同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)01 Deterministic radio propagation modeling and ray tracing - Introduction to deterministic propagation modelling

Alma Mater Studiorum-DEI Deterministic radio propagation modeling and ray tracing Vittorio Degli-Esposti Alma Mater Studiorum-University of Bologna,Italy Department of Electrical,Electronic and Information Engineering(DEl)
Alma Mater Studiorum – DEI Deterministic radio propagation modeling and ray tracing Vittorio Degli-Esposti Alma Mater Studiorum - University of Bologna, Italy Department of Electrical, Electronic and Information Engineering (DEI)

Course outline 1) Introduction to deterministic propagation modelling 2) Geometrical Theory of Propagation I-The ray concept-Reflection and transmission 3) Geometrical Theory of Propagation II-Diffraction,multipath 4) Ray Tracing I 5) Ray Tracing II-Diffuse scattering modelling 6) Deterministic channel modelling I 7) Deterministic channel modelling II-Examples 8) Project -discussion 4
4 1) Introduction to deterministic propagation modelling 2) Geometrical Theory of Propagation I - The ray concept – Reflection and transmission 3) Geometrical Theory of Propagation II - Diffraction, multipath 4) Ray Tracing I 5) Ray Tracing II – Diffuse scattering modelling 6) Deterministic channel modelling I 7) Deterministic channel modelling II – Examples 8) Project - discussion Course outline

Course info 。 Slides and material available at There will be updates during the course Please print slides and take notes aside A"Project"will be assigned based on course content and exercises Last lesson will be on project correction and discussion 5
5 Course info • Slides and material available at … • There will be updates during the course • Please print slides and take notes aside ! • A “Project” will be assigned based on course content and exercises • Last lesson will be on project correction and discussion
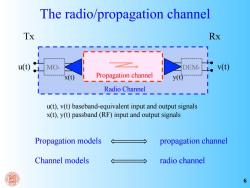
The radio/propagation channel Tx Rx u() MO DEM v(t) Propagation channel y(t) Radio Channel u(t),v(t)baseband-equivalent input and output signals x(t),y(t)passband(RF)input and output signals Propagation models propagation channel Channel models radio channel 6
The radio/propagation channel Tx Rx Propagation models propagation channel Channel models radio channel Radio Channel Propagation channel u(t) MO- DEM- v(t) x(t) y(t) u(t), v(t) baseband-equivalent input and output signals x(t), y(t) passband (RF) input and output signals 6
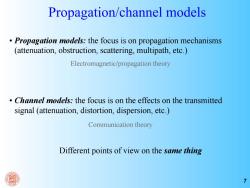
Propagation/channel models Propagation models:the focus is on propagation mechanisms (attenuation,obstruction,scattering,multipath,etc.) Electromagnetic/propagation theory Channel models:the focus is on the effects on the transmitted signal (attenuation,distortion,dispersion,etc.) Communication theory Different points of view on the same thing
7 Propagation/channel models • Propagation models: the focus is on propagation mechanisms (attenuation, obstruction, scattering, multipath, etc.) • Channel models: the focus is on the effects on the transmitted signal (attenuation, distortion, dispersion, etc.) Different points of view on the same thing Electromagnetic/propagation theory Communication theory
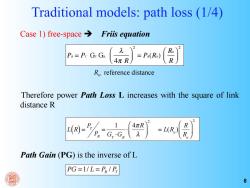
Traditional models:path loss (1/4) Case 1)free-space Friis equation 2 Px=Pr GrGR Ro 4πR =Px(Ro) R Ro reference distance Therefore power Path Loss L increases with the square of link distance R 4πR =L(R) R Path Gain (PG)is the inverse of L PG=1/L=PR/P 8
8 Traditional models: path loss (1/4) Case 1) free-space Friis equation Therefore power Path Loss L increases with the square of link distance R L(R) = PT PR = 1 GT ⋅GR ⋅ 4πR λ ⎛ ⎝ ⎜ ⎞ ⎠ ⎟ 2 = L(R o ) R R o ⎛ ⎝ ⎜ ⎞ ⎠ ⎟ 2 Path Gain (PG) is the inverse of L 1/ / PG = L = PR PT PR = PT GT GR λ 4π R ⎛ ⎝ ⎜ ⎞ ⎠ ⎟ 2 = PR(R0) R0 R ⎛ ⎝ ⎜ ⎞ ⎠ ⎟ 2 Ro reference distance
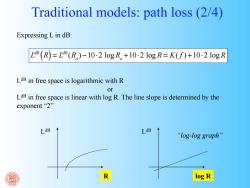
Traditional models:path loss (2/4) Expressing L in dB: L4R (R)=L4R (R)-10.2 logR+10.2 logR=K(f)+10.2 logR LdB in free space is logarithmic with R or LdB in free space is linear with log R.The line slope is determined by the exponent"2” LdB LdB “log-log graph'” log R
Expressing L in dB: LdB (R) = LdB (R o ) −10⋅2 log R o +10⋅2 log R = K( f ) +10⋅2 log R LdB in free space is logarithmic with R or LdB in free space is linear with log R. The line slope is determined by the exponent “2” LdB R LdB log R Traditional models: path loss (2/4) “log-log graph

