电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 01 Continuous-time Signals and Systems

Chapter 1 Continuous-time Signals and Systems
Chapter 1 Continuous-time Signals and Systems

Introduction Any problems about signal analyses and processing may be thought of letting signals trough systems. f(t) h( y(t) From f(t)and h(t),find y(t),Signal processing From f(t)and y(t),find h(t),System design From y(t)and h(t),find f(t),Signal reconstruction
Introduction Any problems about signal analyses and processing may be thought of letting signals trough systems. h(t) f(t) y(t) From f(t) and h(t),find y(t), Signal processing From f(t) and y(t) ,find h(t) ,System design From y(t) and h(t),find f(t) , Signal reconstruction

Introduction There are so many different signals and systems that it is impossible to describe them one by one The best approach is to represent the signal as a combination of some kind of the simplest signals which will pass through the system and produce a response.Combine the responses of all simplest signals,which is the system response for the original input signal. This is the basic approach to study the signal analyses and processing
Introduction There are so many different signals and systems that it is impossible to describe them one by one The best approach is to represent the signal as a combination of some kind of the simplest signals which will pass through the system and produce a response. Combine the responses of all simplest signals, which is the system response for the original input signal. This is the basic approach to study the signal analyses and processing

Continue-time Signal All signals are thought of as a pattern of variations in time and represented as a time function f(t). In the real-world,any signal has a start. Let the start as t=0 that means f()=0 t<0 Call such signals causal
Continue-time Signal All signals are thought of as a pattern of variations in time and represented as a time function f(t). In the real-world, any signal has a start. Let the start as t=0 that means f(t) = 0 t<0 Call such signals causal

Typical signals and their representation Unit Step u(t)(in our textbook u(t)) t>0 t<0 tu(t-to) 0 to u(t)is basic causal signal,multiply which with any non-causal signal to get causal signal
Typical signals and their representation Unit Step u(t) (in our textbook µ(t)) {1 0 0 0 ( ) > = < t t u t u(t) 1 0 t u(t- t0) 1 0 t t 0 u(t) is basic causal signal, multiply which with any non-causal signal to get causal signal

Typical signals and their representation Sinusoidal A sin(ot+o) f(t)=A sin(ot+p)=A sin(2nft+o) A-Amplitude f-frequency (Hz,cycle per second) o=2af angular frequency (radians/sec) -start phase(radians)
Typical signals and their representation Sinusoidal A sin(ωt+φ) f(t) = A sin(ωt+φ)= A sin(2πft+φ) A - Amplitude f – frequency (Hz, cycle per second) ω= 2πf angular frequency (radians/sec) φ – start phase(radians)
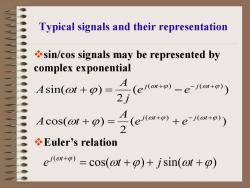
Typical signals and their representation sin/cos signals may be represented by complex exponential )) A Asin(at+p)= cos(t+p)=号 (eo+o)+ejo+p)) Euler's relation e)-cos(@t+p)+jsin(ot+p)
Typical signals and their representation sin/cos signals may be represented by complex exponential ( ) 2 cos( ) ( ) 2 sin( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ω ϕ ω ϕ ω ϕ ω ϕ ω ϕ ω ϕ + − + + − + + = + + = − j t j t j t j t e e A A t e e j A A t Euler’s relation cos( ) sin( ) ( ) ω ϕ ω ϕ ω ϕ = + + + + e t j t j t

Typical signals and their representation Sinusoidal is basic periodic signal which is important both in theory and engineering. Sinusoidal is non-causal signal.All of periodic signals are non-causal because they have no start and no end. f (t)=f(t+mT) m=0,士1,士2,…,士o0
Typical signals and their representation Sinusoidal is basic periodic signal which is important both in theory and engineering. Sinusoidal is non-causal signal. All of periodic signals are non-causal because they have no start and no end. f (t) = f (t + mT) m=0, ±1, ±2, ···, ±∞

Typical signals and their representation Exponential f(t)=eat a is real a 0 growing
Typical signals and their representation Exponential f(t) = eαt •α is real α 0 growing

Typical signals and their representation Exponential f(t)=eat a is complex a=0+jo f(t)=Aeat =Ae(o+jo)t =Aeot cosωt+jAeot sinωt o 0,sinusoidal o >0,growing sinusoidal o<0,decaying sinusoidal (damped)
Typical signals and their representation Exponential f(t) = eαt •α is complex α = σ + jω f(t) = Aeαt = Ae(σ + jω)t = Aeσ t cosωt + j Aeσ t sinωt σ = 0, sinusoidal σ > 0 , growing sinusoidal σ < 0 , decaying sinusoidal (damped)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 00 Introduction.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《微电子器件》课程教学资源(思政教案)高频晶体管设计.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《微电子器件》课程教学资源(思政教案)MOSFET发展方向.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《微电子器件》课程教学资源(思政教案)大注入效应.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《微电子器件》课程教学资源(思政教案)绪论、微电子技术发展现状.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《微电子器件》课程教学资源(教学大纲)Microelectronic Devices.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《移动通信系统》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 未来移动通信系统及其增强技术.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《移动通信系统》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 抗衰落和链路性能增强技术.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《移动通信系统》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 GSM及其增强移动通信系统.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《移动通信系统》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 蜂窝组网技术(移动通信网的基本概念、频率复用和蜂窝小区、多址接入技术).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《移动通信系统》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 移动通信电波传播与传播预测模型.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《移动通信系统》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 移动通信中的信源编码和调制解调技术.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《移动通信系统》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 概述(主讲:雷霞).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《移动通信系统》课程教学资源(授课电子教案,雷霞).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《移动通信系统》课程教学资源(思政案例选录).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《移动通信系统》课程教学资源(教学大纲)Mobile Communication System.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《白话通信与计算 Introduction to Communications and Computations》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 多址接入与功率控制.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《白话通信与计算 Introduction to Communications and Computations》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)03 网络OSI分层结构.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《白话通信与计算 Introduction to Communications and Computations》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)02 信息技术发展史.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《白话通信与计算 Introduction to Communications and Computations》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)01 行业、专业与课程体系.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 02 Discrete-Time Signals and Systems.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 03 Transform-Domain Representation of Discrete-Time Signals.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 04 Frequency-domain Representation of LTI Discrete-Time Systems.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 06 Digital Filter Structures.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 07 Digital Filter Design.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 Analysis of Finite Wordlength Effects.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Multirate Digital Signal Processing.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 Applications of Digital Signal Processing.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)About.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 01 Introduction 1.1 Exampls.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 01 Introduction 1.2 Diagram and elements of Comm.Sys.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 01 Introduction 1.3 Digital Comm.Sys.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 01 Introduction 1.4 Channels and their characteristics.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 04 Information source and source coding 4.1 ADC and PCM.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 04 Information source and source coding 4.2 Modeling of digital source.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.1 Geometric rep.of the sig waveforms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.2 Pulse amplitude modulation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.3 2-d signal waveforms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.4 M-d signal waveforms.pdf
