麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 33_3

Wild type cdc28 mutant cdc7 mutant Images removed due to copyright reasons
Wild type cdc28 mutant cdc7 mutant Images removed due to copyright reasons

What is the basic organization of the cell cycle Are the steps of the cycle mechanistically linked substrate-product"model Is there an autonomous "cell cycle clock"?
What is the basic organization of the cell cycle ? Are the steps of the cycle mechanistically linked ? "substrate-product" model Is there an autonomous "cell cycle clock" ?
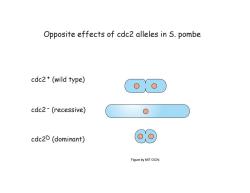
Opposite effects of cdc2 alleles in S.pombe cdc2+(wild type) cdc2-(recessive) cdc2D(dominant) @0 Figure by MIT OCW
Opposite effects of cdc2 alleles in S. pombe cdc2 + (wild type) - cdc2 (recessive) cdc2D (dominant) Figure by MIT OCW

There is there an autonomous "cell cycle clock" which is composed of cyclin CDK The amount of cyclins oscillates throughout the cell cycle However,the steps of the cycle are linked by negative feedback loops known as "checkpoint control"pathways
There is there an autonomous "cell cycle clock" which is composed of cyclin + CDK The amount of cyclins oscillates throughout the cell cycle However, the steps of the cycle are linked by negative feedback loops known as "checkpoint control" pathways
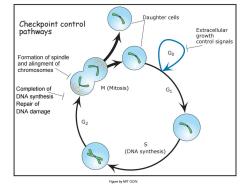
Daughter cells Checkpoint control pathways Extracellular growth control signals Formation of spindle Go and alingment of chromosomes Completion of M(Mitosis) DNA synthesis Repair of DNA damage G2 S (DNA synthesis) Figure by MIT OCW
growth (DNA synthesis) S G1 G0 G2 Formation of spindle and alingment of chromosomes Completion of DNA synthesis Repair of DNA damage Extracellular control signals Daughter cells M (Mitosis) Checkpoint control pathways Figure by MIT OCW

Image removed due to copyright reasons
Image removed due to copyright reasons

General types of oncogenic mutations Activation of growth control pathways signaling quiescent cells to divide inappropriately Inactivation of checkpoints allowing cells with damaged DNA or misaligned chromosomes to divide allowing high mutation rates and chromosome imbalances Inactivation of DNA repair genes allowing high mutation rates causing other oncogenic mutations
General types of oncogenic mutations Activation of growth control pathways signaling quiescent cells to divide inappropriately Inactivation of checkpoints allowing cells with damaged DNA or misaligned chromosomes to divide allowing high mutation rates and chromosome imbalances Inactivation of DNA repair genes allowing high mutation rates causing other oncogenic mutations
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 33_2.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 33_1.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 32 Numerical Chromosomal Abnormalities and Nondisjunction.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 31 Genetic Heterogeneity and Complex Traits.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 29、30 Statistical Evaluation of Genetic Linkage.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 28 Polymorphisms in Human DNA Sequences.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 27.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 26.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 25 Population Genetics.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 24 Transgenes and Gene Targeting in Mice II.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 23 Transgenes and Gene Targeting in Mice I.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 22 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes III.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 21 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes III.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 20 EUKARYOTIC GENES AND GENOMES II.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 19 EUKARYOTIC GENES AND GENOMES I.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 18.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 17.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 16 Gene Regulation.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 15 Gene Cloning.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 9 Gene Fine Structure.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 34 Alterations in different kinds of Genes cause Cancer.pdf
- 麻省理工学院:《动物遗传学 Genetics》课程教学资源(英文讲义)Lecture 35 Alterations in different kinds of Genes cause Cancer.pdf
- 温州医科大学:《微生物免疫学》课程教学资源(练习题,人卫成教专科四版,含答案).pdf
- 《生物统计附试验设计》课程教学资源(教研论文)MSExcel在畜牧兽医统计中应用(六)拟合直线及常用曲线.pdf
- 《生物统计附试验设计》课程教学资源(教研论文)MSExcel在畜牧兽医统计中的应用(五)多元线性回归分析.pdf
- 《生物统计附试验设计》课程教学资源(教研论文)MSExcel在畜牧兽医统计中应用(二)方差分析.pdf
- 《生物统计附试验设计》课程教学资源(教研论文)MSExcel在畜牧兽医统计中的应用(三)直线回归和直线相关分析.pdf
- 《生物统计附试验设计》课程教学资源(教研论文)MSExcel在畜牧兽医统计中的应用(四)卡方检验_x_2检验.pdf
- 《生物统计附试验设计》课程教学资源(教研论文)MSExcel在畜牧兽医统计中的应用(一).pdf
- 《生物统计附试验设计》课程教学资源(教研论文)地方农科院校生物统计学实验教学改革与实践.pdf
- 《生物统计附试验设计》课程教学资源(教研论文)地方院校动物科学专业卓越人才培养模式的探索与实践.pdf
- 《生物统计附试验设计》课程教学资源(教研论文)提高生物统计附试验设计课堂教学效果的几个关键环节.pdf
- 《生物统计附试验设计》课程教学资源(教研论文)生物统计教学改革实践与体会.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物统计附实验设计》课程教学资源(教学大纲)生物技术(动物方向)、生物制品专业四年制本科.doc
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物统计附实验设计》课程教学资源(讲义)响应面(RESPONSE SURFACE)分析讲义.doc
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物统计附实验设计》课程教学资源(讲义)混料设计与分析.doc
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物统计附实验设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第10章 协方差分析.ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物统计附实验设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第12章 试验设计.ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物统计附实验设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第1章 绪论.ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物统计附实验设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第2章 资料的整理.ppt
