上海交通大学:《传热传质学 Heat and Mass Transfer》教学资源(课程讲义)Lecture Notes_ch 8 Internal flow(2/2)

HEAT TRANSFER CHAPTER 8 Internal flow Heat Transfer #1 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 1 HEAT TRANSFER CHAPTER 8 Internal flow
Internal Flow Heat Transfer Where we've been ..... Introduction to internal flow,basic concepts, energy balance. Inviscid flow region Boundary layer region u(r.x) Hydrodynamic entrance region Fully developed regior xd. Where we're going: Developing heat transfer coefficient relationships and correlations for internal flow Heat Transfer #2 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 2 Internal Flow Heat Transfer Where we’ve been …… • Introduction to internal flow, basic concepts, energy balance. Where we’re going: • Developing heat transfer coefficient relationships and correlations for internal flow ro

Internal Flow Heat Transfer KEY POINTS THIS LECTURE Convection correlations Laminar flow Turbulent flow Other topics Non-circular flow channels Concentric tube annulus Heat Transfer #3 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 3 Internal Flow Heat Transfer KEY POINTS THIS LECTURE • Convection correlations – Laminar flow – Turbulent flow • Other topics – Non-circular flow channels – Concentric tube annulus

Convection correlations:laminar flow in circular tubes 1.The fully developed region from the energy equation,we can obtain the exact solution. for constant surface heat flux hD Nup= =4.36 q"=C k for constant surface temperature hD Nup= k =3.66 T、=C Note:the thermal conductivity k should be evaluated at T Heat Transfer #4 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 4 Convection correlations: laminar flow in circular tubes • 1. The fully developed region from the energy equation,we can obtain the exact solution. for constant surface heat flux for constant surface temperature Note: the thermal conductivity k should be evaluated at . 4.36 k hD NuD q s C 3.66 k hD NuD Ts C Tm
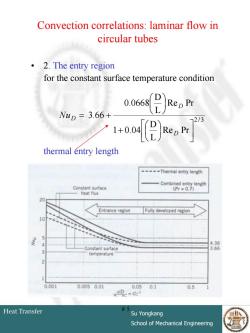
Convection correlations:laminar flow in circular tubes 0 2.The entry region for the constant surface temperature condition Rep Pr Wup=3.66+ 72/3 人1 1+-0.04Rep Pr thermal entry length ----Thermal entry length Combined entry length Constant sorface (Prs0.7) heat flux 20 Entrance region Fulty developed region 10 4.36 Constant surface 3.66 temperature 2 0.001 0.c050.01 0.0501 0.5 Heat Transfer #5 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 5 Convection correlations: laminar flow in circular tubes • 2. The entry region for the constant surface temperature condition thermal entry length 2/3 Re Pr L D 1 0.04 Re Pr L D 0.0668 3.66 D D NuD

Convection correlations:laminar flow in circular tubes .2.The entry region(cont'd) for the combined entry length 0.14 ·For values of [RepPr/(L/DΨ(u/u,P4}≥2 T.=C 0.48≤Pr<16,700 0.0044<(u14,)<9.75 All fluid properties evaluated at the mean T Tm =(Tmi+Tm.o)/2 Heat Transfer #6 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 6 Convection correlations: laminar flow in circular tubes • 2. The entry region(cont’d) for the combined entry length • For values of 1/3 0.14 / Re Pr 1.86 s D D L D Nu Re Pr/( / ) / 2 1/3 0.14 D L D s All fluid properties evaluated at the mean T / 2 Tm Tm,i Tm,o Ts C 0.48 Pr 16,700 0.0044 / 9.75 s

Convection correlations:turbulent flow in circular tubes A lot of empirical correlations are available. For smooth tubes,the fully developed flow Heating: Nup =0.023Res Pr4 Cooling: Nup=0.023Res Pr03 For rough tubes,coefficient increases with wall roughness.For fully developed flows Nua (f/8)ReD-1000)Pr 1+12.7f18)2(Pr23-1) Consider the entry length Short tubes NuD≈Nup,fa NuD C =1+ Nup,fd (x/D)m For liquid metals,see textbook p461. Heat Transfer #7 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 7 Convection correlations: turbulent flow in circular tubes • A lot of empirical correlations are available. • For smooth tubes, the fully developed flow Heating: Cooling: • For rough tubes, coefficient increases with wall roughness. For fully developed flows • Consider the entry length • For liquid metals, see textbook p461. 4/5 0.4 0.023Re Pr NuD D 4/5 0.3 0.023Re Pr NuD D 1 12.7( / 8) (Pr 1) ( / 8)(Re 1000)Pr 1/ 2 2/3 f f Nu D d Nu D NuD, fd or m D fd D x D C Nu Nu ( / ) 1 , Short tubes

Internal convection heat transfer coefficient (summary) 1.For laminar and fully developed flow (S 8.4.1): i.g"constant: Wup=4.36 Eq.8.53 ii.Ts constant: Wup=3.36 Eq.8.55 2.For laminar flow in entry region(before fully developed flow,§8.4.2: i.Ts constant 0.0668 Rep Pr WuD=3.66+- 213 Eq.8.56 1+004 ReoP ii.Combined entry length with full tube: ,1R 0.14 Eq.8.57 3.For turbulent and fully developed (S 8.5) i.Heating Nup =0.023Res Pr04 Eq.8.60 ii.Cooling No=0.023Re5Pr03 All fluid properties evaluated at the mean T Tm =(Tmi+Tmo)/2 Heat Transfer #8 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 8 Internal convection heat transfer coefficient (summary) 1. For laminar and fully developed flow (§8.4.1): i. q ” constant: ii. Ts constant: 2. For laminar flow in entry region (before fully developed flow, §8.4.2: i. Ts constant : ii. Combined entry length with full tube: 3. For turbulent and fully developed (§8.5) i. Heating ii. Cooling 2/3 Re Pr L D 1 0.04 Re Pr L D 0.0668 3.66 D D NuD 1/3 0.14 / Re Pr 1.86 s D D L D Nu All fluid properties evaluated at the mean T / 2 Tm Tm,i Tm,o Eq. 8.53 Eq. 8.55 Eq. 8.56 Eq. 8.57 Eq. 8.60 4/5 0.4 0.023Re Pr NuD D 4/5 0.3 0.023Re Pr NuD D NuD 4.36 NuD 3.36

