电子科技大学:《高级宏观经济学 Advanced Macroeconomics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03b Diamond Model

ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS Lecture 3b Diamond Model 电子科大经管学院马捷
ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS Lecture 3b Diamond Model 电子科大经管学院 马捷 1

Contents ·Background Mathematical Framework ·Dynamics and Speed of Convergence Dynamic Inefficiency Golden Rules 电子科大经管学院马捷 2 元元元元
Contents Background Mathematical Framework Dynamics and Speed of Convergence Dynamic Inefficiency Golden Rules 电子科大经管学院 马捷 2

References David Romer's Advanced Macroeconomics Chapter 2,Part B ·Diamond,Peter(1965).“National debt in a neoclassical growth model." American Economic Review,55,pp. 1026-50. 2021/4/17 3
2021/4/17 3 References • David Romer's Advanced Macroeconomics Chapter 2, Part B • Diamond, Peter (1965). “National debt in a neoclassical growth model.” American Economic Review, 55, pp. 1026-50

Reflects of the debate on the Ricardian equivalence In the 1980s,US had run large budget deficits Traditional view:C~current income 'Budget deficits→C increases→Saving drop→ growth Ricardian Equiv:a shift from tax to bond finance has no influence on capital accumulation During recession periods,government often cut taxes.But if Ricardian equiv holds,these efforts are futile. It is important for us to know which view is closer to the fact. 2021/4/17
2021/4/17 4 In the 1980s, US had run large budget deficits • Traditional view: C~current income Budget deficits C increases Saving drop growth • Ricardian Equiv: a shift from tax to bond finance has no influence on capital accumulation During recession periods, government often cut taxes. But if Ricardian equiv holds, these efforts are futile. It is important for us to know which view is closer to the fact. Reflects of the debate on the Ricardian equivalence

Debate on the Ricardian equivalence Since the implications of the Ramsey model for public finance are so strong,it is worth pausing to consider which assumptions are essential. The debate has centered around Ricardian equivalence. 。Infinite horizon→Diamond's OG model Perfect capital markets>liquidity constraints are key assumptions underlying Ricardian equivalence 2021/4/17 5
2021/4/17 5 Debate on the Ricardian equivalence Since the implications of the Ramsey model for public finance are so strong, it is worth pausing to consider which assumptions are essential. The debate has centered around Ricardian equivalence. • Infinite horizon Diamond’s OG model • Perfect capital markets liquidity constraints are key assumptions underlying Ricardian equivalence

The Diamond Model Part 1: 1.Model environment 2.Consumption decision 3.Saving rate 2021/4/17 6
2021/4/17 6 The Diamond Model Part 1: 1. Model environment 2. Consumption decision 3. Saving rate
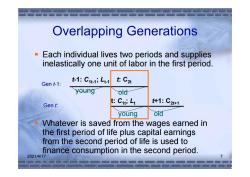
Overlapping Generations Each individual lives two periods and supplies inelastically one unit of labor in the first period. Gen t-1: t-1:C1t1;Lt1 t:C2t young old Gen t: t:Cuti Lt +1:C2t+1 young old Whatever is saved from the wages earned in the first period of life plus capital earnings from the second period of life is used to finance consumption in the second period. 2021/4/17
2021/4/17 7 Overlapping Generations Each individual lives two periods and supplies inelastically one unit of labor in the first period. Whatever is saved from the wages earned in the first period of life plus capital earnings from the second period of life is used to finance consumption in the second period. t-1: C1t-1; Lt-1 young old Gen t-1: t: C2t t: C1t; Lt young old Gen t: t+1: C2t+1

Overlapping Generations Agents live in two periods:working age, retirement C1,t=consumption of working agent in period t C2.t consumption of retired agent in period t S:=saving of working agent in period t R1=1+r+1=gross interest rate on savings held from period t to t+1 w,=period-t wage rate 2021/4/17 8
2021/4/17 8 Overlapping Generations Agents live in two periods: working age, retirement C1,t = consumption of working agent in period t C2,t = consumption of retired agent in period t St = saving of working agent in period t Rt+1 = 1+rt+1 = gross interest rate on savings held from period t to t+1 wt = period‐t wage rate

