上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec17_mainmemory

CHAPTER 8:MAIN MEMORY
CHAPTER 8: MAIN MEMORY

CHAPTER 8:MEmory mAnagement o Background o Swapping o Contiguous Memory allocation o Paging o Structure of the Page Table o Segmentation o Example:The Intel Pentium
CHAPTER 8: MEMORY MANAGEMENT Background Swapping Contiguous Memory Allocation Paging Structure of the Page Table Segmentation Example: The Intel Pentium

REVIEW o Protection o Address binding ·Static ·Dynamic o Memory Management ·Partition o fixed o variable
REVIEW Protection Address binding Static Dynamic Memory Management Partition fixed variable http://wenku.baidu.com/course/study/77f1dcccda38376ba f1fae94#665ea0c7aa00b52acfc7ca94

MULTISTEP PROCESSING OF A USER PROGRAM source program compiler or compile assembler time object module other object modules linkage editor load load module time system library loader dynamically loaded system library in-memory binary executio dynamic linking time (run memory image time)
MULTISTEP PROCESSING OF A USER PROGRAM

DYNAMIC LOADING o Routine is not loaded until it is called o Better memory-space utilization;unused routine is never loaded o Useful when large amounts of code are needed to handle infrequently occurring cases o No special support from the operating system is required implemented through program design
DYNAMIC LOADING Routine is not loaded until it is called Better memory-space utilization; unused routine is never loaded Useful when large amounts of code are needed to handle infrequently occurring cases No special support from the operating system is required implemented through program design

DYNAMIC LINKING o Linking postponed until execution time o Small piece of code,stub,used to locate the appropriate memory-resident library routine o Stub replaces itself with the address of the routine,and executes the routine o Operating system needed to check if routine is in processes'memory address o Dynamic linking is particularly useful for libraries o System also known as shared libraries
DYNAMIC LINKING Linking postponed until execution time Small piece of code, stub, used to locate the appropriate memory-resident library routine Stub replaces itself with the address of the routine, and executes the routine Operating system needed to check if routine is in processes’ memory address Dynamic linking is particularly useful for libraries System also known as shared libraries

SWAPPING A process can be swapped temporarily out of memory to a backing store,and then brought back into memory for continued execution o Backing store-fast disk large enough to accommodate copies of all memory images for all users;must provide direct access to these memory images o Roll out,roll in-swapping variant used for priority-based scheduling algorithms;lower-priority process is swapped out so higher-priority process can be loaded and executed 0 Major part of swap time is transfer time;total transfer time is directly proportional to the amount of memory swapped 0 Modified versions of swapping are found on many systems (i.e., UNIX,Linux,and Windows) o System maintains a ready queue of ready-to-run processes which have memory images on disk
SWAPPING A process can be swapped temporarily out of memory to a backing store, and then brought back into memory for continued execution Backing store – fast disk large enough to accommodate copies of all memory images for all users; must provide direct access to these memory images Roll out, roll in – swapping variant used for priority-based scheduling algorithms; lower-priority process is swapped out so higher-priority process can be loaded and executed Major part of swap time is transfer time; total transfer time is directly proportional to the amount of memory swapped Modified versions of swapping are found on many systems (i.e., UNIX, Linux, and Windows) System maintains a ready queue of ready-to-run processes which have memory images on disk
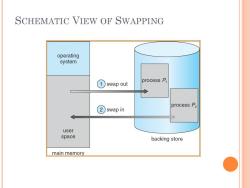
SCHEMATIC VIEW OF SWAPPING operating system process P swap out process P2 2) swap in user space backing store main memory
SCHEMATIC VIEW OF SWAPPING

CONTIGUOUS ALLOCATION o Main memory usually into two partitions: Resident operating system,usually held in low memory with interrupt vector User processes then held in high memory o Relocation registers used to protect user processes from each other,and from changing operating-system code and data Base register contains value of smallest physical address Limit register contains range of logical addresses- each logical address must be less than the limit register MMU maps logical address dynamically
CONTIGUOUS ALLOCATION Main memory usually into two partitions: Resident operating system, usually held in low memory with interrupt vector User processes then held in high memory Relocation registers used to protect user processes from each other, and from changing operating-system code and data Base register contains value of smallest physical address Limit register contains range of logical addresses – each logical address must be less than the limit register MMU maps logical address dynamically

CONTIGUOUS ALLOCATION (CONT. o Multiple-partition allocation Hole-block of available memory;holes of various size are scattered throughout memory When a process arrives,it is allocated memory from a hole large enough to accommodate it Operating system maintains information about: a)allocated partitions b)free partitions (hole) oS os os os process 5 process 5 process 5 process 5 process 9 process 9 process 8 process 10 process 2 process 2 process 2 process 2
CONTIGUOUS ALLOCATION (CONT.) Multiple-partition allocation Hole – block of available memory; holes of various size are scattered throughout memory When a process arrives, it is allocated memory from a hole large enough to accommodate it Operating system maintains information about: a) allocated partitions b) free partitions (hole) OS process 5 process 8 process 2 OS process 5 process 2 OS process 5 process 2 OS process 5 process 9 process 2 process 9 process 10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec16_mainmemory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Introduction_Lec3.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Introduction_Lec2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Introduction_Lec1.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-deadlock_Lec15.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-cpuscheduling_Lec11.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-cpuscheduling_Lec10.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2讲 C++语言的基本数据类型与表达式.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《C++程序设计与实践》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1讲 绪论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源《面向对象软件工程实践指南》教材资料(WORD版).docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)面向对象软件工程实践指南-2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)小组作业5-最终交付.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)小组作业4.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)小组作业3.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)小组作业2.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)小组作业1.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)5.Test&Deploy&Close_软件验收报告.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)5.Test&Deploy&Close_软件项目总结报告.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)5.Test&Deploy&Close_软件测试计划.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)5.Test&Deploy&Close_软件测试总结报告.docx
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec18_mainmemory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec19_virtual memory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec20_virtual memory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec21_file system interface.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec22_file system implementation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec23_file system implementation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec24_DISK MANAGEMENT AND I/O.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Lec24_Review.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Process Synchronization_Lec12.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Process Synchronization_Lec13.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-Process Synchronization_Lec14.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec4.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec5.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec6.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec7.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-process_Lec8.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-semaphore EXERCISES.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-OPERATING SYSTEMS(LINUX SYSTEM CALLS).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)OS-thread.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《操作系统 Operating System》课程教学资料(Java)Java Introduction.docx