Example:Oil at 150C flows slowly through a long,thin- walled pipe of 30-mm inner diameter.The pipe is suspended in a room for which the air temperature is 20 C and the convection coefficient at the outer tube surface is 11W/m2.K. Estimate the heat loss per unit length of tube. KNOWN:Oil flowing slowly through a long,thin-walled pipe suspended in a room. FIND:Heat oss pernt of the pipe, SCHEMATIC: Koom air ho=11W/m2 Tm=20℃ 1hinD 1haMD Ppe,D30m -Tm-150℃ ASSUMPTIONS:(1)Steady-state conditions,(2)Tube wall thermal resistance negligible,(3) Fully developed flow,(4)Radiation exchange between pipe and room negligble PROPERTIES:Table 4-5,Unused engine oil (Tm=150C=423K):k=0.133 W/mK. Heat Transfer #9 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 9 Example: Oil at 150℃ flows slowly through a long, thin- walled pipe of 30-mm inner diameter. The pipe is suspended in a room for which the air temperature is 20 ℃ and the convection coefficient at the outer tube surface is 11W/m2 .K. Estimate the heat loss per unit length of tube

ANALYSIS:The rate quation,for a unit length of the pipe,can be written as oym-1o) Rt where the thermal resistance is comprised of two elements, ,11 R财DDD 1,1 hi ho The convection cofficient for intemal flow,h,must be estimated from an appropriate correlation. From practical considerations,we recognize that the oil flow rate cannot be large enough to achieve turbulent flow conditions.Hence,the flow is am,and ifthe pipe is very long,the flow will be fully developed.The appropriate correlation is n p-366 h1=Nup kD=366x0.13W0.030m=162wm2K m.K The heat rate per unit length of the pipe is (150-20)°C =80.3W/m. < 1 1,1 m.K π(0.030m) 162+i W COMMENTS:This problem requires making a judgment that the oil flow will be laminar rather than turbulent.Why is this a reasonable assumption?Recognize that the correlation applies to a constant surface temperature condition. Heat Transfer #1 Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering
Heat Transfer Su Yongkang School of Mechanical Engineering # 10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《传热传质学 Heat and Mass Transfer》教学资源(课程讲义)Lecture Notes_ch 8 Internal flow(1/2).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《传热传质学 Heat and Mass Transfer》教学资源(课程讲义)Lecture Notes_Ch 7 External flow.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液液萃取_Extraction_2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液液萃取_Extraction_1.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体精馏_Equilibrium_6.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体精馏_Equilibrium_5.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体精馏_Equilibrium_4.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体精馏_Equilibrium_3.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体精馏_Equilibrium_2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体精馏_Equilibrium_1.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_干燥_Drying 第四节 干燥器.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_干燥_Drying 第三节 干燥过程计算.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_干燥_Drying 第一节 概述 第二节 干燥静力学.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_气体吸收_Absorption_5.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_气体吸收_Absorption_4.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_气体吸收_Absorption_3.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_气体吸收_Absorption_2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_气体吸收_Absorption_1.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_液体搅拌_液体搅拌.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程单元操作原理》课程教学资源_流体输送机械_流体机械_2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热传质学 Heat and Mass Transfer》教学资源(课程讲义)Lecture Notes_hch6 INTRODUCTION(2/2).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《传热传质学 Heat and Mass Transfer》教学资源(课程讲义)Lecture Notes_hch6 INTRODUCTION(1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《对流换热 Convection Heat Transfer》教学资源_教学资料_Chapter 6 and Appendix D Sections 6.1 through 6.8 and D.1 through D.3.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)微观和介观尺度的绿色工程——化学物质对生态环境和人类健康的影响(1/2).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)微观和介观尺度的绿色工程——化学物质对生态环境和人类健康的影响(2/2).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)概述、资源、环境与可持续发展(清华大学:韩明汉).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)微观和介观尺度的绿色工程——绿色化学(韩明汉).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绿色单元(物流行业)绿色物流 Green Logistics(靳强).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绿色单元操作(绿色化工).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)微观和介观尺度的绿色工程——绿色工程方案的评估和选择.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绿色建筑整体解决方案.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绿色过程(工业生产原理)Green Process(Industrial Process Principle).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绿色过程(清洁生产审核案例)清洁生产审核汇报.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)通信行业节能减排综述及思路.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《绿色工程概论 Green Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绿色过程(清洁生产审核)Green Process(Clean Production Auditing).ppt
- 《催化学报》:(Ag/Al2O3+Cu/Ce(x)/AI2O3)组合催化剂催化乙醇选择性还原NOx及其副产物的消除.pdf
- 东莞理工学院:《专业综合实训一》课程教学资源(教学大纲)涂军令,元武智-20级化学工艺1班.doc
- 东莞理工学院:《专业综合实训一》课程教学资源(教学大纲)涂军令,元武智-20级能源化学1班.doc
- 东莞理工学院:《专业综合实训三》课程教学资源(教学大纲)涂军令,钟国玉-19级化学工艺1班.doc
- 东莞理工学院:《专业综合实训三》课程教学资源(教学大纲)涂军令,钟国玉-2019级能源化学工程1班.doc
