同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Generic channel models

@月命大凳 Chapter 3 Generic channel models Graduate course:Propagation Channel Characterization,Parameter Estimation and Modeling 52/199
Graduate course: Propagation Channel Characterization, Parameter Estimation and Modeling 52 / 199 Chapter 3 Generic channel models

@月冷大学 3.1 Physical propagation mechanisms Reflection,diffraction and scattering are three basic propagation mechanism. They occur depending on the size L of the object compared with the wavelength入. When a plane electromagnetic wave encounters an obstacle much larger than the wavelength,i.e.L,reflection occurs. Diffraction happens when the obstacle's size is in the same order of the wavelength,i.e.L≈λ. Scattering happens when a plane wave encounters an obstacle much smaller than the wavelength,i.e.L<<.This obstacle becomes a new source emitting waves towards multiple directions. Graduate course:Propagation Channel Characterization,Parameter Estimation and Modeling 53/199
3.1 Physical propagation mechanisms Graduate course: Propagation Channel Characterization, Parameter Estimation and Modeling 53 / 199 ■ Reflection, diffraction and scattering are three basic propagation mechanism. ■ They occur depending on the size L of the object compared with the wavelength λ. ◆ When a plane electromagnetic wave encounters an obstacle much larger than the wavelength, i.e. L ≫ λ, reflection occurs. ◆ Diffraction happens when the obstacle’s size is in the same order of the wavelength, i.e. L ≈ λ. ◆ Scattering happens when a plane wave encounters an obstacle much smaller than the wavelength, i.e. L << λ. This obstacle becomes a new source emitting waves towards multiple directions
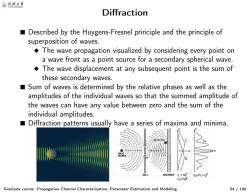
@月合大等 Diffraction Described by the Huygens-Fresnel principle and the principle of superposition of waves. The wave propagation visualized by considering every point on a wave front as a point source for a secondary spherical wave. The wave displacement at any subsequent point is the sum of these secondary waves. Sum of waves is determined by the relative phases as well as the amplitudes of the individual waves so that the summed amplitude of the waves can have any value between zero and the sum of the individual amplitudes. ■ Diffraction patterns usually have a series of maxima and minima. 122h,+h Graduate course:Propagation Channel Characterization,Parameter Estimation and Modeling 54/199
Diffraction Graduate course: Propagation Channel Characterization, Parameter Estimation and Modeling 54 / 199 ■ Described by the Huygens-Fresnel principle and the principle of superposition of waves. ◆ The wave propagation visualized by considering every point on a wave front as a point source for a secondary spherical wave. ◆ The wave displacement at any subsequent point is the sum of these secondary waves. ■ Sum of waves is determined by the relative phases as well as the amplitudes of the individual waves so that the summed amplitude of the waves can have any value between zero and the sum of the individual amplitudes. ■ Diffraction patterns usually have a series of maxima and minima

@月冷大学 Experimental propagation constellation Parameter estimation algorithms estimated direction of arrival, direction of departure,delay,Doppler frequency and complex attenuation of plane waves ■ With knowledge of the locations of the Tx and Rx,propagation paths especially for those with one-bounce can be constructed. Estimated paths overlapping with the photographs of the background. Estimated Directions of Arrival(DoAs) Reconstructed Paths D T11 B2 Estimated Directions of Departure(DoDs) Graduate course:Propagation Channel Characterization,Parameter Estimation and Modeling 55/199
