上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec4

OPERATING SYSTEMS 1 龚玲 lgong@sjtu.edu.cn
OPERATING SYSTEMS 龚玲 lgong@sjtu.edu.cn 1

REVIEW o Interrupt o Dual Mode o System Calls vs.APIs o Multiprogramming/Concurrency ohttp://wenku.baidu.com/course/study/77fldcccda38376ba flfae94#665ea0c7aa00b52acfc7ca94
REVIEW Interrupt Dual Mode System Calls vs. APIs Multiprogramming/Concurrency http://wenku.baidu.com/course/study/77f1dcccda38376ba f1fae94#665ea0c7aa00b52acfc7ca94
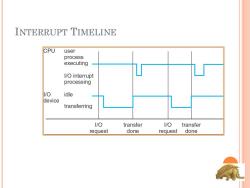
INTERRUPT TIMELINE CPU user process executing L I/O interrupt processing l/O idle device transferring 1/0 transfer V/O transfer request done request done
INTERRUPT TIMELINE

COMMON FUNCTIONS OF INTERRUPTS o Interrupt transfers control to the interrupt service routine generally,through the interrupt vector, which contains the addresses of all the service routines. o Interrupt architecture must save the address of the interrupted instruction. o Incoming interrupts are disabled while another interrupt is being processed to prevent a lost interrupt. o A trap is a software-generated interrupt caused either by an error or a user request. o An operating system is interrupt driven
COMMON FUNCTIONS OF INTERRUPTS Interrupt transfers control to the interrupt service routine generally, through the interrupt vector, which contains the addresses of all the service routines. Interrupt architecture must save the address of the interrupted instruction. Incoming interrupts are disabled while another interrupt is being processed to prevent a lost interrupt. A trap is a software-generated interrupt caused either by an error or a user request. An operating system is interrupt driven

OPERATING-SYSTEM OPERATIONS o Interrupt driven by hardware o Software error or request creates exception or trap Division by zero,request for operating system service o Other process problems include infinite loop, processes modifying each other or the operating system
OPERATING-SYSTEM OPERATIONS Interrupt driven by hardware Software error or request creates exception or trap Division by zero, request for operating system service Other process problems include infinite loop, processes modifying each other or the operating system
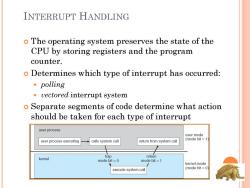
INTERRUPT HANDLING o The operating system preserves the state of the CPU by storing registers and the program counter. o Determines which type of interrupt has occurred: ·polling vectored interrupt system o Separate segments of code determine what action should be taken for each type of interrupt user process user mode user process executing calls system call return from system call (mode bit=1) kernel trap return mode bit =0 mode bit =1 kernel mode execute system call (mode bit =0)
INTERRUPT HANDLING The operating system preserves the state of the CPU by storing registers and the program counter. Determines which type of interrupt has occurred: polling vectored interrupt system Separate segments of code determine what action should be taken for each type of interrupt

OPERATING SYSTEM STRUCTURE o Multiprogramming needed for efficiency Single user cannot keep CPU and I/O devices busy at all times Multiprogramming organizes jobs (code and data)so CPU always has one to execute A subset of total jobs in system is kept in memory One job selected and run via job scheduling When it has to wait (for I/O for example),OS switches to another job
OPERATING SYSTEM STRUCTURE Multiprogramming needed for efficiency Single user cannot keep CPU and I/O devices busy at all times Multiprogramming organizes jobs (code and data) so CPU always has one to execute A subset of total jobs in system is kept in memory One job selected and run via job scheduling When it has to wait (for I/O for example), OS switches to another job
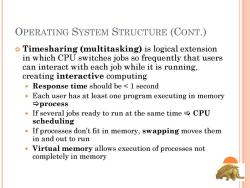
OPERATING SYSTEM STRUCTURE (CONT.) Timesharing (multitasking)is logical extension in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing Response time should be 1 second Each user has at least one program executing in memory →process If several jobs ready to run at the same timeCPU scheduling If processes don't fit in memory,swapping moves them in and out to run Virtual memory allows execution of processes not completely in memory
OPERATING SYSTEM STRUCTURE (CONT.) Timesharing (multitasking) is logical extension in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing Response time should be < 1 second Each user has at least one program executing in memory process If several jobs ready to run at the same time CPU scheduling If processes don’t fit in memory, swapping moves them in and out to run Virtual memory allows execution of processes not completely in memory
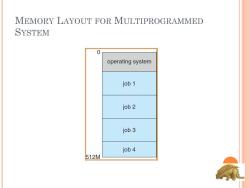
MEMORY LAYOUT FOR MULTIPROGRAMMED SYSTEM 0 operating system job 1 job2 job 3 job 4 512M
MEMORY LAYOUT FOR MULTIPROGRAMMED SYSTEM

CONCURRENCY o What problem does concurrent mechanism solve? o Why use concurrent mechanism?
CONCURRENCY What problem does concurrent mechanism solve? Why use concurrent mechanism?
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Process Synchronization_Lec14.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Process Synchronization_Lec13.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Process Synchronization_Lec12.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec24_Review.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec24_DISK MANAGEMENT AND I/O.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec23_file system implementation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec22_file system implementation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec21_file system interface.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec20_virtual memory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec19_virtual memory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec18_mainmemory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec17_mainmemory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec16_mainmemory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Introduction_Lec3.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Introduction_Lec2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Introduction_Lec1.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-deadlock_Lec15.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-cpuscheduling_Lec11.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-cpuscheduling_Lec10.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2讲 C++语言的基本数据类型与表达式.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec5.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec6.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec7.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec8.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-semaphore EXERCISES.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-OPERATING SYSTEMS(LINUX SYSTEM CALLS).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-thread.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java Introduction.docx
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec1.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec2.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec3.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec4.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(JAVA PPT)lec5.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java Primer.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java多线程应用实例(制作烟花效果).doc
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java多线程编程.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)JAVA多线程编程详解(详细操作例子).doc
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java学习笔记(JAVA的面向对象编程——课堂笔记).doc
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料_管程.docx
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料_往年试卷.pdf
