上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)09_Procurement and Outsourcing(2)(2012)

Procurement and Outsourcing Xiaohong Pang Automation Department Shanghai Jiaotong University
Procurement and Outsourcing Xiaohong Pang Automation Department Shanghai Jiaotong University

Lecture Outline Introduction Outsourcing Benefits and Risks A Framework for Buy/Make Decisions ■ e-Procurement A Framework for e-Procurement Case Study:FreeMarkets Online
Introduction Outsourcing Benefits and Risks A Framework for Buy/Make Decisions e-Procurement A Framework for e-Procurement Case Study: FreeMarkets Online Lecture Outline

E-Procurement In the mid to late 90s,business to business automation was considered a trend. It would have a profound impact on supply chain performance. Between 1998 and 2000,hundreds of e-markets were established in dozens of industries.from chemicals and steels to utilities and human resources. These e-markets promised increased market reach for both buyers and suppliers,reduced procurement costs and paperless transactions
E-Procurement In the mid to late 90s, business to business automation was considered a trend. It would have a profound impact on supply chain performance. Between 1998 and 2000, hundreds of e-markets were established in dozens of industries, from chemicals and steels to utilities and human resources. These e-markets promised increased market reach for both buyers and suppliers, reduced procurement costs and paperless transactions

Why Holding High Expectations for E-Procurement In the mid 90s,many companies wanted to outsource their procurement functions, since the procurement process is highly complex,it requires significant expertise, and is very costly. These companies need help with their procurement functions
Why Holding High Expectations for E-Procurement In the mid 90s, many companies wanted to outsource their procurement functions, since the procurement process is highly complex, it requires significant expertise, and is very costly. These companies need help with their procurement functions
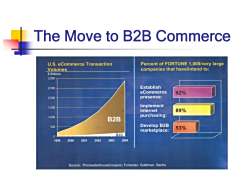
The Move to B2B Commerce U.S.eCommerce Transaction Percent of FORTUNE 1,000/very large Volumes companies that have/intend to: Billions 3,000 2,500 Establish eCommerce 92% 2,000 presence: 1.500 Implement Internet 89% 1.000 B2B purchasing: 500 Develop B2B marketplace: 53% 0 B2C 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 Source:PricewaterhouseCoopers;Forrester;Goldman,Sachs
The Move to B2B Commerce
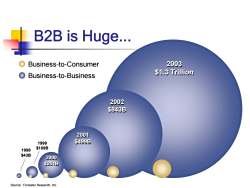
B2B is Huge... Business-to-Consumer 2003 O Business-to-Business $1.3 Trillion 2002 $843B 2001 1999 $499B 1998 $109B $43B 2000 $25列B Source:Forrester Research,Inc
B2B is Huge... 2003 $1.3 Trillion 2003 $1.3 Trillion 2002 $843B 2002 $843B 2001 $499B 2001 $499B 2000 $251B 2000 $251B 1998 $43B 1998 $43B Business-to-Business Source: Forrester Research, Inc. 1999 $109B 1999 $109B Business-to-Consumer

B2B Software vendors Oracle(Indirect and Direct) i2 Technologies and Manugistics(Direct) Ariba (Indirect and Direct) Commerce One (Indirect and Direct) ■Agile(Direct) VerticalNet (Indirect)
B2B Software Vendors Oracle (Indirect and Direct) i2 Technologies and Manugistics (Direct) Ariba (Indirect and Direct) Commerce One (Indirect and Direct) Agile (Direct) VerticalNet (Indirect)