Experimental propagation constellation Graduate course: Propagation Channel Characterization, Parameter Estimation and Modeling 55 / 199 ■ Parameter estimation algorithms estimated direction of arrival, direction of departure, delay, Doppler frequency and complex attenuation of plane waves ■ With knowledge of the locations of the Tx and Rx, propagation paths especially for those with one-bounce can be constructed. Estimated paths overlapping with the photographs of the bac E kground. Estimated Directions of Arrival (DoAs) Reconstructed Paths Estimated Directions of Departure (DoDs) 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 17 18 1615 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 5 7 6 4 3 2 1 Azimuth [°] Coelevation [°] 40 30 20 10 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -50 85 90 95 100 105 110 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 98 674532 1 Azimuth [°] Coelevation [°] 150 100 50 0 -50 -100 -150 60 80 100 120 Relative delay [ns] 0 82 164 246 329 23 22 21 12 25 24 7 Tx 2 1 15 6 5 10 3 4 13 11 16 17 Rx 9 18 14 8 19 20
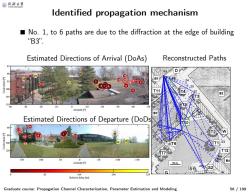
@月合大等 Identified propagation mechanism ■ No.1,to 6 paths are due to the diffraction at the edge of building “B3 Estimated Directions of Arrival (DoAs) Reconstructed Paths D (10 ①u0⊙0 11 10 110 10 Azimuth[] B3 Estimated Directions of Departure (DoDs U10 222 100 120 10 0 -50 -100 -150 Azimuth [ 10m 82 164 246 Relative delay [ns] Graduate course:Propagation Channel Characterization,Parameter Estimation and Modeling 56/199
Identified propagation mechanism Graduate course: Propagation Channel Characterization, Parameter Estimation and Modeling 56 / 199 ■ No. 1, to 6 paths are due to the diffraction at the edge of building “B3”. Estimated Directions of Arrival (DoAs) Reconstructed Paths Estimated Directions of Departure (DoDs) 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 17 18 1615 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 5 7 6 4 3 2 1 Azimuth [°] Coelevation [°] 40 30 20 10 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -50 85 90 95 100 105 110 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 98 674532 1 Azimuth [°] Coelevation [°] 150 100 50 0 -50 -100 -150 60 80 100 120 Relative delay [ns] 0 82 164 246 329 23 22 21 12 25 24 7 Tx 2 1 15 6 5 10 3 4 13 11 16 17 Rx 9 18 14 8 19 20
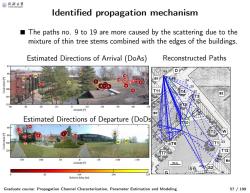
@月冷大等 ldentified propagation mechanism The paths no.9 to 19 are more caused by the scattering due to the mixture of thin tree stems combined with the edges of the buildings. Estimated Directions of Arrival (DoAs) Reconstructed Paths 81 T11 105 -10 Azimuth Estimated Directions of Departure (DoDs 10 U10 18)2 0 -100 -10 Azimuth 10m. 16 24 Relative delay[ns】 Graduate course:Propagation Channel Characterization,Parameter Estimation and Modeling 57/199
Identified propagation mechanism Graduate course: Propagation Channel Characterization, Parameter Estimation and Modeling 57 / 199 ■ The paths no. 9 to 19 are more caused by the scattering due to th e mixture of thin tree stems combined with the edges of the buildings. Estimated Directions of Arrival (DoAs) Reconstructed Paths Estimated Directions of Departure (DoDs) 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 17 18 1615 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 5 7 6 4 3 2 1 Azimuth [°] Coelevation [°] 40 30 20 10 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -50 85 90 95 100 105 110 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 98 674532 1 Azimuth [°] Coelevation [°] 150 100 50 0 -50 -100 -150 60 80 100 120 Relative delay [ns] 0 82 164 246 329 23 22 21 12 25 24 7 Tx 2 1 15 6 5 10 3 4 13 11 16 17 Rx 9 18 14 8 19 20
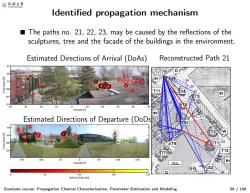
@月合大等 Identified propagation mechanism The paths no.21,22,23,may be caused by the reflections of the sculptures,tree and the facade of the buildings in the environment Estimated Directions of Arrival (DoAs) Reconstructed Path 21 ①tEoo 100 0 11 105 110 10 Azimuth[ Estimated Directions of Departure (DoDs U10 222 100 120 10 0 0 -50 -100 -150 Azimuth [ 10m 82 164 246 Relative delay [ns] Graduate course:Propagation Channel Characterization,Parameter Estimation and Modeling 58/199
