《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Nonspecific Immunity

Nonspecific Immunity Immunity is mediated by humoral and cellular effectors.Certain immune responses are antigen specific.They are provoked by unique determinants of the antigens and effectors produce antibodies or T cells which are antigen specific.This requires selection of effectors of appropriate specificity for clonal expansion before an effective response can be observed.In contrast,other imune responses can be evoked by infectious agents or injury in a generalized,antigen nonspecific manner.These responses are not induced by unique determinants.In addition,the effectors produced recognize conserved,rather than unique,determinants. Anti gen Speci fic and Anti gen nonspecific Immuni ty Antigen Specific Immunity Nonspecific Immunity Innate immunity Taesels T and B Cells not needed Antibodies and T cells and sp ecifically Rapidly evoked,generalized Activated defense and activated in a nonspecific manner
Nonspecific Immunity Immunity is mediated by humoral and cellular effectors. Certain immune responses are antigen specific. They are provoked by unique determinants of the antigens and effectors produce antibodies or T cells which are antigen specific. This requires selection of effectors of appropriate specificity for clonal expansion before an effective response can be observed. In contrast, other immune responses can be evoked by infectious agents or injury in a generalized, antigen nonspecific manner. These responses are not induced by unique determinants. In addition, the effectors produced recognize conserved, rather than unique, determinants
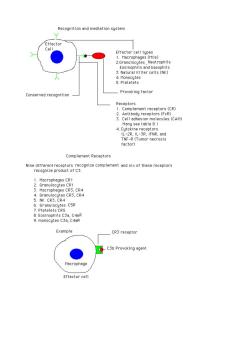
Recognition and mediation system Effecto cell tupe Macrophages(MOs) nd h 3.Netural Killer cells (NK) Conserved recognitio Provoking factor TNE-ST factor) Complement Receptors Nine different receptors recognize complement and six of these receptors recognize product of C3. 1.Macrophages CR1 Rca7, K L es CSR Example CR3 receptor C3b Provoking agent Macrophage Effector cell
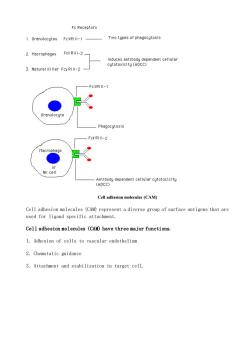
FcReceptors 1.Granulocytes FcYRIlI-1 Two types of phagocytosis 2.Macrophages FCY RIII-2_ aoi6nnty08ecterendentceluia 3.Natural Killer Fcy RIll-2 -FCYRIlI-1 Phagocytosis FcY RIII-2 Macrophage NK cell Cell adhesion molecules(CAM) Cell adhesion molecules(CAM)represent a diverse group of surface antigens that are used for ligand specific attachment. Cell adhesion molecules (CAM)have three major functions. 1.Adhesion of cells to vascular endothelium 2.Chemotatic guidance 3.Attachment and stabilization in target cell
Cell adhesion molecules (CAM) Cell adhesion molecules (CAM) represent a diverse group of surface antigens that are used for ligand specific attachment. Cell adhesion molecules (CAM) have three major functions. 1. Adhesion of cells to vascular endothelium 2. Chemotatic guidance 3. Attachment and stabilization in target cell
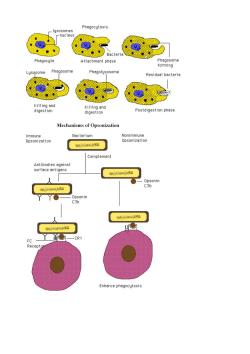
Phagocytosis lusosomes Attachment phase Phagosome forming Phagosome Phagolysosome Residual bacteria Killing and digestion Postdigestion phase Mechanisms of Opsonization mmune Bacterium Nonimmune Opsonization Opsonizatior 7】 Complement Opsonin Enhance phagocytosis
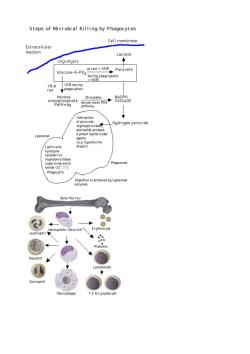
Steps of Microbial Killing by Phagocytes Cell membrane Lactate Glycolysis Glucose-6-PO, phago Stimulates _Hydrogen peroxide Phagosome h2atinisetieve时y1ygeo3somal Bone Marrov Basophil acrophage B Lymphocyte

