《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)EM application Magnetoquasistatic Forces
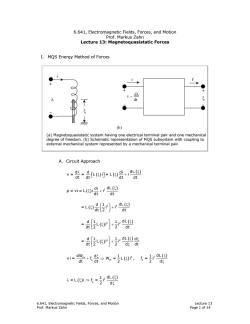
6.641,Electromagnetic Fields,Forces,and Motion Prof.Markus Zahn Lecture 13:Magnetoquasistatic Forces I.MQS Energy Method of Forces V= dx dt (b) (a)Magnetoquasistatic system having one electrical terminal pair and one mechanical degree of freedom.(b)Schematic representation of MQS subsystem with coupling to external mechanical system represented by a mechanical terminal pair. A.Circuit Approach v-0-品(0-L(e+9 dt p=i=L()+包 dt -L6{ =2(r小r9 =2ge i-0+5w=(0P,专=图 dt d =L=5-围 、d 6.641,Electromagnetic Fields,Forces,and Motion Lecture 13 Prof.Markus Zahn Page 1 of 14
6.641, Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Lecture 13 Prof. Markus Zahn Page 1 of 14 6.641, Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Prof. Markus Zahn Lecture 13: Magnetoquasistatic Forces I. MQS Energy Method of Forces A. Circuit Approach () () λ (ξ) ⎡ ⎤ ξ ξ+ ⎣ ⎦ d d di dL v= = L i =L i dt dt dt dt ( ) (ξ) ξ + 2 di dL p = vi = L i i dt dt ( ) ( ) 2 2 d 1 dL =L i i dt 2 dt ⎛ ⎞ ξ ξ + ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ⎠ ( ) ( ) 2 2 d1 1 dL = Li i dt 2 2 dt ⎡ ⎤ ξ ξ + ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ ⎦ ( ) ( ) 2 2 d1 1 d dL = Li i dt 2 2 d dt ⎡ ⎤ ξ ξ ξ + ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ ⎦ ξ ( ) ( ) m 2 2 m dW d1 1 dL vi= f W = L i , f = i dt dt 2 2 d ξ ξ ξ ξ +⇒ ξ ξ ( ) ( ) ξ ξ λ ξ⇒ ξ 2 1 dL =L i f = i 2 d
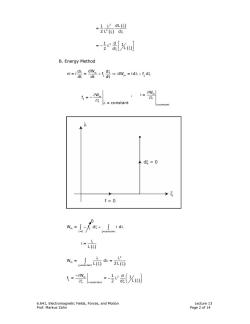
河想 =-品{Xl B.Energy Method vi.idds aWm i=o a形 01 λ=constant =constant 本d战=0 →5 f=0 w.ds ∫id -cons tant 1=L 入 w府=z λ2 5-w/ ah=constant -(e 6.641,Electromagnetic Fields,Forces,and Motion Lecture 13 Prof.Markus Zahn Page 2 of 14
6.641, Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Lecture 13 Prof. Markus Zahn Page 2 of 14 ( ) ( ) 2 2 1 dL = 2 d L λ ξ ξ ξ ( ) = 1 d 2 1 2 d L ⎡ ⎤ − λ ⎢ ⎥ ξ ξ ⎣ ⎦ B. Energy Method ξ ξ λ ξ + ⇒ λ− ξ m m d d dW vi = i = f dW = id f d dt dt dt m m =constant W W , i= f = = constant ξ ξ ∂ ∂ − ∂λ ∂ξ λ 0 ξ λ= ξ= − ξ+ λ m ∫ ∫ 0 cons tan t W = f d id ( ) i = L λ ξ ( ) ( ) ξ = λ λ λ ξ ξ ∫ 2 m cons tan t W= d= L 2L ( ) m 2 cons tan t W 1 d f= = 1 2 d L ξ λ = −∂ ⎛ ⎞ − λ ⎜ ⎟ ∂ξ ξ ξ ⎝ ⎠
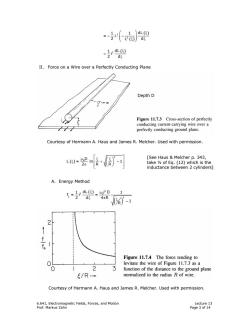
1 dL() d II.Force on a Wire over a Perfectly Conducting Plane Depth D 00 Figure 11.7.3 Cross-section of perfectly conducting current-carrying wire over a perfectly conducting ground plane. Courtesy of Hermann A.Haus and James R.Melcher.Used with permission. [See Haus Melcher p.343, take 12 of Eq.(12)which is the inductance between 2 cylinders] A.Energy Method 专r但0 1 de 4πR )-1 f。 Figure 11.7.4 The force tending to levitate the wire of Figure 11.7.3 as a 2 3 function of the distance to the ground plane ξ/R- normalized to the radius R of wire. Courtesy of Hermann A.Haus and James R.Melcher.Used with permission. 6.641,Electromagnetic Fields,Forces,and Motion Lecture 13 Prof.Markus Zahn Page 3 of 14
