上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec2

CS3101-3 Programming Language-Java Fall 2004 Sept.22
CS3101-3 Programming Language – Java Fall 2004 Sept. 22

Road map today ●Brief review ●Details of class OConstructor Othis reference OInheritance OOverloading ODynamic binding ●Interface ●Exceptions
Road map today lBrief review lDetails of class ¡Constructor ¡this reference ¡Inheritance ¡Overloading ¡Dynamic binding lInterface lExceptions

What is Java OA programming language OA virtual machine JVM OA runtime environment -JRE OPredefined libraries ●Portable,but slow OInterpreter OJIT helps
What is Java lA programming language lA virtual machine – JVM lA runtime environment – JRE ¡Predefined libraries lPortable, but slow ¡Interpreter ¡JIT helps

Object and class ●A class is a blueprint OAn object is an instance created from that blueprint DAll objects of the same class have the same set of attributes OEvery Person object have name,weight,height o But different value for those attributes Oke.name=Ke Wang,sal.name=Sal Stolfo
Object and class lA class is a blueprint lAn object is an instance created from that blueprint lAll objects of the same class have the same set of attributes ¡Every Person object have name, weight, height lBut different value for those attributes ¡ke.name=Ke Wang, sal.name=Sal Stolfo
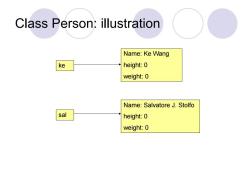
Class Person:illustration Name:Ke Wang ke height:0 weight:0 Name:Salvatore J.Stolfo sal height:0 weight:0
Class Person: illustration Name: Ke Wang height: 0 weight: 0 Name: Salvatore J. Stolfo height: 0 weight: 0 ke sal

Reference Person ke; //only created the reference,not an object. It points to nothing now(null). ke new Person(); //create the object (allocate storage in memory),and ke is initialized. ke.name=“Ke Wang”; //access the object through the reference Can have multiple reference to one object No reference means the object is inaccessible forever goes to garbage collector
Reference Person ke; //only created the reference, not an object. It points to nothing now (null). ke = new Person(); //create the object (allocate storage in memory), and ke is initialized. ke.name=“Ke Wang”; //access the object through the reference Can have multiple reference to one object No reference means the object is inaccessible forever – goes to garbage collector
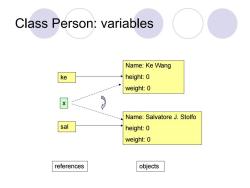
Class Person:variables Name:Ke Wang ke height:0 weight:0 Name:Salvatore J.Stolfo sal height:0 weight:0 references objects
Class Person: variables Name: Ke Wang height: 0 weight: 0 Name: Salvatore J. Stolfo height: 0 weight: 0 ke sal x references objects

Visibility of fields and methods Generally make fields private and provide public getField()and setField()accessor functions O-O term:encapsulation o Private fields and methods cannot be accessed from outside of the class
Visibility of fields and methods lGenerally make fields private and provide public getField() and setField() accessor functions lO-O term: encapsulation lPrivate fields and methods cannot be accessed from outside of the class

Static vs.non-static oStatic:class variable/method o Non-static:instance variable/method Static ones are associated with class,not object.Can be called using class name directly ●main()is static OEven though it's in a class definition,no instance of the class exist when main starts executing
Static vs. non-static lStatic: class variable/method lNon-static: instance variable/method lStatic ones are associated with class, not object. Can be called using class name directly lmain() is static ¡Even though it’s in a class definition, no instance of the class exist when main starts executing

Static vs.non-static (cont. o Instance fields define an object;the values of those fields make one object distinct from another o Instance method operates on an instance of a class (object)instead of operating on the class itself. o Class methods can only use class fields; while instance methods can use both instance fields and class fields
Static vs. non-static (cont.) lInstance fields define an object; the values of those fields make one object distinct from another lInstance method operates on an instance of a class (object) instead of operating on the class itself. lClass methods can only use class fields; while instance methods can use both instance fields and class fields
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec1.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java Introduction.docx
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-thread.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-OPERATING SYSTEMS(LINUX SYSTEM CALLS).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-semaphore EXERCISES.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec8.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec7.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec6.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec5.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec4.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Process Synchronization_Lec14.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Process Synchronization_Lec13.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Process Synchronization_Lec12.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec24_Review.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec24_DISK MANAGEMENT AND I/O.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec23_file system implementation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec22_file system implementation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec21_file system interface.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec20_virtual memory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec19_virtual memory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec3.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec4.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec5.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java Primer.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java多线程应用实例(制作烟花效果).doc
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java多线程编程.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)JAVA多线程编程详解(详细操作例子).doc
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java学习笔记(JAVA的面向对象编程——课堂笔记).doc
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料_管程.docx
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料_往年试卷.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture01.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture02.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture03 CONDITIONALS AND SEQUENCES Strings, lists and file objects.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture04 MODULAR PROGRAMMING Functions.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture05 ITERATION Control Structure.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture06 OBJECTS AND GRAPHICS GUI.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture07 OBJECT ORIENTED DEVELOPMENT Class and Object.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture08 DATA COLLECTION Massive data representation and processing.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture09 SIMULATION AND DESIGN Real-world problem.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture10 ALGORITHM DESIGN AND ANALYSIS To the Classic.pdf
