《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)The Impacts of Adoption of Genetically Engineered Crops on Yields, Pesticide Use and Economic Returns in the USA

The Impacts of Adoption of Genetically Engineered Crops on Yields,Pesticide Use and Economic Returns in the USA Jorge Fernandez-Cornejo Economic Research Service, U.S.Department of Agriculture Presented at the Farm Foundation Conference on Biotechnology Washington,DC,January 16,2008 ●● ●●● ●●●
Presented at the Farm Foundation Conference on Biotechnology Washington, DC, January 16, 2008 Jorge Fernandez-Cornejo Economic Research Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture The Impacts of Adoption of Genetically Engineered Crops on Yields, Pesticide Use and Economic Returns in the US A

Objective To summarize the experience of the first 12 years of adoption of genetically engineered (GE)crops by U.S.farmers. ●● ●●● ●●●
To summarize the experience of the first 12 years of adoption of genetically engineered (GE) crops by U.S. farmers. Objective

Insect Resistant(Bt)Crops Bt crops carry the gene from the soil bacterium Bacilus Thuringiensis. Crops containing the Bt gene are able to produce proteins that are toxic when ingested by certain insects: -Bt corn protects against the European corn borer(and/or the corn rootworm). -Bt cotton protects against the tobacco budworm,the bollworm, and the pink bollworm. ●●习 ●●● ●●●
Insect Resistant (Bt) Crops ♦ Bt crops carry the gene from the soil bacterium Bacilus Thuringiensis. ♦ Crops containing the Bt gene are able to produce proteins that are toxic when ingested by certain insects: - Bt corn protects against the European corn borer (and/or the corn rootworm). - Bt cotton protects against the tobacco budworm, the bollworm, and the pink bollworm

Herbicide Tolerant (HT)Crops HT crops contain traits that allow them to survive certain herbicides that previously would have destroyed the crop along with the targeted weeds,allowing farmers to use more effective herbicides. ●● ●●● ●●●
♦ HT crops contain traits that allow them to survive certain herbicides that previously would have destroyed the crop along with the targeted weeds, allowing farmers to use more effective herbicides. Herbicide Tolerant (HT) Crops
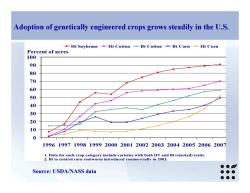
Adoption of genetically engineered crops grows steadily in the U.S. -Ht Soybeans -Ht Cotton -Bt Cotton -Bt Corn -Ht Corn Percent of acres 100 90 60 000 199619971998199920002001200220032004200520062007 1.Data for each crop category include varieties with both HT and Bt(stacked)traits. 2.Bt to control corn rootworm introduced commercially in 2003 ●● Source:USDA/NASS data ●●● ●●●
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Ht Soybeans Ht Cotton Bt Cotton Bt Corn Ht Corn Percent of acres 1. Data for each crop category include varieties with both HT and Bt (stacked) traits. 2. Bt to control corn rootworm introduced commercially in 2003. Source: USDA/NASS data Adoption of genetically engineered crops grows steadily in the U.S
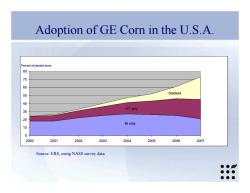
Adoption of GE Corn in the U.S.A. ercent of planted acres 80 70 60 50 Stacked 40 30 HT only 品 Btonly 10 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Source:ERS,using NASS survey data ●● ●●● ●●●
Source: ERS, using NASS survey data Adoption of GE Corn in the U.S.A. Bt only HT only Stacked 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Percent of planted acres

Why are U.S.farmers adopting GE crops? According to USDA surveys,the main reasons stated by U.S.farmers for adopting GE crops are: 1.To increase yields 2.To save management time and make other practices easier. 3.To decrease pesticide input costs. ●●a ●●● ●●●
Why are U.S. farmers adopting GE crops? According to USDA surveys, the main reasons stated by U.S. farmers for adopting GE crops are: 1. To increase yields 2. To save management time and make other practices easier. 3. To decrease pesticide input costs

Farm Level Effects of Adoption ●● ●●● ●●●
. Farm Level Effects of Adoption

Evaluating Adoption Impacts To examine the impacts of adoption on yields, pesticide use and returns we need to control for other factors like input and output prices,weather/infestation levels,farm size,managerial ability,and other production practices. To do this we use an econometric model. ●●a ●●● ●●●
Evaluating Adoption Impacts ♦ To examine the impacts of adoption on yields, pesticide use and returns we need to control for other factors like input and output prices, weather/infestation levels, farm size, managerial ability, and other production practices. ♦ To do this we use an econometric model

The Data Used for the Impact Studies .U.S.farm-level data are obtained from the Agricultural Resource Management Survey (ARMS)developed and carried out by the USDA. ARMS is the major source of integrated information on production practices,acreage planted and harvested,resource use,and financial conditions among U.S.farms,as well as the characteristics of farm households. Most biotech studies are based on 1997-2001 survey data ●● ●●● ●●●
The Data Used for the Impact Studies ♦ U.S. farm-level data are obtained from the Agricultural Resource Management Survey (ARMS) developed and carried out by the USDA. ♦ ARMS is the major source of integrated information on production practices, acreage planted and harvested, resource use, and financial conditions among U.S. farms, as well as the characteristics of farm households. ♦ Most biotech studies are based on 1997-2001 survey data
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Storage and Disposal.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Plastic Pesticide Container Recycling.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticides.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticides Analysis with the new Agilent 6220 6460 and 6530.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticide Waste Challenges.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticide Toxicology and Risk Assessment.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticide Toxicity.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticide Safety and Toxicity(PPT).ppt
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticide Registration for Minor Crops and Crop Grouping Effort in Japan.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticide Laws and Regulations.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticide Health Hazards - Exposure and Personal Protective Equipment.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticide Hazards and First Aid(PPT).ppt
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticide Formulas and Properties.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticide Contamination in Rural Areas.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Pesticide Toxicology(PPT).ppt
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Oklahoma Unwanted Pesticide Disposal Program.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)No Spray Buffers Lawsuits & Toxicology.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Labels and Pesticide Formulations.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)IPMA Primer.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Integrated Pest Management for Urban Landscapes.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)The Influence of Secondary Standards on Pesticide Use.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Toxic Effects of Pesticides.pdf
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)TOXICOLOGY III Risk Assessment(PPT).ppt
- 《植物化学保护》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Work and Residential Characteristics Related to Pesticide Exposure among Latino Farmworkers.pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学大纲(负责人:王敏).pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程授课教案(讲义,共五篇).docx
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验一 昆虫体躯的基本结构和昆虫的头部.pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验二 昆虫的胸部和腹部.pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验三 昆虫的卵、胚胎发育和胚后发育.pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验四 昆虫纲分目(Ⅰ).pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验五 昆虫纲分目(Ⅱ).pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验六 等翅目、直翅目和缨翅目分科.pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验七 半翅目和脉翅目分科.pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验八 同翅目分科.pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验九 鞘翅目分科.pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验十 鳞翅目分科(成虫).pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验十一 鳞翅目分科(幼虫).pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验十二 双翅目科.pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验十三 膜翅目分科.pdf
- 华南农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验十四 昆虫内部器官的位置、体壁、消化系统.pdf