6.641, Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Lecture 13 Prof. Markus Zahn Page 3 of 14 ( ) ( ) 2 2 1 1 dL = 2 d L ⎛ ⎞ ξ −λ−⎜ ⎟ ξ ξ ⎝ ⎠ ( ) 2 1 dL i 2 d ξ = ξ II. Force on a Wire over a Perfectly Conducting Plane Courtesy of Hermann A. Haus and James R. Melcher. Used with permission. ( ) 2 0D L = ln 1 2 RR ⎡ ⎤ µ ξ ξ ⎛ ⎞ ξ +− ⎢ ⎥ ⎜ ⎟ π ⎝ ⎠ ⎣ ⎦ A. Energy Method ( ) ( ) 2 2 0 2 1 1 dL i D f= i = 2 d 4R 1 R ξ ξ µ ξ π ξ − [See Haus & Melcher p. 343, take ½ of Eq. (12) which is the inductance between 2 cylinders] Courtesy of Hermann A. Haus and James R. Melcher. Used with permission. Depth D
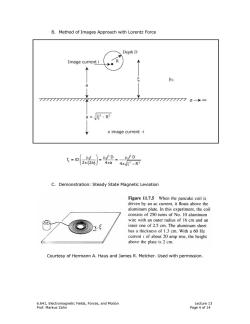
B.Method of Images Approach with Lorentz Force Depth D Image current i R ● 个 o 7777777777777777777777777777 777777777777777∞ 2-R2 x image current-i f iD oi) =2D-2D 2π(2a) 4πa 4π√g2-R2 C.Demonstration:Steady State Magnetic Leviation Figure 11.7.5 When the pancake coil is driven by an ac current,it floats above the aluminum plate.In this experiment,the coil consists of 250 turns of No.10 aluminum wire with an outer radius of 16 cm and an inner one of 2.5 cm.The aluminum sheet has a thickness of 1.3 cm.With a 60 Hz current i of about 20 amp rms.the height above the plate is 2 cm. Courtesy of Hermann A.Haus and James R.Melcher.Used with permission. 6.641,Electromagnetic Fields,Forces,and Motion Lecture 13 Prof.Markus Zahn Page 4 of 14
6.641, Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Lecture 13 Prof. Markus Zahn Page 4 of 14 B. Method of Images Approach with Lorentz Force ( ) 2 2 00 0 2 2 i iD iD f = iD = = 2 2a 4 a 4 R ξ ⎛ ⎞ µµ µ ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ⎠ π π πξ− C. Demonstration: Steady State Magnetic Leviation Courtesy of Hermann A. Haus and James R. Melcher. Used with permission
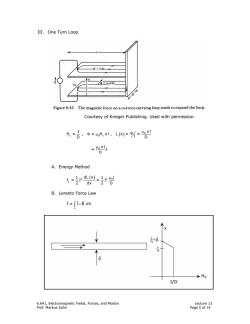
III.One Turn Loop K=I/D- B=LoI/D. Figure 6-35 The magnetic force on a current-carrying loop tends to expand the loop. Courtesy of Krieger Publishing.Used with permission. H=6,=Hx1,L)=%= D HoxlI D A.Energy Method 专rA-r时 dx 2 D B.Lorentz Force Law f=∫JxB dV 5+8 →H2 I/D 6.641,Electromagnetic Fields,Forces,and Motion Lecture 13 Prof.Markus Zahn Page 5 of 14
6.641, Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Lecture 13 Prof. Markus Zahn Page 5 of 14 III. One Turn Loop Courtesy of Krieger Publishing. Used with permission. ( ) µ Φ µ Φ 0 z 0z I x l H = , = H xl , L x = = D D I µ0 x l = I D A. Energy Method ( ) 2 2 0 x 1 1 dL x l f= I = I 2 dx 2 D µ B. Lorentz Force Law V f = J B dV × ∫

