上海交通大学:《传热传质学 Heat and Mass Transfer》教学资源(课程讲义)Lecture Notes_hch6 INTRODUCTION(1/2)
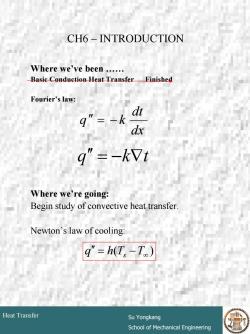
CH6-INTRODUCTION Where we've been...... Basic Conduction Heat Transfer Finished Fourier's law: q"=-k dt dx g"=-kVt Where we're going: Begin study of convective heat transfer. Newton's law of cooling: q"=h(T,-T) Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
# 4 Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering CH6 – INTRODUCTION Where we’ve been …… Basic Conduction Heat Transfer Finished Fourier’s law: Where we’re going: Begin study of convective heat transfer. Newton’s law of cooling: dx dt q ′′ = − k q ′′ = −k∇t ( ) = − ∞ q ′′ h Ts T

Convective transfer problem A FAMILY CIRCUS 2-6 D2o02 BIKeane,nt Dt tyKng Frmn世Srd hEAM FIRCUS. 蒸 "I forget.Does holding the door open let the cold air in,or the warm out?" Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
# 5 Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering Convective transfer problem

CH6 INTRODUCTION KEY POINTS THIS CHAPTER What are the key variables when analyzing convection heat transfer? Review boundary layer concept and significance General idea of relationship between velocity and thermal profiles in a boundary layer. Effect of laminar versus turbulent flow on heat transfer potential Boundary layer similarity This chapter will be taught in two lectures: the first includes text book sections 6.1 to 6.4 the other includes text book sections 6.5 to 6.10 Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
# 6 Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering CH6 INTRODUCTION KEY POINTS THIS CHAPTER • What are the key variables when analyzing convection heat transfer? • Review boundary layer concept and significance • General idea of relationship between velocity and thermal profiles in a boundary layer. • Effect of laminar versus turbulent flow on heat transfer potential • Boundary layer similarity • This chapter will be taught in two lectures: the first includes text book sections §6.1 to 6.4 the other includes text book sections §6.5 to 6.10
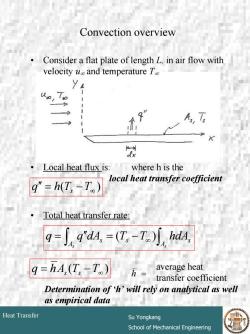
Convection overview Consider a flat plate of length L,in air flow with velocity u and temperature To yA 1 1 Local heat flux is: where h is the local heat transfer coefficient q"=h(T,-T) Total heat transfer rate: 9=∫9d4,=(T,-T) hdA. q=hA,(Ts-T) 万= average heat transfer coefficient Determination of h'will rely on analytical as well as empirical data Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
# 7 Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering Convection overview • Consider a flat plate of length L, in air flow with velocity u∞ and temperature T∞ • Local heat flux is: where h is the local heat transfer coefficient • Total heat transfer rate: ( ) = − ∞ q ′′ h Ts T ∫ ∞ ∫ = ′′ = − s As s s A s q q dA (T T ) hdA ( ) q = hAs Ts −T∞ average heat transfer coefficient h = Determination of ‘h’ will rely on analytical as well as empirical data

Convection overview(Cont'd) Same principal applies to any arbitrary shape,not just a flat plate dAs As:Ts Average convection heat transfer coefficient: or,for unit width: d So,we need to know how h varies with x,the distance from the leading edge...... What do you think key parameters that might influence h? Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
# 8 Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering Convection overview (Cont’d) • Same principal applies to any arbitrary shape, not just a flat plate • Average convection heat transfer coefficient: So, we need to know how h varies with x, the distance from the leading edge…….. What do you think key parameters that might influence h? q ′′ dAs As Ts , or, for unit width: ∫ = As s s hdA A h 1 ∫ = L hdx L h 0 1

Key parameters Transfer potential:forced flow or free flow Phase change:boiling and condensation Flow conditions:laminar or turbulent flow Geometries:shape,size,position and roughness. Properties:density,viscosity,thermal conductivity,specific heat,and so on. Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