Identified propagation mechanism Graduate course: Propagation Channel Characterization, Parameter Estimation and Modeling 58 / 199 ■ The paths no. 21, 22, 23, may be caused by the reflections of the sculptures, tree and the facade of the buildings in the environment. Estimated Directions of Arrival (DoAs) Reconstructed Path 21 Estimated Directions of Departure (DoDs) 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 17 18 1615 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 5 7 6 4 3 2 1 Azimuth [°] Coelevation [°] 40 30 20 10 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -50 85 90 95 100 105 110 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 98 674532 1 Azimuth [°] Coelevation [°] 150 100 50 0 -50 -100 -150 60 80 100 120 Relative delay [ns] 0 82 164 246 329 23 22 21 12 25 24 7 Tx 2 1 15 6 5 10 3 4 13 11 16 17 Rx 9 18 14 8 19 20
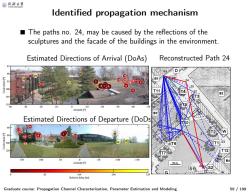
@月冷大等 ldentified propagation mechanism The paths no.24,may be caused by the reflections of the sculptures and the facade of the buildings in the environment. Estimated Directions of Arrival (DoAs) Reconstructed Path 24 D T11 105 -10 Azimuth Estimated Directions of Departure (DoDs 10 18 0 -100 -150 Azimuth 10m. 164 24 Relative delay[ns】 Graduate course:Propagation Channel Characterization,Parameter Estimation and Modeling 59/199
Identified propagation mechanism Graduate course: Propagation Channel Characterization, Parameter Estimation and Modeling 59 / 199 ■ The paths no. 24, may be caused by the reflections of the sculptures and the facade of the buildings in the environment. Estimated Directions of Arrival (DoAs) Reconstructed Path 24 Estimated Directions of Departure (DoDs) 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 17 18 1615 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 5 7 6 4 3 2 1 Azimuth [°] Coelevation [°] 40 30 20 10 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -50 85 90 95 100 105 110 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 98 674532 1 Azimuth [°] Coelevation [°] 150 100 50 0 -50 -100 -150 60 80 100 120 Relative delay [ns] 0 82 164 246 329 23 22 21 12 25 24 7 Tx 2 1 15 6 5 10 3 4 13 11 16 17 Rx 9 18 14 8 19 20
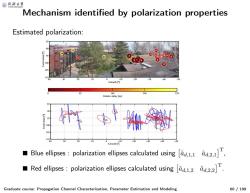
@月命卡 Mechanism identified by polarization properties Estimated polarization: 164 A Relative delay [ns 卉产·光 Blue ellipses:polarization ellipses calculated using d,1,1 d2,1, Red ellipses:polarization ellipses calculated using d1,2 0d.221T Graduate course:Propagation Channel Characterization,Parameter Estimation and Modeling 60/199
Mechanism identified by polarization properties Graduate course: Propagation Channel Characterization, Parameter Estimation and Modeling 60 / 199 Estimated polarization: 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 17 18 1615 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 5 7 6 4 3 2 1 Azimuth [°] Coelevation [°] 40 30 20 10 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -50 85 90 95 100 105 110 Relative delay [ns] 0 82 164 246 329 40 30 20 10 0 −10 −20 −30 −40 −50 85 90 95 100 105 110 1 2 3 4 5 7 6 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Azimuth [°] Coelevation [°] ■ Blue ellipses : polarization ellipses calculated using aˆd, 1,1 aˆd, 2,1 T , ■ Red ellipses : polarization ellipses calculated using aˆd, 1,2 aˆd, 2,2 T .����
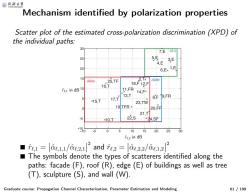
@月冷大学 Mechanism identified by polarization properties Scatter plot of the estimated cross-polarization discrimination (XPD)of the individual paths: 30 7,E G刃 25 55E3F 4,E 20 6,Ex 1,E (G2a) 25,TF 16, 网 fe.I in dB 10 11,FR 14,F× 13,T 8,F9,FR ×15,T 17T 23,TW 19TFB× 20,FF 21,T -5 ×10,T 22,S *24,SF 5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 f.in dB 2 12 ■fe,1=ae,1,1/ae2,1 and fe,2=d0,2,2/ae,1,21 The symbols denote the types of scatterers identified along the paths:facade(F),roof (R),edge(E)of buildings as well as tree (T),sculpture (S),and wall (W) Graduate course:Propagation Channel Characterization,Parameter Estimation and Modeling 61/199
