上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Experiments_Sample Reports_Risk Pooling_Risk Pooling Report_杨健

Report of“Risk Pooling”Game 杨健0120329038 1.Experiment Data a.Default Settings Centralized Decentralized Profit Fill Rate Profit Fill Rate 1 5151 96% 4947.5 97% 2 2433 98% 2110 99% 3 3157 99% 2890 100% b-1.Strong Positive Centralized Decentralized Profit Fill Rate Profit Fill Rate 1 3040 98% 2717 99% 2 3719 96% 3546 97% 3 4099 96% 3762 96% b-2.Strong Negative Centralized Decentralized Profit Fill Rate Profit Fill Rate 3679.5 98% 3080.5 97% 2 3731 98% 3354.5 98% 3 4040 99% 3580 98% c-1.STD=15 Centralized Decentralized Profit Fill Rate Profit Fill Rate 1 4110 99% 3355.5 100% 2 3162.5 99% 2273.5 99% 3 3636 97% 2971.5 99% c-2.STD=5 Centralized Decentralized Profit Fill Rate Profit Fill Rate 1 4061 99% 4180.5 98% 2 4640.5 97% 4776 97% 3 4348.5 98% 4449 97%
Report of “Risk Pooling” Game 杨健 0120329038 1. Experiment Data a. Default Settings Centralized Decentralized Profit Fill Rate Profit Fill Rate 1 5151 96% 4947.5 97% 2 2433 98% 2110 99% 3 3157 99% 2890 100% b-1. Strong Positive Centralized Decentralized Profit Fill Rate Profit Fill Rate 1 3040 98% 2717 99% 2 3719 96% 3546 97% 3 4099 96% 3762 96% b-2. Strong Negative Centralized Decentralized Profit Fill Rate Profit Fill Rate 1 3679.5 98% 3080.5 97% 2 3731 98% 3354.5 98% 3 4040 99% 3580 98% c-1. STD=15 Centralized Decentralized Profit Fill Rate Profit Fill Rate 1 4110 99% 3355.5 100% 2 3162.5 99% 2273.5 99% 3 3636 97% 2971.5 99% c-2. STD=5 Centralized Decentralized Profit Fill Rate Profit Fill Rate 1 4061 99% 4180.5 98% 2 4640.5 97% 4776 97% 3 4348.5 98% 4449 97%
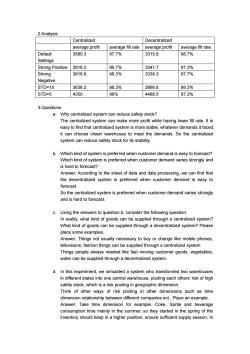
2.Analysis Centralized Decentralized average profit average fill rate average profit average fill rate Default 3580.3 97.7% 3315.8 98.7% Settings Strong Positive 3916.3 96.7% 3341.7 97.3% Strong 3816.8 98.3% 3338.3 97.7% Negative STD=15 3636.2 98.3% 2866.8 99.3% STD=5 4350 98% 4468.5 97.3% 3.Questions a.Why centralized system can reduce safety stock? The centralized system can make more profit while having lower fill rate.It is easy to find that centralized system is more stable,whatever demands it faced. it can choose closer warehouse to meet the demands.So the centralized system can reduce safety stock for its stability. b.Which kind of system is preferred when customer demand is easy to forecast? Which kind of system is preferred when customer demand varies strongly and is hard to forecast? Answer:According to the sheet of data and data processing,we can find that the decentralized system is preferred when customer demand is easy to forecast. So the centralized system is preferred when customer demand varies strongly and is hard to forecast. c.Using the answers to question b,consider the following question: In reality,what kind of goods can be supplied through a centralized system? What kind of goods can be supplied through a decentralized system?Please place some examples. Answer:Things not usually necessary to buy or change like mobile phones, televisions,fashion things can be supplied through a centralized system Things people always needed like fast moving customer goods,vegetables, water can be supplied through a decentralized system. d.In this experiment,we simulated a system who transformed two warehouses in different states into one central warehouse,pooling each others'risk of high safety stock,which is a risk pooling in geographic dimension. Think of other ways of risk pooling in other dimensions such as time dimension relationship between different companies ect..Place an example. Answer:Take time dimension for example.Coke,Sprite and beverage consumption time mainly in the summer,so they started in the spring of the inventory should keep in a higher position,ensure sufficient supply season;In
2.Analysis Centralized Decentralized average profit average fill rate average profit average fill rate Default Settings 3580.3 97.7% 3315.8 98.7% Strong Positive 3916.3 96.7% 3341.7 97.3% Strong Negative 3816.8 98.3% 3338.3 97.7% STD=15 3636.2 98.3% 2866.8 99.3% STD=5 4350 98% 4468.5 97.3% 3.Questions a. Why centralized system can reduce safety stock? The centralized system can make more profit while having lower fill rate. It is easy to find that centralized system is more stable, whatever demands it faced, it can choose closer warehouse to meet the demands. So the centralized system can reduce safety stock for its stability. b. Which kind of system is preferred when customer demand is easy to forecast? Which kind of system is preferred when customer demand varies strongly and is hard to forecast? Answer: According to the sheet of data and data processing, we can find that the decentralized system is preferred when customer demand is easy to forecast. So the centralized system is preferred when customer demand varies strongly and is hard to forecast. c. Using the answers to question b, consider the