Model srace currenKs volume current of small thickness I Jy=D8 xH=j→股=-小,=→片=5x-(传+训 I f.H dx dy dz -器}k-e+ax ÷号-6时+ ++号+的 12 comes from integrating uniform volume current over small thickness 8 General formula:f=[KxBav ds 0 For our case:B= B2+B业= 2 2 6.641,Electromagnetic Fields,Forces,and Motion Lecture 13 Prof.Markus Zahn Page 6 of 14
6.641, Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Lecture 13 Prof. Markus Zahn Page 6 of 14 Model surface current y I K = D as volume current of small thickness δ y I J = Dδ ( ) ( ) z y z H I I H=J = J = H = x xD D ∂ ∇× ⇒ − − ⇒ − − ξ + δ ∂ δδ 0 I I = D D −µ δ ( ) ( ) + x= x lD ξ δ ξ ⎛ ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ − ξ+δ ⎝ ⎠ δ ∫ dx ( ) 2 2 0 2 x I l x = x D 2 ξ+δ =ξ −µ ⎡ ⎤ ⎢ ⎥ − ξ+δ δ ⎣ ⎦ ( ) ()() 2 2 2 2 0 2 I l = D 2 2 −µ ⎡ ⎤ ξ+δ ξ ⎢ ⎥ − − ξ+δ +ξ ξ+δ δ ⎣ ⎦ ( ) 2 2 2 0 2 I l 1 = D 2 2 −µ ⎡ ⎤ ξ ⎢ ⎥ − ξ + δ + + ξδ δ ⎣ ⎦ 2 0 2 2 I l 1 = D 2 −µ ⎡ ⎤ − δ ⎢ ⎥ δ ⎣ ⎦ 2 0 S 1 1 I l = f = K B dS 2D 2 µ +⇒ × ∫ ½ comes from integrating uniform volume current over small thickness δ General formula: av S f = K B dS × ∫ 0 For our case: metal air av air B B 1 B= =B 2 2 + µ x y0z ∫ V f = J H dx dy dz

IV.Lifting of Magnetic Fluid i(t) →∞ o Depth d A magnetizable liquid is pushed upward into the field region between the pole faces by the forces on magnetic dipoles in the fringing region at the bottom. A.Energy Method Approach H=Ni Φ=H[μg+μo0-)]d =9[贱+,0-5明 =No=g2[g+0- L同=子=9[5+0- 专=吃登-9e-w) .gndd(w) -i时 6.641,Electromagnetic Fields,Forces,and Motion Lecture 13 Prof.Markus Zahn Page 7 of 14
6.641, Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Lecture 13 Prof. Markus Zahn Page 7 of 14 IV. Lifting of Magnetic Fluid A. Energy Method Approach Φ µξ + µ − ξ =H l d ⎡ ⎤ 0 ( ) ⎣ ⎦ ⎡ ⎤ µξ + µ − ξ ( ) ⎣ ⎦ 0 Nd = li s λ Φ µξ + µ − ξ ⎡ ⎤ ( ) ⎣ ⎦ 2 0 N d =N = l i s ( ) ( ) λ ξ µ⎡ ⎤ ξ + µ − ξ ⎣ ⎦ 2 0 N d L == l i s ξ ( ) µ − µ ξ 2 2 2 0 1 dL 1 N i d f= i = 2d 2 s ξ ρ ( ) µ−µ 2 2 m 0 1N i d f = ghds = 2 s 2 2 1 Ni d h = 2 ρ 2 s gd m ( ) µ−µ0 Ni H = s

B.Magnetization force Fx Ho (M.V)Hx =0 z 7×H=j=0→=a ay Ox B=明=h佰+网==(片-1 E=[能-農+货,袋 =供-[2w+ f=[F dx dy dz -但2212+)axyz X=-y=0Z=0 s,儿 2 =-)dN吧 2。 -u-)a 6.641,Electromagnetic Fields,Forces,and Motion Lecture 13 Prof.Markus Zahn Page 8 of 14
6.641, Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Lecture 13 Prof. Markus Zahn Page 8 of 14 B. Magnetization force F= M H X0 x µ ∇ ( ) i xxx 0x y z HHH =M M M xyz ⎡ ⎤ ∂∂∂ µ ++ ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ ⎦ ∂∂∂ = 0 z ∂ ∂ ∂ ∂ ∇× ⇒ ∂ ∂ Hx Hy H= J=0 = y x x y X 0x y H H F= M M x x ⎡ ⎤ ∂ ∂ µ + ⎢ ⎥ ∂ ∂ ⎣ ⎦ ( ) ⎛ ⎞ µ µ µ +⇒ − ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ⎠ µ 0 0 B= H= H M M= 1 H x y x0 x y 0 0 H H F= 1H 1H x x ⎡ ⎤ ⎛⎞ ⎛⎞ µ µ ∂ ∂ µ − +− ⎢ ⎥ ⎜⎟ ⎜⎟ µ ∂µ ∂ ⎣ ⎦ ⎝⎠ ⎝⎠ ( ) 2 2 0 xy 0 1 = 1 HH x 2 ⎛ ⎞ µ ∂ ⎡ ⎤ µ− + ⎜ ⎟ ⎢ ⎥ ⎝ ⎠ µ ∂ ⎣ ⎦ x x f = F dx dy dz ∫ ( ) ( ) h sd 0 2 2 x y x y 0z 0 = H H dx dy dz 2 x =−∞ = = µ−µ ∂ + ∂ ∫ ∫∫ ( ) ( ) =−∞ µ−µ + h 0 2 2 x y x = ds H H 2 (µ−µ0 ) = ds 2 2 2 2 N i s ( ) µ−µ 2 2 0 1 Ni = d 2 s