Preference: U,= 1 1-01+p1-0 CRRA coefficient:0>0,determines the willingness of a household to shift first-period consumption to the second period. the smaller is 0 the more willing is the household to shift consumption to gain utility, the higher is 0 the more risk-averse the household is which means she prefers to consume current income in the current period and would ask for a high return on savings before he shifts a small fraction of income. Time discount rate:p>-1 If p is greater(smaller)than zero the household places a greater (lower)weight on first period consumption than on second-period consumption 2021/4/17 9
2021/4/17 9 Preference: CRRA coefficient: θ>0, determines the willingness of a household to shift first-period consumption to the second period. • the smaller is θ the more willing is the household to shift consumption to gain utility, • the higher is θ the more risk-averse the household is which means she prefers to consume current income in the current period and would ask for a high return on savings before he shifts a small fraction of income. Time discount rate: > -1 • If is greater (smaller) than zero the household places a greater (lower) weight on first period consumption than on second-period consumption. 1 1 1 21 1 1 11 t t t C C U

CRTS production function Y=F(K AL) Exogenous constant growth of population,n. L people are born in period t,L=(1+n)L Exogenous constant growth rate of labor augmenting technical change: A,=(1+8)A1 where effective labor is 4,L 2021/4/17 10
2021/4/17 10 CRTS production function Exogenous constant growth of population, n. Lt people are born in period t, Lt = (1+n) Lt-1 Exogenous constant growth rate of labor augmenting technical change: At = (1+g) At-1 where effective labor is At Lt Yt=F(Kt, AtLt)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《高级宏观经济学 Advanced Macroeconomics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03a Ramsey Model.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高级宏观经济学 Advanced Macroeconomics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Solow-Swan Growth Model.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高级宏观经济学 Advanced Macroeconomics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 01 Introduction(马捷).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高级宏观经济学 Advanced Macroeconomics》课程教学资源(教学大纲).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)07 风险投资退出.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)06 投后管理协调.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)05 风险投资过程.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 创业企业估值.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)03 撰写商业计划.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)02 融资需求分析.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)01 认识创业企业.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(教学大纲).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《电子金融 Electronic Finance》课程教学资源(教学大纲).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际财务管理》课程教学资源(授课教案)第八讲 境外资金管理.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际财务管理》课程教学资源(授课教案)第六讲 跨国公司资本预算.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际财务管理》课程教学资源(授课教案)第七讲 全球融资管理.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际财务管理》课程教学资源(授课教案)第四讲 国际金融的平价条件.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际财务管理》课程教学资源(授课教案)第五讲 外汇风险管理.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际财务管理》课程教学资源(授课教案)第三讲 外币衍生金融工具.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《国际财务管理》课程教学资源(授课教案)第二讲 外汇市场(蒋屏).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高级宏观经济学 Advanced Macroeconomics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 New Growth Theory.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高级宏观经济学 Advanced Macroeconomics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Real Business Cycle Theory(RBC).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高级宏观经济学 Advanced Macroeconomics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Traditional Keynesian Theory.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高级宏观经济学 Advanced Macroeconomics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 07 Micro Foundations of Incomplete Nominal Adjustment.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高级宏观经济学 Advanced Macroeconomics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 08 Consumption.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高级宏观经济学 Advanced Macroeconomics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 09 Investment.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)01 认识创业企业.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)02 融资需求分析.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)03 撰写商业计划.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 创业企业估值.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)05 风险投资过程.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)06 投后管理协调.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《风险投资与创业融资 Venture Capital and the Financing of Entrepreneurship》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)07 风险投资退出.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《应用随机过程 Applied Stochastic Processes》课程教学资源(教学大纲).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《应用随机过程 Applied Stochastic Processes》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 课程导论(吴卫星、邓军).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《应用随机过程 Applied Stochastic Processes》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 随机过程定义和分类(随机过程的基本概念与类型).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《应用随机过程 Applied Stochastic Processes》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 随机过程的概率论基础.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《应用随机过程 Applied Stochastic Processes》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 泊松过程(Poisson过程).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《应用随机过程 Applied Stochastic Processes》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 Brown布朗运动(维纳过程).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《应用随机过程 Applied Stochastic Processes》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 鞅 Martingale.pdf