Traditional models:path loss(3/4) Case 2)real environment> Hata-like models 40 L(1000) (R)=L(R,) R R。 2 100 Z(R)=K(f,)+10·a logR An attenuation law similar to free space is assumed but with a different exponent: a path loss exponent or path loss factor 0u>2 a is derived through fitting(regression line)on a set of measured path loss data →empirical modeling 10
10 An attenuation law similar to free space is assumed but with a different exponent: α path loss exponent or path loss factor α > 2 α is derived through fitting (regression line) on a set of measured path loss data empirical modeling Traditional models: path loss (3/4) Case 2) real environment Hata-like models LdB (R) = K( f ,α) +10⋅α log R L(R) = L(R o ) R R o ⎛ ⎝ ⎜ ⎞ ⎠ ⎟ α
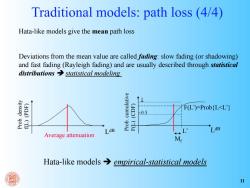
Traditional models:path loss (4/4) Hata-like models give the mean path loss Deviations from the mean value are called fading:slow fading (or shadowing) and fast fading (Rayleigh fading)and are usually described through statistical distributions statistical modeling (add)(T Bane nuno 'qold (ado)(Da F(L)=Prob L<L' 0.5 LdB LdB Average attenuation M Hata-like models→ empirical-statistical models 11
Hata-like models give the mean path loss Deviations from the mean value are called fading: slow fading (or shadowing) and fast fading (Rayleigh fading) and are usually described through statistical distributions statistical modeling Average attenuation Prob. density f(L) (PDF) Prob. cumulative F(L) (CDF) LdB ~0.5 1 LdB F(L’)=Prob{L<L’} L’ Traditional models: path loss (4/4) Mf Hata-like models empirical-statistical models 11

Other functional dependences of L However,in some cases not only achanges w.r.t.free space,but the overall functional dependance with R changes.Ex:indoors: Tx Rx office rooms L (R)=I4H (R)+IN=K+20logR- Multi-wall R model Ex:propagation through a lossy medium Specific attenuation [dB/m] L(R=L(R+[dBIm·R Linear model 12
12 However, in some cases not only αchanges w.r.t. free space, but the overall functional dependance with R changes. Ex: indoors: Tx Rx office rooms LdB (R) = L 0 dB (R) + L W dB ⋅ NW = K + 20log R + L W dBNW R ⎛ ⎝ ⎜ ⎜ ⎞ ⎠ ⎟ ⎟ ⋅ R Specific attenuation [dB/m] Other functional dependences of L Ex: propagation through a lossy medium LdB (R) = L 0 dB (R) + α S R [dB / m]⋅ R Tx Rx Multi-wall model Linear model
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Generic channel models.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Characterization of Propagation Channels.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 Introduction - History of Channel Characterization and Modeling.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 09 Practices - channel modeling for modern communication systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 08 Measurement based statistical channel modeling.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 07 Statistical channel parameter estimation.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 06 Deterministic channel parameter estimation.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 05 Channel measurements.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 04 Geometry based stochastic channel modeling.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 03 Generic channel models.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 02 Characterization of Propagation Channels.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Introduction.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Propagation Channel Characterization, Parameter Estimation, and Modeling for Wireless Communications - Preface.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《现代电信交换》课程PPT教学课件(程控交换)第6章 ATM交换与B-ISDN(异步传送模式——宽带综合业务数字网).ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《现代电信交换》课程PPT教学课件(程控交换)第5章 分组交换与分组交换网.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《现代电信交换》课程PPT教学课件(程控交换)第4章 信令系统.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《现代电信交换》课程PPT教学课件(程控交换)第3章 电路交换与电话通信网.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《现代电信交换》课程PPT教学课件(程控交换)第2章 交换网络.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《现代电信交换》课程PPT教学课件(程控交换)第1章 交换概论(负责人:龙敏,主讲:蔡春娥).ppt
- 清华大学:《模拟电子技术基础》课程电子教案(教学课件)模拟电子技术基础讲稿(共十章).pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)02 Geometrical Theory of Propagation I - The ray concept – Reflection and transmission.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)03 Geometrical Theory of Propagation II - Diffraction, multipath.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)04 Ray Tracing I - Deterministic ray models.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)05 Ray Tracing II – Diffuse scattering modelling.pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)06 Deterministic channel modelling I(static channel case).pdf
- 同济大学:《传播信道特征估计和建模》课程教案讲义(射线追踪)07 Deterministic channel modelling II – Examples.pdf
- 数字电子技术基础学习方法.doc
- 模拟电子技术学习方法.doc
- 电子技术基础学习方法探索.pdf
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(一).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(二).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(三).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(四).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(五).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(六).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(七).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(八).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(九).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学模式试题及参考答案(十).doc
- 山东第一医科大学:《医学影像电子学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)医学影像电子学习题与答案(一)常用半导体器件.doc
