上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)04-Supply Contracts(2013Fall with script)

Supply Contracts Xiaohong Pang Automation Department Shanghai Jiaotong University
Supply Contracts Xiaohong Pang Automation Department Shanghai Jiaotong University

SnowTime Costs Production cost per unit(C):$80 o Selling price per unit(S):$125 o Salvage value per unit (V):$20 Fixed production cost(F):$100,000 Q is production quantity,D is demand Profit Revenue-Variable Cost-Fixed Cost Salvage
SnowTime : Costs Production cost per unit (C): $80 Selling price per unit (S): $125 Salvage value per unit (V): $20 Fixed production cost (F): $100,000 Q is production quantity, D is demand Profit = Revenue - Variable Cost - Fixed Cost + Salvage

Key Insights from this Model The optimal order quantity is not necessarily equal to average demand. The optimal quantity depends on the relationship between marginal profit and marginal cost As order quantity increases,average profit first increases,and then decreases. As production quantity increases,risk increases.In other words,the probability of large gains and of large losses increases
Key Insights from this Model The optimal order quantity is not necessarily equal to average demand. The optimal quantity depends on the relationship between marginal profit and marginal cost. As order quantity increases, average profit first increases, and then decreases. As production quantity increases, risk increases. In other words, the probability of large gains and of large losses increases

How to Increase the Profits Retailer optimal order quantity is 12.000 units Retailer expected profit is $470,000 Manufacturer profit is $440,000 Supply Chain Profit is $910,000 How can the retailer and manufacturer increase the profit of both?
How to Increase the Profits Retailer optimal order quantity is 12,000 units Retailer expected profit is $470,000 Manufacturer profit is $440,000 Supply Chain Profit is $910,000 How can the retailer and manufacturer increase the profit of both?

Think-Pair-Share Take 2 min.to read example 4-1(p105),consider the following questions,then discuss with your neighbors. 1.Who takes the risk of low demand? 2.What would the manufacturer like the retailer to do?
1. Who takes the risk of low demand? 2. What would the manufacturer like the retailer to do? Think – Pair – Share Take 2 min. to read example 4-1(p105), consider the following questions, then discuss with your neighbors
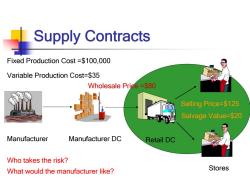
_Supply Contracts Fixed Production Cost =$100,000 Variable Production Cost=$35 Wholesale Price =$80 Selling Price=$125 Salvage Value=$20 Manufacturer Manufacturer DC Retail DC Who takes the risk? What would the manufacturer like? Stores
Manufacturer Manufacturer DC Retail DC Stores Fixed Production Cost =$100,000 Variable Production Cost=$35 Selling Price=$125 Salvage Value=$20 Wholesale Price =$80 Who takes the risk? What would the manufacturer like? Supply Contracts
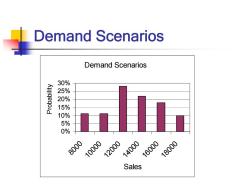
Demand Scenarios Demand Scenarios 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0% 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 Sales
Demand Scenarios Demand Scenarios 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 Sales Probability
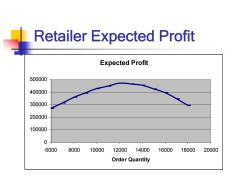
Retailer Expected Profit Expected Profit 500000 400000 300000 200000 100000 0 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 20000 Order Quantity
Retailer Expected Profit Expected Profit 0 100000 200000 300000 400000 500000 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 20000 Order Quantity
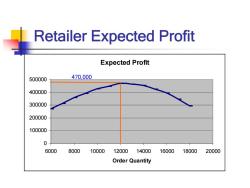
Retailer Expected Profit Expected Profit 500000 470,000 400000 300000 200000 100000 0 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 20000 Order Quantity
Retailer Expected Profit Expected Profit 0 100000 200000 300000 400000 500000 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 18000 20000 Order Quantity 470,000

Supply Contracts Retailer optimal order quantity is 12.000 units Retailer expected profit is $470,000 Manufacturer profit is $440,000 Supply Chain Profit is $910,000 How can the retailer and manufacturer increase the profit of both?
Supply Contracts Retailer optimal order quantity is 12,000 units Retailer expected profit is $470,000 Manufacturer profit is $440,000 Supply Chain Profit is $910,000 How can the retailer and manufacturer increase the profit of both?
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)03_Logistics Network Configuration(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)02-Inventory Management(2)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)02-Inventory Management(1)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)01-Introduction to Supply Chain Management(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)00-Introduction to Course(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)09_Procurement and Outsourcing(2)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Experiments_Sample Reports_Risk Pooling_Risk Pooling Report_杨健.docx
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)09_Procurement and Outsourcing(1)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)08_Strategic Alliances(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)06_Supply Chain Integration(2)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)06_Supply Chain Integration(1)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)05_The Value of Information(2)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)05_The Value of Information(1)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)04-Supply Contracts(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)03_Logistics Network Configuration(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)02-Inventory Management(2)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)02-Inventory Management(1)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)01-Introduction to Supply Chain Management(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)00-Introduction to Course(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Group Work_合作学习指导手册.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)05_The Value of Information(1)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)05_The Value of Information(2)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)06_Supply Chain Integration(1)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)06_Supply Chain Integration(2)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)08_Strategic Alliances(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《风险管理》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(课堂讲义)导论.doc
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(课堂讲义)Finance management in public sector.doc
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源_人民币银行结算账户管理办法.doc
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 投资管理(张录法).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 支出管理.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 负债管理.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 资产管理.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 财务分析.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 财务清算和报告.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 收入管理.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济与管理》课程教学资料_课程介绍.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济与管理》课程教学资料_工程管理分析方法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济与管理》课程教学资料_案例——海外项目风险.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济与管理》课程教学资料_案例——建设行业信用管理.pdf