# 9 Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering Key parameters • Transfer potential: forced flow or free flow • Phase change: boiling and condensation • Flow conditions: laminar or turbulent flow • Geometries: shape, size, position and roughness. • Properties: density, viscosity, thermal conductivity, specific heat, and so on
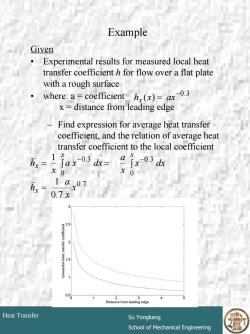
Example Given Experimental results for measured local heat transfer coefficient h for flow over a flat plate with a rough surface 0.3 where:a=coefficienth(x)=ax x=distance from leading edge Find expression for average heat transfer coefficient,and the relation of average heat transfer coefficient to the local coefficient 万x= I jax03ds=ajx3d X0 hx 1ax07 0.7x 2.5 1.5 050 2 Distance from leading edge Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
# 10 Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering Example Given • Experimental results for measured local heat transfer coefficient h for flow over a flat plate with a rough surface • where: a = coefficient x = distance from leading edge – Find expression for average heat transfer coefficient, and the relation of average heat transfer coefficient to the local coefficient ( ) −0.3 h x = ax x 0.7 0 0.3 0 0.3 0.7 1 1 x x a h x dx x a a x dx x h x x x x = = ∫ = ∫ − −
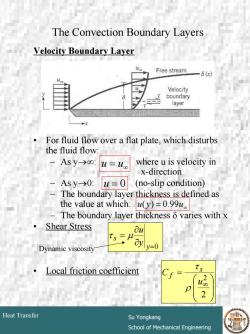
The Convection Boundary Layers Velocity Boundary Layer Free stream 一6(x) Velocity boundary layer For fluid flow over a flat plate,which disturbs the fluid flow: -ASy→0: u=uo where u is velocity in x-direction Asy-→0: u=0 (no-slip condition) The boundary layer thickness is defined as the value at which: u(y)=0.99u。 - The boundary layer thickness 8 varies with x Shear Stress Bu ay Dynamic viscosity y=0 Local friction coefficient u 2 Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
# 11 Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering The Convection Boundary Layers Velocity Boundary Layer • For fluid flow over a flat plate, which disturbs the fluid flow: – As y→∞: where u is velocity in x-direction – As y→0: (no-slip condition) – The boundary layer thickness is defined as the value at which: – The boundary layer thickness δ varies with x • Shear Stress • Local friction coefficient =0 ∂ ∂ = y s y u τ µ ⎟ ⎟ ⎠ ⎞ ⎜ ⎜ ⎝ ⎛ = ∞ 2 2 u C s f ρ τ = ∞ u u u = 0 = ∞ u( y) 0.99u Dynamic viscosity
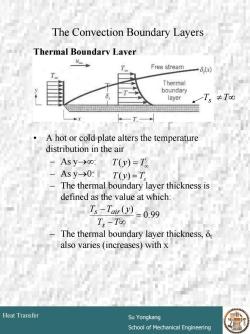
The Convection Boundary Layers Thermal Boundary Layer Free stream 6,x) Thermal boundary layer 一T,≠To T. A hot or cold plate alters the temperature distribution in the air -Asy-→o:T(y)=T - Asy→0:T(y)=T, The thermal boundary layer thickness is defined as the value at which: T,-Tair(y)=0.99 Ts-Too The thermal boundary layer thickness,t also varies (increases)with x Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
# 12 Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering The Convection Boundary Layers Thermal Boundary Layer • A hot or cold plate alters the temperature distribution in the air – As y→∞: – As y→0: – The thermal boundary layer thickness is defined as the value at which: – The thermal boundary layer thickness, δt also varies (increases) with x 0.99 ( ) = − ∞ − T T T T y s s air Ts ≠ T∞ = T∞ T( y) Ts T( y) =
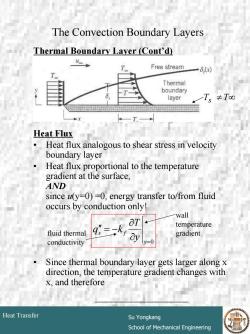
The Convection Boundary Layers Thermal Boundary Layer (Cont'd) Free stream 6,) Thermal boundary layer 一T,≠T0 T Heat Flux 0 Heat flux analogous to shear stress in velocity boundary layer Heat flux proportional to the temperature gradient at the surface, AND since u(y=0)-0,energy transfer to/from fluid occurs by conduction only! wall at temperature fluid thermal gradient conductivity y=0 Since thermal boundary layer gets larger along x direction,the temperature gradient changes with x,and therefore Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