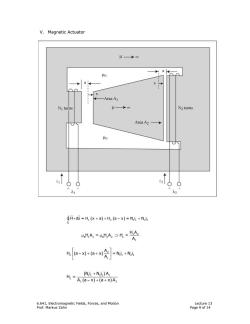
V.Magnetic Actuator μ→∞ a长 0 ←-Area A N]turns μ→∞ N2 turns Area A2→ 40 M .d5=H仪+a+片(a-x)=N4+Nh A=A=H=冷 h[a-刘+(a+2] =N,i +N2iz (Ni +Ni2)A H=A(a-x为)+a+x)A: 6.641,Electromagnetic Fields,Forces,and Motion Lecture 13 Prof.Markus Zahn Page 9 of 14
6.641, Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Lecture 13 Prof. Markus Zahn Page 9 of 14 V. Magnetic Actuator 1 2 11 22 ( ) ( ) C H ds = H x a H a x = N i N i ++ − + ∫ i v 2 2 011 02 2 1 1 H A HA = HA H = A µ µ⇒ ( )( ) 2 2 11 22 1 A H a x a x =Ni Ni A ⎡ ⎤ ⎢ ⎥ −++ + ⎣ ⎦ ( ) ( )( ) 11 22 1 2 1 2 Ni Ni A H = A a x a xA + −++
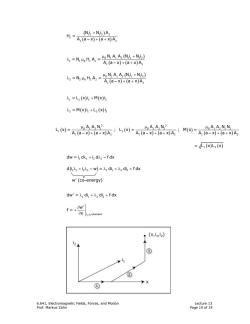
(Ni+N22)A2 H-A(a-x)+(a+为A =N,HA=。NAA+N) A(a-x)+(a+)A2 女=A=会奇哈 入1=L(X)5+M(X)52 2=M(x)1+L2(x)12 b肉=A阳岭8:与肉=AB产8:M网A。合8不 “AA2N22 =1(x)L2(x dw=i da+i dx2-fdx d(i+iz-w)=di +72 diz +f dx w'(co-energy) dw'=λ1di+2di2+fdx f=+0w' ox i,iconstant (x,,2) ③ ③ ① 6.641,Electromagnetic Fields,Forces,and Motion Lecture 13 Prof.Markus Zahn Page 10 of 14
6.641, Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion Lecture 13 Prof. Markus Zahn Page 10 of 14 ( ) ( )( ) 11 22 2 1 1 2 Ni Ni A H = A a x a xA + −++ ( ) ( )( ) 0 1 1 2 11 22 1 101 1 1 2 N A A Ni Ni =N H A = A a x a xA µ + λ µ −++ ( ) ( )( ) 0 2 1 2 11 22 2 202 2 1 2 N A A Ni Ni =N H A = A a x a xA µ + λ µ −++ () () λ + 111 2 =L x i M x i () () λ + 2 12 2 =M x i L x i ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) 2 2 0 1 21 0 1 22 0 1 212 1 2 1 2 1 21 2 A A N A A N A A NN L x= ; L x= ; Mx= A a x a xA A a x a xA A a x a xA µ µµ −++ −++ −++ = L xL x 1 2 () () dw = i d i d f dx 112 2 λ+ λ− ( ) λ + λ − λ +λ + d i i w = di di f dx 11 22 1 1 2 2 w’ (co−energy) dw' = di di f dx 11 22 λ +λ + 1 2 i ,i cons tan t w' f = x ∂ + ∂
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)EM application Electroquasistatic Forces.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)EM application Chapter 1 Fields.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(教材讲义)麦克斯韦方程组 Chapter 13 Maxwell’s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(教材讲义)磁场的能量 Chapter 11 Inductance and Magnetic Energy.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(教材讲义)交流电 Chapter 12 Alternating-Current Circuits.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(教材讲义)稳恒电流 Chapter 7 DC Circuits.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(教材讲义)静电场中的导体与电介质 Chapter 5 Capacitance and Dielectrics.