《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Secondary Lymphoid Organs of the Immune System

Secondary Lymphoid Organs of the Immune System Organs of the secondary lymphoid system are spleen,Adenoids,tonsils,peyer's patches of the gut,and appendix.The secondary lymphoid organs are where mature T and B cells have ethe bind antigen and undergo o fur he antigen dependen differentiation.The active immune response both cell mediated and humoral immunity begins.All of the secondary lymphoid organs are capable of trapping antigen which normally involves macrophages.These organs contain recirculating lymphocytes,which pass from the blood through the lymphoid tissues back to the blood,it virtually ensures that circulating antigen react with lymphocytes with the proper receptors The size of the lymphocyte pool suggest that there are lymphocytes available to fi any type of antigen. During the course of normal lymphocyte circulation,lymphocytes leave the blood and accumulate in lymphatic tissues,as if by a homing instinct,to set up B and T cell areas.Here they reside temporarily before returning to the circulation.The steadily input and output of e11 ong the lympho id organ: is dis ted ring a primary mmune response. Within 24 hours the antigen becomes localized in the lymph nodes and spleen and this depletes antigen-reactive cells from the circulating pool of lymphocytes.This temporary cessation of lymphocyte recirculation is called lymph node shutdown.Three day later,activated lymphocytes are released into the circulation.This delivers cells of the immune r onse (Band T cells)to tissu and blood stream.The B cell release antibodies and theTcell release lymphokines and antigen-specific effector T cells
Secondary Lymphoid Organs of the Immune System Organs of the secondary lymphoid system are spleen, Adenoids, tonsils, peyer's patches of the gut, and appendix. The secondary lymphoid organs are where mature T and B cells have the opportunity to bind antigen and undergo further antigen dependent differentiation. The active immune response both cell mediated and humoral immunity begins. All of the secondary lymphoid organs are capable of trapping antigen which normally involves macrophages. These organs contain recirculating lymphocytes, which pass from the blood through the lymphoid tissues back to the blood, it virtually ensures that circulating antigen react with lymphocytes with the proper receptors. The size of the lymphocyte pool suggest that there are lymphocytes available to fit any type of antigen. During the course of normal lymphocyte circulation, lymphocytes leave the blood and accumulate in lymphatic tissues, as if by a homing instinct, to set up B and T cell areas. Here they reside temporarily before returning to the circulation. The steadily input and output of cells among the lymphoid organs is disrupted during a primary immune response. Within 24 hours the antigen becomes localized in the lymph nodes and spleen and this depletes antigen-reactive cells from the circulating pool of lymphocytes. This temporary cessation of lymphocyte recirculation is called lymph node shutdown. Three day later, activated lymphocytes are released into the circulation. This delivers cells of the immune response (B and T cells) to tissue and blood stream. The B cell release antibodies and the T cell release lymphokines and antigen-specific effector T cells
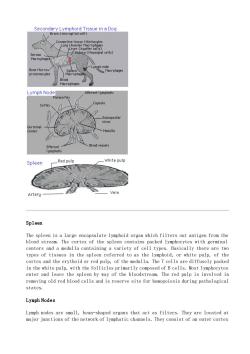
Connective tissue Histiocytes 11 one Mar rov Lymph Node Afferent lumphatic sul Cortex Spleer Red pul White pulp Artery Vein Spleen The sple is a large lymphoid rgn ich filters out antigen from the blood stream. s with germinal types of tissues in the spleen referred to as the lymphoid,or white pulp,of the cortex and the erythoid or red pulp,of the medulla.The T cells are diffusely packed in the white pulp.with the follicles primarily composed of b cells.Most ivmphocytes enter and leave the spleen by way of the bloodstream.The red pulp is involved in removing old red blood cells and is reserve site for hemopoiesis during pathological states. Lymph Nodes Lymph nodes are small,bean-shaped organs that act as filters.They are located at major junctions of the network of lymphatic channels.They consist of an outer cortex
Spleen The spleen is a large encapsulate lymphoid organ which filters out antigen from the blood stream. The cortex of the spleen contains packed lymphocytes with germinal centers and a medulla containing a variety of cell types. Basically there are two types of tissues in the spleen referred to as the lymphoid, or white pulp, of the cortex and the erythoid or red pulp, of the medulla. The T cells are diffusely packed in the white pulp, with the follicles primarily composed of B cells. Most lymphocytes enter and leave the spleen by way of the bloodstream. The red pulp is involved in removing old red blood cells and is reserve site for hemopoiesis during pathological states. Lymph Nodes Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs that act as filters. They are located at major junctions of the network of lymphatic channels. They consist of an outer cortex

and an inner medulla.If antigens enter the body via the respiratory or gastrointestinal tracts,they must pass through the lymph nodes. B cells and plasma cells are accumulated in subcapsular follicles,while T cells occupy space between them in the diffuse cortex. Return This page is maintained by the Natural Toxins Research Center at Texas A&M University -Kingsville
and an inner medulla. If antigens enter the body via the respiratory or gastrointestinal tracts, they must pass through the lymph nodes. B cells and plasma cells are accumulated in subcapsular follicles, while T cells occupy space between them in the diffuse cortex. Return This page is maintained by the Natural Toxins Research Center at Texas A&M University - Kingsville
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Nonspecific Immunity.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Natural Killer Cells.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Myeloma Proteins.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Introduction to Techniques in Immunology.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Humoral Response, Miguel Perez III.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Histocompatibility.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)ELISA技术.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)complement(有图).doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Complement.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Classes of Antibodies.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Cells, Tissue, and Organs of the Immune System.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Cells and Tissue of the Immune Response.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Cell Mediated Immunity.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Antibody Structure.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Antibody Production 2.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Antibody Production 1.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome 1.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome 2.doc
- 广东海洋大学:《动物免疫学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,完整讲稿,共十三章,主讲:徐春厚).ppt
- 中国农业出版社:《兽医免疫学》课程教学资源(书籍教材)兽医免疫学 veterinary immunology(PDF电子版,共二十五章,主编:崔治中、崔保安).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)T and B cells 1.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)T and B cells 2.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)STUDY OF DISEASE AND PHYSIOLOGY IN THE 1979 HOMING STUDY HATCHERY STOCKS——A SUPPLEMENT TO - IMPRINTING SALMON AND STEELHEAD TROUT FOR HOMING, 1979 BY SLATICK, GILBREATH, AND WALCH.pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)免疫应答(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)免疫系统的细胞(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗体(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原处理过程(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原抗体结合(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原被淋巴细胞识别(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原递呈给淋巴细胞(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗微生物蛋白和肽(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体受体(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体激活的旁路途径(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体激活的末端途径(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体激活的经典途径(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体的检测法(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体缺陷性疾病(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体调节蛋白(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体 Complement(英文)2.pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体 Complement(英文)1.pdf
