more volatile when securities are accounted for in market value terms The distinction between motives is important because of account treatment The difference between market value and par value equals the unrealized gain or loss on the security Mkt value - par value = unrealized gain (loss)

Safety or preservation of capital A primary objective is to p preserve capital by purchasing securities when there is only a small risk of principal loss. Regulators encourage this policy by requiring that banks concentrate their holdings in investment grade securities,those rated Baa or higher. 的资5+号
Safety or preservation of Safety or preservation of capital capital A primary objective is to preserve capital by purchasing securities when there is only a small risk of principal loss. Regulators encourage this policy by requiring that banks concentrate their holdings in investment grade securities, those rated Baa or higher

Liquidity Commercial banks purchase debt securities to help meet liquidity requirements. Securities with maturities under one year can be readily sold for cash near par value and are classified as liquid investments. Liquid securities are often viewed as only those which can be sold at a gain, regardless of the remaining term to maturity,credit quality,and issue size. 的资5土号
Liquidity Liquidity Commercial banks purchase debt securities to help meet liquidity requirements. Securities with maturities under one year can be readily sold for cash near par value and are classified as liquid investments. Liquid securities are often viewed as only those which can be sold at a gain, regardless of the remaining term to maturity, credit quality, and issue size
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 12 Customer Profitability Analysis and Loan Pricing.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 11 Evaluating Consumer Loans.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 10 Evaluating Commercial Loan Requests.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 09 Overview of Credit Policy and Loan Characteristics.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 08 Liquidity Planning and Managing Cash Assets.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 07 The Effective Use of Capital.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 06 Managing Liabilities.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 05 Managing Interest Rate Risk:Duration Gap and Market Value of Equity.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 04 Managing Interest Rate Risk:Gap and Earnings Sensitivity Sensitivity.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 03 Managing Noninterest Income and Noninterest Expense.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 02 Analyzing Bank Performance.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(授课教案课件)Chapter 01 Fundamental Forces of Change in Banking.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(试题)期末考试试卷(B卷)答案.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(试题)期末考试试卷(B卷)试题.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(试题)期末考试试卷(A卷)答案.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(试题)期末考试试卷(A卷)试题.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(作业习题).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《银行管理学 Bank Management》课程教学资源(教学大纲).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际运输与物流管理》课程教学课件(授课教案)第十章 国际物流.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际运输与物流管理》课程教学课件(授课教案)第八章 采购与供应管理.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(教学大纲,沈四宝).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(作业习题)第一章 绪论(沈四宝).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(作业习题)第二章 代理法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(作业习题)第三章 合伙企业法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(作业习题)第五章 外商投资企业法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(作业习题)第四章 公司法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(作业习题)第七章 买卖法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(作业习题)第六章 合同法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(作业习题)第九章 票据法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(作业习题)第八章 产品责任法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(作业习题)第十章 商事仲裁.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(授课教案)第一章 绪论(沈四宝).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(授课教案)第二章 代理法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(授课教案)第三章 合伙企业法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(授课教案)第四章 公司法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(授课教案)第五章 外商投资企业法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(授课教案)第六章 合同法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(授课教案)第七章 买卖法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(授课教案)第九章 票据法.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际商法 International Business Law》课程教学资源(授课教案)第八章 产品责任法.pdf
