《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Myeloma Proteins
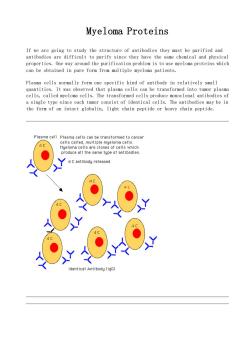
Myeloma proteins If we are going to study the structure of antibodies they must be purified and antibodies are difficult to purify since they have the same chemical and physical properties.One way around the purification problem is to use myeloma proteins which can be obtained in pure form from multiple myeloma patients. Plasma cells normally form one specific kind of antibody in relatively small quantities.It was observed that plasma cells can be transformed into tumor plasma cells,called myeloma cells.The transformed cells produce monoclonal antibodies of a single type since each tumor consist of identical cells.The antibodies may be in the form of an intact globulin,light chain peptide or heavy chain peptide. s of cells which 4C entibody released dentical Antibody(IgG)
Myeloma Proteins If we are going to study the structure of antibodies they must be purified and antibodies are difficult to purify since they have the same chemical and physical properties. One way around the purification problem is to use myeloma proteins which can be obtained in pure form from multiple myeloma patients. Plasma cells normally form one specific kind of antibody in relatively small quantities. It was observed that plasma cells can be transformed into tumor plasma cells, called myeloma cells. The transformed cells produce monoclonal antibodies of a single type since each tumor consist of identical cells. The antibodies may be in the form of an intact globulin, light chain peptide or heavy chain peptide
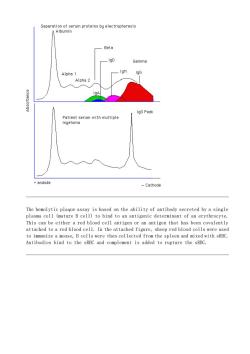
S6parntinmomanmproteinstyolectroptorosie Beta IgG Peak Patient serum with multiple myeloma andode -Cethode The hemolytic plaque assay is based on the ability of antibody secreted by a single plasma cell (mature B cell)to bind to an antigenic determinant of an erythrocyte. This can be either a red blood cell antigen or an antigen that has been covalently sheep red blood cells were used Antibodies bind to the sRBC and complement is added to rupture the sRBC
The hemolytic plaque assay is based on the ability of antibody secreted by a single plasma cell (mature B cell) to bind to an antigenic determinant of an erythrocyte. This can be either a red blood cell antigen or an antigen that has been covalently attached to a red blood cell. In the attached figure, sheep red blood cells were used to immunize a mouse, B cells were then collected from the spleen and mixed with sRBC. Antibodies bind to the sRBC and complement is added to rupture the sRBC
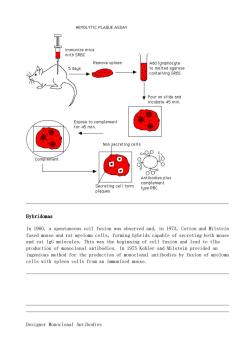
HEMOLYTIC PLAQUE ASSAY Remove spleer Add lymphocyte 5 days Pour on slide and incubate 45 min. Non secreting cells CompTement 9 Antibodies plus Hybridomas In 1960,a spontaneous cell fusion was observed and,in 1973,Cotton and Milstein and rat IgG molecules ingenious method for the production of monoclonal antibodies by fusion of myeloma cells with spleen cells from an immunized mouse. Designer Monoclonal Antibodies
Hybridomas In 1960, a spontaneous cell fusion was observed and, in 1973, Cotton and Milstein fused mouse and rat myeloma cells, forming hybrids capable of secreting both mouse and rat IgG molecules. This was the beginning of cell fusion and lead to tlhe production of monoclonal antibodies. In 1975 Kohler and Milstein provided an ingenious method for the production of monoclonal antibodies by fusion of myeloma cells with spleen cells from an immunized mouse. Designer Monoclonal Antibodies
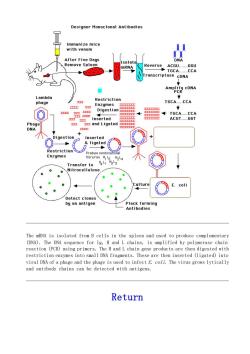
Designer Monoclonal Antibodies mice After Five Days emove Spleen ◆ CDNA Restriction ..CCA Enzymes Digestion 品 and Ligated Digestion Inserted Restriction Enzymes 124 Transfer to E.coli Detect clones by an antigen Ahi6ooging The mRNA is isolated from B cells in the spleen and used to produce complementary (DNA).The DNA sequence for Ig,H and L chains,is amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)using primers.The H and L chain gene products are then digested with restriction enzymes into small DNA fragments.These are then inserted(ligated)into viral DNA of a phage and the phage is used to infect E.coli.The virus grows lytically and antibody chains can be detected with antigens. Return
The mRNA is isolated from B cells in the spleen and used to produce complementary (DNA). The DNA sequence for Ig, H and L chains, is amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using primers. The H and L chain gene products are then digested with restriction enzymes into small DNA fragments. These are then inserted (ligated) into viral DNA of a phage and the phage is used to infect E. coli. The virus grows lytically and antibody chains can be detected with antigens. Return

This page is maintained by the Natural Toxins Research Center at Texas A&M University -Kingsville
This page is maintained by the Natural Toxins Research Center at Texas A&M University - Kingsville
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Introduction to Techniques in Immunology.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Humoral Response, Miguel Perez III.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Histocompatibility.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)ELISA技术.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)complement(有图).doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Complement.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Classes of Antibodies.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Cells, Tissue, and Organs of the Immune System.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Cells and Tissue of the Immune Response.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Cell Mediated Immunity.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Antibody Structure.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Antibody Production 2.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Antibody Production 1.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome 1.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome 2.doc
- 广东海洋大学:《动物免疫学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,完整讲稿,共十三章,主讲:徐春厚).ppt
- 中国农业出版社:《兽医免疫学》课程教学资源(书籍教材)兽医免疫学 veterinary immunology(PDF电子版,共二十五章,主编:崔治中、崔保安).pdf
- 广东海洋大学:《动物免疫学》授课教案(打印版)免疫学 Immunology(生物技术专业).pdf
- 广东海洋大学:《动物免疫学》授课教案(打印版)动物免疫学 Animal Immunology(动物医学专业).pdf
- 广东海洋大学:《动物免疫学》课程实验指导(打印版)动物免疫学实验指导(第二版).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Natural Killer Cells.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Nonspecific Immunity.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Secondary Lymphoid Organs of the Immune System.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)T and B cells 1.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)T and B cells 2.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)STUDY OF DISEASE AND PHYSIOLOGY IN THE 1979 HOMING STUDY HATCHERY STOCKS——A SUPPLEMENT TO - IMPRINTING SALMON AND STEELHEAD TROUT FOR HOMING, 1979 BY SLATICK, GILBREATH, AND WALCH.pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)免疫应答(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)免疫系统的细胞(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗体(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原处理过程(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原抗体结合(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原被淋巴细胞识别(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原递呈给淋巴细胞(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗微生物蛋白和肽(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体受体(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体激活的旁路途径(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体激活的末端途径(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体激活的经典途径(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体的检测法(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体缺陷性疾病(英文).pdf