Mechanism identified by polarization properties Graduate course: Propagation Channel Characterization, Parameter Estimation and Modeling 61 / 199 Scatter plot of the estimated cross-polarization discrimination (XPD) of the individual paths: rˆℓ,1 in dB rˆℓ,2 in dB ■ rˆℓ, 1 = αˆℓ, 1,1 / αˆℓ, 2,1 2 and rˆℓ, 2 = αˆℓ, 2,2 / αˆℓ, 1,2 2 ■ The symbols denote the types of scatterers identified along the paths: facade (F), roof (R), edge (E) of buildings as well as tree (T), sculpture (S), and wall (W)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Characterization of Propagation Channels.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 Introduction - History of Channel Characterization and Modeling.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 09 Practices - channel modeling for modern communication systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 08 Measurement based statistical channel modeling.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 07 Statistical channel parameter estimation.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 06 Deterministic channel parameter estimation.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 05 Channel measurements.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 04 Geometry based stochastic channel modeling.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 03 Generic channel models.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 02 Characterization of Propagation Channels.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Introduction.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Propagation Channel Characterization, Parameter Estimation, and Modeling for Wireless Communications - Preface.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《现代电信交换》课程PPT教学课件(程控交换)第6章 ATM交换与B-ISDN(异步传送模式——宽带综合业务数字网).ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《现代电信交换》课程PPT教学课件(程控交换)第5章 分组交换与分组交换网.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《现代电信交换》课程PPT教学课件(程控交换)第4章 信令系统.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《现代电信交换》课程PPT教学课件(程控交换)第3章 电路交换与电话通信网.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《现代电信交换》课程PPT教学课件(程控交换)第2章 交换网络.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《现代电信交换》课程PPT教学课件(程控交换)第1章 交换概论(负责人:龙敏,主讲:蔡春娥).ppt
- 清华大学:《模拟电子技术基础》课程电子教案(教学课件)模拟电子技术基础讲稿(共十章).pdf
- 私立华联学院:《汽车电工电子技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 常用电工仪器仪表.pptx
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)01 Deterministic radio propagation modeling and ray tracing - Introduction to deterministic propagation modelling.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)02 Geometrical Theory of Propagation I - The ray concept – Reflection and transmission.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)03 Geometrical Theory of Propagation II - Diffraction, multipath.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)04 Ray Tracing I - Deterministic ray models.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)05 Ray Tracing II – Diffuse scattering modelling.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)06 Deterministic channel modelling I(static channel case).pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)07 Deterministic channel modelling II – Examples.pdf
- 数字电子技术基础学习方法.doc
- 模拟电子技术学习方法.doc
- 电子技术基础学习方法探索.pdf
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(一).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(二).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(三).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(四).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(五).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(六).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(七).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(八).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(九).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(十).doc
