电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 01 Introduction 1.4 Channels and their characteristics

Examples of communication Diagram and elements of Comm.Sys Digital Comm.Sys. Channels and their characteristics UESTC-Introduction Prof李晓峰 2

Channels and their characteristics Physical channel includes: 1.a pair of wires carrying electrical waveforms 2. an optical fiber passing light beam 3. free space for microwave propagation 4. water for acoustic signals 5. storage media,like magnetic tape,optical disk. UESTC-Introduction Prof李晓峰 3

Channels and their characteristics Channel effects are: 1. Signal attenuation is due to loss in the media 2. Additive noise is essential for electronic systems.Electronic components such as resistors introduce noise,which often called thermal noise. UESTC-Introduction Prof李晓峰 4

Channels and their characteristics Channel effects are: 1. Signal attenuation is due to loss in the media 2. Additive noise is essential for electronic systems.Electronic components such as resistors introduce noise,which often called thermal noise. 3.Bandwidth reflects how fast the media can follow the change of signals UESTC-Introduction Prof李晓峰 5

Channels and their characteristics Channel effects are: 1. Signal attenuation is due to loss in the media 2 Additive noise is essential for electronic systems.Electronic components such as resistors introduce noise,which often called thermal noise. 3.Bandwidth reflects how fast the media can follow the change of signals 4.Interference may be generated by nature and other systems,like thunders,signals of other users,spikes due to nearby car ignitions,etc. 5. Distortion of signal in amplitude or phase unflat UESTC-Introduction Prof李晓峰 6

Channels and their characteristics Channel effects are: 1. Signal attenuation 2. Additive noise 3. Bandwidth 4. Interference 5. Distortion Two fundamental limits for communication: ■ SNR---Increasing power of transmitting signal may less the effect of noise and interference. Channel of large bandwidth supports transmission of much information. UESTC-Introduction Prof李晓峰 7

Models for channels For the convenience of design and study of sys,we often use models instead of real physical channels. The most simple and useful model for a channel is the additive noise channel. r(t)a x s(t)+n(t) where a is the attenuation factor and n(t)is the noise. For convenience,we often normalize the expression as, r(t)=s(t)+n(t) where r(t)and n(t)represent the equivalent received signal and noise. UESTC-Introduction Prof李晓峰 8
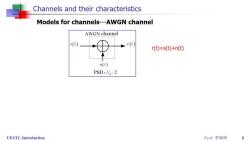
Channels and their characteristics Models for channels---AWGN channel AWGN channel s(r) r(t) r(t)=s(t)+n(t) n(r) PSD:N。/2 UESTC-Introduction Prof李晓峰 9
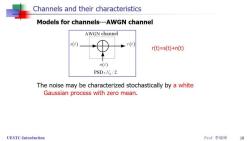
Channels and their characteristics Models for channels---AWGN channel AWGN channel s(t) r(t) r(t)=s(t)+n(t) n(r) PSD:N。/2 The noise may be characterized stochastically by a white Gaussian process with zero mean. UESTC-Introduction Prof李晓峰 10
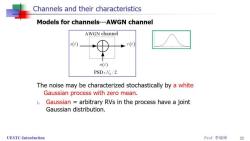
Channels and their characteristics Models for channels---AWGN channel AWGN channel s(t) r(t) n(r) PSD:N。/2 The noise may be characterized stochastically by a white Gaussian process with zero mean. 1.Gaussian arbitrary RVs in the process have a joint Gaussian distribution. UESTC-Introduction Prof李晓峰 11
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 01 Introduction 1.3 Digital Comm.Sys.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 01 Introduction 1.2 Diagram and elements of Comm.Sys.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 01 Introduction 1.1 Exampls.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)About.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 Applications of Digital Signal Processing.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Multirate Digital Signal Processing.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 Analysis of Finite Wordlength Effects.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 07 Digital Filter Design.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 06 Digital Filter Structures.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 04 Frequency-domain Representation of LTI Discrete-Time Systems.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 03 Transform-Domain Representation of Discrete-Time Signals.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 02 Discrete-Time Signals and Systems.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 01 Continuous-time Signals and Systems.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 00 Introduction.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《微电子器件》课程教学资源(思政教案)高频晶体管设计.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《微电子器件》课程教学资源(思政教案)MOSFET发展方向.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《微电子器件》课程教学资源(思政教案)大注入效应.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《微电子器件》课程教学资源(思政教案)绪论、微电子技术发展现状.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《微电子器件》课程教学资源(教学大纲)Microelectronic Devices.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 04 Information source and source coding 4.1 ADC and PCM.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 04 Information source and source coding 4.2 Modeling of digital source.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.1 Geometric rep.of the sig waveforms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.2 Pulse amplitude modulation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.3 2-d signal waveforms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.4 M-d signal waveforms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.5 Opt.reception for the sig.in AWGN.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.5.2 Opt.reception for the sig.in AWGN.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.5.3 Opt.reception for the sig.in AWGN.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.6.1 Optimal receivers and probs of err.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.6.2 Optimal receivers and probs of err.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.6.3 OptRecv-MPSK-QAM-MFSK.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 05 Digital transmission through the AWGN channel 5.6.4 Optimal receivers and probs of err.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 06 Digital transmission through band-limited AWGN channels 6.1 ISI and zero-ISI condition.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 06 Digital transmission through band-limited AWGN channels 6.2 Design of BL signals for zero-ISI.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 06 Digital transmission through band-limited AWGN channels 6.3 OFDM.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数字通信基础 Digital Communications》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,图片版)Chapter 08 Wireless communications.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代网络理论与综合 Theory and Synthesize of Electric Network》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1讲 电路元件(陈会).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代网络理论与综合 Theory and Synthesize of Electric Network》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2讲 电路元件及转换.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代网络理论与综合 Theory and Synthesize of Electric Network》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7讲 状态方程列写.pdf
