上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture08 DATA COLLECTION Massive data representation and processing

上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Computational Thinking and Approach Lecture 8 Dr.Jialiang LU Jialiang.lu@situ.edu.cn
Computational Thinking and Approach Lecture 8 Dr. Jialiang LU Jialiang.lu@sjtu.edu.cn

上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Massive data representation and processing DATA COLLECTION
DATA COLLECTION Massive data representation and processing

上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Examples of data collection: Simple Statistics 。 Many programs deal with large collections of similar information. Words in a document Students in a course Data from an experiment Customers of a business Graphics objects drawn on the screen Cards in a deck 3
Examples of data collection: Simple Statistics • Many programs deal with large collections of similar information. – Words in a document – Students in a course – Data from an experiment – Customers of a business – Graphics objects drawn on the screen – Cards in a deck 3

上游充通大粤 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Sample Problem: Simple Statistics Let's review our code of average: average4.py 井 A program to average a set of numbers # Illustrates sentinel loop using empty string as sentinel def main(): sum 0.0 count =0 xStr raw input ("Enter a number (to quit)>>" while xStr!="": x eval(xStr) sumsum x count count 1 xStr raw input ("Enter a number (to quit)>>" print "\nThe average of the numbers is",sum count main ( 4
Sample Problem: Simple Statistics Let‟s review our code of average: # average4.py # A program to average a set of numbers # Illustrates sentinel loop using empty string as sentinel def main(): sum = 0.0 count = 0 xStr = raw_input("Enter a number ( to quit) >> ") while xStr != "": x = eval(xStr) sum = sum + x count = count + 1 xStr = raw_input("Enter a number ( to quit) >> ") print "\nThe average of the numbers is", sum / count main() 4

上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Sample Problem: Simple Statistics This program allows the user to enter a sequence of numbers,but the program itself doesn't keep track of the numbers that were entered it only keeps a running total. Suppose we want to extend the program to compute not only the mean,but also the median and standard deviation. 5
Sample Problem: Simple Statistics • This program allows the user to enter a sequence of numbers, but the program itself doesn‟t keep track of the numbers that were entered – it only keeps a running total. • Suppose we want to extend the program to compute not only the mean, but also the median and standard deviation. 5

上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Sample Problem: Simple Statistics The median is the data value that splits the data into equal-sized parts. For the data 2,4,6,9,13,the median is 6, since there are two values greater than 6 and two values that are smaller. One way to determine the median is to store all the numbers,sort them,and identify the middle value. 6
Sample Problem: Simple Statistics • The median is the data value that splits the data into equal-sized parts. • For the data 2, 4, 6, 9, 13, the median is 6, since there are two values greater than 6 and two values that are smaller. • One way to determine the median is to store all the numbers, sort them, and identify the middle value. 6

上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Sample Problem: Simple Statistics The standard deviation is a measure of how spread out the data is relative to the mean. If the data is tightly clustered around the mean, then the standard deviation is small.If the data is more spread out,the standard deviation is larger. The standard deviation is a yardstick to measure/express how exceptional the data is. 7
Sample Problem: Simple Statistics • The standard deviation is a measure of how spread out the data is relative to the mean. • If the data is tightly clustered around the mean, then the standard deviation is small. If the data is more spread out, the standard deviation is larger. • The standard deviation is a yardstick to measure/express how exceptional the data is. 7
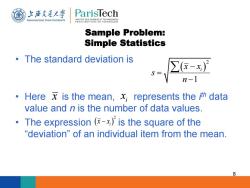
上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Sample Problem: Simple Statistics The standard deviation is 2 Here x is the mean,x represents the ith data value and n is the number of data values. The expression (-x)is the square of the "deviation of an individual item from the mean. 8
Sample Problem: Simple Statistics • The standard deviation is • Here is the mean, represents the i th data value and n is the number of data values. • The expression is the square of the “deviation” of an individual item from the mean. 8 2 1 i x x s n x i x 2 i x x

上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Sample Problem: Simple Statistics The numerator is the sum of these squared “deviations”across all the data. Suppose our data was 2,4,6,9,and 13. The mean is 6.8 The numerator of the standard deviation is (6.8-2)}+(6.8-4)2+(6.8-6)}2+(6.8-9)2+(6.8-13)°=149.6 s9574-61 9
Sample Problem: Simple Statistics • The numerator is the sum of these squared “deviations” across all the data. • Suppose our data was 2, 4, 6, 9, and 13. – The mean is 6.8 – The numerator of the standard deviation is 9 2 2 2 2 2 6.8 2 6.8 4 6.8 6 6.8 9 6.8 13 149.6 149.6 37.4 6.11 5 1 s

上游充通大 ParisTech SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY INSTITUT DES SCIENCES ET TECHNOLOGIES PARIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Sample Problem: Simple Statistics As you can see,calculating the standard deviation not only requires the mean (which can't be calculated until all the data is entered), but also each individual data element! We need some way to remember these values as they are entered. 10
Sample Problem: Simple Statistics • As you can see, calculating the standard deviation not only requires the mean (which can‟t be calculated until all the data is entered), but also each individual data element! • We need some way to remember these values as they are entered. 10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture07 OBJECT ORIENTED DEVELOPMENT Class and Object.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture06 OBJECTS AND GRAPHICS GUI.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture05 ITERATION Control Structure.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture04 MODULAR PROGRAMMING Functions.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture03 CONDITIONALS AND SEQUENCES Strings, lists and file objects.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture02.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture01.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料_往年试卷.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料_管程.docx
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java学习笔记(JAVA的面向对象编程——课堂笔记).doc
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)JAVA多线程编程详解(详细操作例子).doc
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java多线程编程.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java多线程应用实例(制作烟花效果).doc
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java Primer.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec5.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec4.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec3.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec2.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec1.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java Introduction.docx
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture09 SIMULATION AND DESIGN Real-world problem.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture10 ALGORITHM DESIGN AND ANALYSIS To the Classic.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Computational Thinking and Approach》教学资源(课件讲稿)Something You Should Know.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(学习资料)C++练习(题目).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(学习资料)C++练习(答案).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(学习资料)基于MFC的对话框程序.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)总复习(共八讲).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(讲稿)第1讲 C++语言概述及数据类型(何其昌).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(讲稿)第2讲 C++程序的流程控制.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(讲稿)第3讲 函数与结构化程序设计.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(讲稿)第4讲 数组与结构.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(讲稿)第5讲 指针与引用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(讲稿)第6讲 C++类(1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(讲稿)第7讲 C++类(2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(讲稿)第8讲 Windows应用程序设计.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(讲义)方波生成器项目报告书.doc
- 《中文信息学报》:中文组织机构名称与简称的识别.pdf
- 《计算机系统结构》课程教学资源(电子书籍)《Computer Organization and Design》THE HARDWARE / SOFTWARE INTERFACE(DAVID A. PATTERSON JOHN L. HENNESSY,Fourth Edtion,彩色版).pdf
- 《计算机系统结构》课程教学资源(电子书籍)《Computer Systems》A Programmer's Perspective(Randal E. Bryant、David R. O'Hallaron,THIRD EDITION).pdf
- 机械工业出版社:计算机科学丛书《计算机组成与设计:硬件、软件接口》电子教材(中文第4版).pdf