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(教材讲义)静电场中的导体与电介质 Chapter 5 Capacitance and Dielectrics.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(教材讲义)真空中的静电场(光子质量)Terrestrial and Extraterrestrial Limits on The Photon Mass.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(教材讲义)真空中的静电场(库仑定理)Physical implications of Coulomb’s Law.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(教材讲义)真空中的静电场 Chapter 3 Electric Potential.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(教材讲义)库仑定律验证 Improved result for the accuracy of Coulomb's law:A review of the Williams, Faller, and Hill experiment.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(教材讲义)真空中的静电场 Chapter 2 Coulomb’s Law.pdf
- 物理奥林匹克竞赛:全国物理奥林匹克竞赛第35届决赛试题(含参考答案).pdf
- 物理奥林匹克竞赛:全国物理奥林匹克竞赛第34届决赛试题(含参考答案).pdf
- 物理奥林匹克竞赛:全国物理奥林匹克竞赛第34届复赛试题(含参考答案).pdf
- 物理奥林匹克竞赛:全国物理奥林匹克竞赛第34届初赛试题(参考答案).pdf
- 物理奥林匹克竞赛:全国物理奥林匹克竞赛第33届决赛试题(试题).pdf
- 物理奥林匹克竞赛:全国物理奥林匹克竞赛第33届决赛试题(解答).pdf
- 物理奥林匹克竞赛:全国物理奥林匹克竞赛第33届复赛试题(含参考答案).pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)EM application Magnetization.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)EM application Polarization and Conduction.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)EM application Method of Images.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)EM application Electroquasistatic and Magnetoquasistatic Fields and Boundary Conditions.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)Exam and Solutions Exam One Solutions.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)MIT-ED Classical Electrodynamics.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)Exam and Solutions Exam 1 Practice Problems Solutions.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)Exam and Solutions Exam 2 Practice Problems Part 1 Solutions.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)麦克斯韦方程和规范理论的观念起源(杨振宁)maxwell-y.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)MIT-ID Interference and Diffraction.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)超导电性与磁性.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)等离子体物理及应用.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)反物质探索(主讲:叶邦角).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)铁电物理研究新进展 New Progress in Ferroelectrics(主讲:王忆).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)加速器与同步辐射(主讲:戚伯云).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)物质的磁性及其应用(主讲:张泰永).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)Using Multi-gap Resistive Plate Chamber as TOF.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)单原子分子测控(主讲:徐春凯).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)只是应用于iPOD的GMR——漫谈2007诺贝尔物理奖(主讲:朱弘).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)表面分析中的电与磁(主讲:张增明).pdf