Bone Marro Neutrophil P8gsororelgnndeadcene 3 dependent cellur 4.Rapid mobility in response to chemotatic migration Bone Marro Eosinophil 1234 ae9oAiapsenoeicptentia1s and can mediate ADCC 5.Histamine release
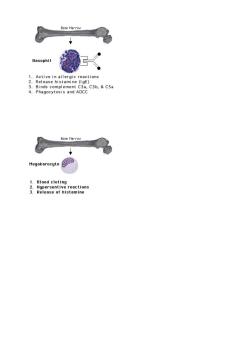
Bone Merrow ●】 Basophil Active in alleraic re i ons nagocytosis anc Bone Marrow 12 3.Release of histamine

Bone Merrow (FC.MHC. Inflammatory Responses 1.Redness (Increase blood flow)vessels dilate. 2.Heat (Increase blood flow)vesseks dilate. Transudate (0.2%protein) Exudate (5%protein) Serous exudate (no cells) Purulent exudate (rich in cells manily neutrophils) Hemorrhagic exudate (blood) Fibrinous exudate (fibrin) 3.Swelling (Increase vasular permeability) 4.Pain
Inflammatory Responses 1. Redness (Increase blood flow) vessels dilate. 2. Heat (Increase blood flow) vesseks dilate. Transudate (0.2% protein) Exudate (5% protein) Serous exudate (no cells) Purulent exudate (rich in cells manily neutrophils) Hemorrhagic exudate (blood) Fibrinous exudate (fibrin) 3. Swelling (Increase vasular permeability) 4. Pain
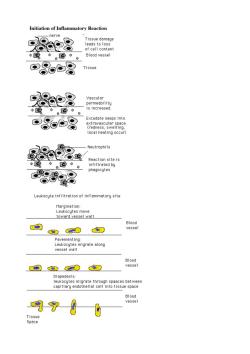
Initiation of Inflammatory Reaction nerve Tissue damage of cell content 减。。©。。 Blood vessel 8 Tissue 。。运9。 is increased Excudate seeps into local heating occur) Neutrophils Reaction site is 。。。 8 Leukocute infiltration of inflammatory site toward vessel wall C种0 羽 Bedl nigraotealong vessel wall od 60羽 Diapedesis: 8习美
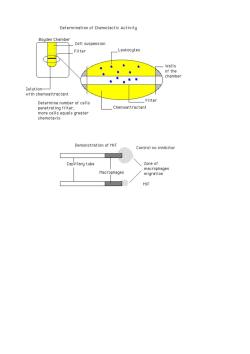
Determination of Chemotactic Activity Bouden Chamber Cell suspensior _Filter _Leukocytes Walls Determine number of cells penetrating filter: Demonstration of MIF Control no inhibitor Copiary tube macrophages ge: migration MIF
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Natural Killer Cells.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Myeloma Proteins.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Introduction to Techniques in Immunology.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Humoral Response, Miguel Perez III.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Histocompatibility.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)ELISA技术.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)complement(有图).doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Complement.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Classes of Antibodies.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Cells, Tissue, and Organs of the Immune System.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Cells and Tissue of the Immune Response.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Cell Mediated Immunity.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Antibody Structure.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Antibody Production 2.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Antibody Production 1.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome 1.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome 2.doc
- 广东海洋大学:《动物免疫学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,完整讲稿,共十三章,主讲:徐春厚).ppt
- 中国农业出版社:《兽医免疫学》课程教学资源(书籍教材)兽医免疫学 veterinary immunology(PDF电子版,共二十五章,主编:崔治中、崔保安).pdf
- 广东海洋大学:《动物免疫学》授课教案(打印版)免疫学 Immunology(生物技术专业).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Secondary Lymphoid Organs of the Immune System.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)T and B cells 1.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)T and B cells 2.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)STUDY OF DISEASE AND PHYSIOLOGY IN THE 1979 HOMING STUDY HATCHERY STOCKS——A SUPPLEMENT TO - IMPRINTING SALMON AND STEELHEAD TROUT FOR HOMING, 1979 BY SLATICK, GILBREATH, AND WALCH.pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)免疫应答(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)免疫系统的细胞(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗体(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原处理过程(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原抗体结合(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原被淋巴细胞识别(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原递呈给淋巴细胞(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗微生物蛋白和肽(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体受体(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体激活的旁路途径(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体激活的末端途径(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体激活的经典途径(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体的检测法(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体缺陷性疾病(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体调节蛋白(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体 Complement(英文)2.pdf