following question: In reality, what kind of goods can be supplied through a centralized system? What kind of goods can be supplied through a decentralized system? Please place some examples. Answer: Things not usually necessary to buy or change like mobile phones, televisions, fashion things can be supplied through a centralized system Things people always needed like fast moving customer goods, vegetables, water can be supplied through a decentralized system. d. In this experiment, we simulated a system who transformed two warehouses in different states into one central warehouse, pooling each others’ risk of high safety stock, which is a risk pooling in geographic dimension. Think of other ways of risk pooling in other dimensions such as time dimension relationship between different companies ect.. Place an example. Answer: Take time dimension for example. Coke, Sprite and beverage consumption time mainly in the summer, so they started in the spring of the inventory should keep in a higher position, ensure sufficient supply season; In

winter,the soft drink sales very little,so begins from the autumn should reduce their stock,in order to save money.Relatively,sales of dairy products is stable, time varying haven't changed much,so should keep relatively stable inventory
winter, the soft drink sales very little, so begins from the autumn should reduce their stock, in order to save money. Relatively, sales of dairy products is stable, time varying haven't changed much, so should keep relatively stable inventory
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)09_Procurement and Outsourcing(1)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)08_Strategic Alliances(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)06_Supply Chain Integration(2)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)06_Supply Chain Integration(1)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)05_The Value of Information(2)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)05_The Value of Information(1)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)04-Supply Contracts(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)03_Logistics Network Configuration(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)02-Inventory Management(2)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)02-Inventory Management(1)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)01-Introduction to Supply Chain Management(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)00-Introduction to Course(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Group Work_合作学习指导手册.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Group Work_Research Reports_The application of RFID in cool chain.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Group Work_Research Reports_RFID and Ticketing-Group Research.doc
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Group Work_GroupPresentationPPT_The application of RFID in cool chain.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Group Work_GroupPresentationPPT_RFID & BARCODE.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Experiments_Sample Reports_Risk Pooling_riskpooling_金梦珂.docx
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Experiments_Sample Reports_Risk Pooling_RiskPoolExperimentReport.docx
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Experiments_Sample Reports_Risk Pooling_Risk Pooling 罗岩.doc
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)09_Procurement and Outsourcing(2)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)00-Introduction to Course(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)01-Introduction to Supply Chain Management(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)02-Inventory Management(1)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)02-Inventory Management(2)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)03_Logistics Network Configuration(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)04-Supply Contracts(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)05_The Value of Information(1)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)05_The Value of Information(2)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)06_Supply Chain Integration(1)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)06_Supply Chain Integration(2)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)08_Strategic Alliances(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《风险管理》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(课堂讲义)导论.doc
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(课堂讲义)Finance management in public sector.doc
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源_人民币银行结算账户管理办法.doc
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 投资管理(张录法).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 支出管理.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 负债管理.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 资产管理.ppt