Highly Fragmented Most product categories are highly fragmented,with numerous suppliers each offering different level of quality, service and pricing options Buyers incur significant cost in the actual purchase process A buyer must invest internal resources to manage the process of collecting,analyzing and acting upon all the information in the market In addition to purchase price companies spend over 10%in additional procurement costs On the suppliers side,there are significant costs in using the manufacturing reps These commissions range from 4%to 7%of purchase price
Highly Fragmented Most product categories are highly fragmented, with numerous suppliers each offering different level of quality, service and pricing options Buyers incur significant cost in the actual purchase process A buyer must invest internal resources to manage the process of collecting, analyzing and acting upon all the information in the market In addition to purchase price companies spend over 10% in additional procurement costs On the suppliers side, there are significant costs in using the manufacturing reps These commissions range from 4% to 7% of purchase price

e-Marketplaces: The Initial (95-99)business model The e-marketplace concept started as a new way to procure products,particularly non-production items. E-marketplaces can: Expand everyone's market reach Generate lower price for the buyers Cut operational costs for buyers and suppliers Automating the procurement process will reduce processing cost per order from as high as $150 to as low as $5 per order ■Focus on liquidity Transaction fee paid by the suppliers Serve as a virtual distributor
e-Marketplaces: The Initial (95-99) business model The e-marketplace concept started as a new way to procure products, particularly non-production items. E-marketplaces can: Expand everyone’s market reach Generate lower price for the buyers Cut operational costs for buyers and suppliers Automating the procurement process will reduce processing cost per order from as high as $150 to as low as $5 per order Focus on liquidity Transaction fee paid by the suppliers Serve as a virtual distributor

Value Proposition for Buyers by e-Markets RFQ:a standard business process whose purpose is to invite suppliers into a bidding process to bid on specific products. Putting together specifications,drawings,lot sizes, documentation and RFQs Serving as an intermediary between buyers and suppliers Identifying potential saving opportunities Increasing the number of suppliers involved in the biding event(出价,投标) The focus was on reducing procurement cost.But long-term relationships are not important. If a long-term relationship is important.How to select a supplier from e-markets?
Value Proposition for Buyers by e-Markets Putting together specifications, drawings, lot sizes, documentation and RFQs Serving as an intermediary between buyers and suppliers Identifying potential saving opportunities Increasing the number of suppliers involved in the biding event (出价,投标) Identifying, qualifying and supporting suppliers Conducting the auction (拍卖) Providing post bid analysis and support RFQ: a standard business process whose purpose is to invite suppliers into a bidding process to bid on specific products. The focus was on reducing procurement cost. But long-term relationships are not important. If a long-term relationship is important. How to select a supplier from e-markets?
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Experiments_Sample Reports_Risk Pooling_Risk Pooling Report_杨健.docx
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)09_Procurement and Outsourcing(1)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)08_Strategic Alliances(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)06_Supply Chain Integration(2)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)06_Supply Chain Integration(1)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)05_The Value of Information(2)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)05_The Value of Information(1)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)04-Supply Contracts(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)03_Logistics Network Configuration(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)02-Inventory Management(2)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)02-Inventory Management(1)(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)01-Introduction to Supply Chain Management(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(PostG)00-Introduction to Course(2012).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Group Work_合作学习指导手册.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Group Work_Research Reports_The application of RFID in cool chain.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Group Work_Research Reports_RFID and Ticketing-Group Research.doc
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Group Work_GroupPresentationPPT_The application of RFID in cool chain.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Group Work_GroupPresentationPPT_RFID & BARCODE.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Experiments_Sample Reports_Risk Pooling_riskpooling_金梦珂.docx
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)Experiments_Sample Reports_Risk Pooling_RiskPoolExperimentReport.docx
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)00-Introduction to Course(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)01-Introduction to Supply Chain Management(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)02-Inventory Management(1)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)02-Inventory Management(2)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)03_Logistics Network Configuration(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)04-Supply Contracts(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)05_The Value of Information(1)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)05_The Value of Information(2)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)06_Supply Chain Integration(1)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)06_Supply Chain Integration(2)(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《供应链管理 Supply Chain Management》课程教学资源(讲义资料)LectureNote(UnderG)08_Strategic Alliances(2013Fall with script).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《风险管理》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(课堂讲义)导论.doc
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(课堂讲义)Finance management in public sector.doc
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源_人民币银行结算账户管理办法.doc
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 投资管理(张录法).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 支出管理.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 负债管理.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 资产管理.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《公共组织财务管理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 财务分析.ppt