# 13 Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering The Convection Boundary Layers Thermal Boundary Layer (Cont’d) Heat Flux • Heat flux analogous to shear stress in velocity boundary layer • Heat flux proportional to the temperature gradient at the surface, AND since u(y=0) =0, energy transfer to/from fluid occurs by conduction only! • Since thermal boundary layer gets larger along x direction, the temperature gradient changes with x, and therefore Ts ≠ T∞ fluid thermal conductivity wall temperature gradient ____________________ =0 ∂ ∂ ′′ = − y s f y T q k
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《传热传质学 Heat and Mass Transfer》教学资源(课程讲义)Lecture Notes_hch6 INTRODUCTION(2/2).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《传热传质学 Heat and Mass Transfer》教学资源(课程讲义)Lecture Notes_ch 8 Internal flow(2/2).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《传热传质学 Heat and Mass Transfer》教学资源(课程讲义)Lecture Notes_ch 8 Internal flow(1/2).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《传热传质学 Heat and Mass Transfer》教学资源(课程讲义)Lecture Notes_Ch 7 External flow.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液液萃取_Extraction_2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液液萃取_Extraction_1.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体精馏_Equilibrium_6.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体精馏_Equilibrium_5.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体精馏_Equilibrium_4.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体精馏_Equilibrium_3.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体精馏_Equilibrium_2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体精馏_Equilibrium_1.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_干燥_Drying 第四节 干燥器.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_干燥_Drying 第三节 干燥过程计算.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_干燥_Drying 第一节 概述 第二节 干燥静力学.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_气体吸收_Absorption_5.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_气体吸收_Absorption_4.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_气体吸收_Absorption_3.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_气体吸收_Absorption_2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_气体吸收_Absorption_1.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《对流换热 Convection Heat Transfer》教学资源_教学资料_Chapter 6 and Appendix D Sections 6.1 through 6.8 and D.1 through D.3.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)微观和介观尺度的绿色工程——化学物质对生态环境和人类健康的影响(1/2).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)微观和介观尺度的绿色工程——化学物质对生态环境和人类健康的影响(2/2).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)概述、资源、环境与可持续发展(清华大学:韩明汉).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)微观和介观尺度的绿色工程——绿色化学(韩明汉).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绿色单元(物流行业)绿色物流 Green Logistics(靳强).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绿色单元操作(绿色化工).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)微观和介观尺度的绿色工程——绿色工程方案的评估和选择.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绿色建筑整体解决方案.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绿色过程(工业生产原理)Green Process(Industrial Process Principle).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绿色过程(清洁生产审核案例)清洁生产审核汇报.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)通信行业节能减排综述及思路.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绿色过程(清洁生产审核)Green Process(Clean Production Auditing).ppt
- 《催化学报》:(Ag/Al2O3+Cu/Ce(x)/AI2O3)组合催化剂催化乙醇选择性还原NOx及其副产物的消除.pdf
- 东莞理工学院:《专业综合实训一》课程教学资源(教学大纲)涂军令,元武智-20级化学工艺1班.doc
- 东莞理工学院:《专业综合实训一》课程教学资源(教学大纲)涂军令,元武智-20级能源化学1班.doc
- 东莞理工学院:《专业综合实训三》课程教学资源(教学大纲)涂军令,钟国玉-19级化学工艺1班.doc
- 东莞理工学院:《专业综合实训三》课程教学资源(教学大纲)涂军令,钟国玉-2019级能源化学工程1班.doc
- 东莞理工学院:《分析化学实验》课程教学资源(教学大纲)易莉芝楚家玉-2021化学工艺.docx
- 东莞理工学院:《分析化学实验》课程教学资源(教学大纲)易莉芝楚家玉-2021能源化学工程.docx
