《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)彩色图像处理 6.2 伪彩色和全彩色图像处理

Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Color Fundamentals and models Pseudo-Color Image Processing Full-color Image processing 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Color Fundamentals and models Pseudo-Color Image Processing Full-color Image processing

Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Pseudocolor Image Processing Pseudocolor (also called false color)image processing consists of assigning colors to gray values based on a specified criterion. The principal use of pseudocolor is for human visualization and interpretation of gray-scale events in an image or sequence of images. 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez &R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Pseudocolor Image Processing Pseudocolor (also called false color) image processing consists of assigning colors to gray values based on a specified criterion. The principal use of pseudocolor is for human visualization and interpretation of gray-scale events in an image or sequence of images
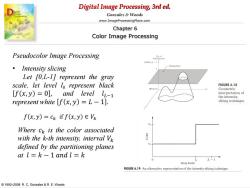
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Pseudocolor Image Processing (Whice)L1 ·Intensity slicing Let [0,L-1]represent the gray scale,let level lo represent black FIGURE 6.18 Geometric [f(x,y)=0],and level lL-1 tereo represent white [f(x,y)=L-1]. slicing technique f(x,y)=ck if f(x,y)E Vk Where ck is the color associated with the k-th intensity,interval Vk defined by the partitioning planes at l=k-1and l=k L-1 Gray levels FIGURE 6.19 An alternative representation of the intensity-slicing technique. 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Pseudocolor Image Processing • Intensity slicing Let [0,L-1] represent the gray scale, let level l0 represent black 𝑓 𝑥, 𝑦 = 0 , and level 𝑙𝐿−1 represent white 𝑓 𝑥, 𝑦 = 𝐿 − 1 . 𝑓 𝑥, 𝑦 = 𝑐𝑘 if 𝑓 𝑥, 𝑦 ∈ 𝑉𝑘 Where 𝑐𝑘 is the color associated with the k-th intensity, interval 𝑉𝑘 defined by the partitioning planes at 𝑙 = 𝑘 − 1 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑙 = 𝑘
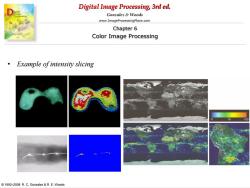
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez&Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Example of intensity slicing 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • Example of intensity slicing

Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Intensity to color transformations The idea is to perform three independent transformations Red FIGURE 6.23 on the intensity of any input transformation fr(x.y) Functional block diagram for pixel. pseudocolor edto fxy)口 Green transformation fc(x.y) corresponding red,green,and blue inputs of an RGB color monitor. Blue transformation fg(x.y) 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • Intensity to color transformations • The idea is to perform three independent transformations on the intensity of any input pixel

Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing 。 Example:Use of pseudocolor for highlighting explosives contained in luggage L-1 L- be Intensit Explosive 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • Example: Use of pseudocolor for highlighting explosives contained in luggage
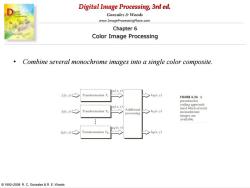
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Combine several monochrome images into a single color composite. 1g1(x,y) x,)> Transformation T hR(x.y) FIGURE 6.26 A pseudocolor 82(x,y) 6,)> Transformation T Additiona >hc(x,y) processing monochrome images are available gx(x.y) fk(x.y) Transformation Tg hg(x.y) 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • Combine several monochrome images into a single color composite

Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Example: Color coding of multispectral images. TABLE 1.1 Band No. Name Thematic bands Wavelength(um)Characteristics and Uses in NASA's 1 Visible blue 0.45-0.52 Maximum water LANDSAT penetration satellite. 2 Visible green 0.52-0.60 Good for measuring plant vigor 2 Visible red 0.63-0.69 Vegetation discrimination Near infrared 0.76-0.90 Biomass and shoreline mapping Middle infrared 155-1.75 Moisture content of soil and vegetation 6 Thermal infrared 10.4-12.5 Soil moisture:thermal mapping 7 Middle infrared 2.08-2.35 Mineral mapping FIGURE 6.27 (a)-(d)Images in bands 1-4 in Fig.1.10 (see Table 1.1).(e)Color a b composite image obtained by treating (a),(b).and (c)as the red,green,blue com- ponents of an RGB image.(f)Image obtained in the same manner,but using in the red channel the near-infrared image in (d).(Original multispectral images courtesy 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez &R.E.Woods of NASA.)
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • Example: Color coding of multispectral images

Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Color Fundamentals and models Pseudo-Color Image Processing Full-color Image processing 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Color Fundamentals and models Pseudo-Color Image Processing Full-color Image processing

Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez&Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Basic of Full-Color Image Processing Let c represent an arbitrary vector in RGB color space: TCR] CR(x,y)] [R(x,y) C三 G c(x,y)= cc(x,y) G(x,y) LCB LB」 cB(x,y)] B(x,y)] ab FIGURE 6.29 Spatial masks for gray-scale and (y) RGB color (x.y) Spatial mask Spatial mask images. Gray-scale image RGB color image 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Basic of Full-Color Image Processing • Let c represent an arbitrary vector in RGB color space: 𝑐 = 𝑐𝑅 𝑐𝐺 𝑐𝐵 = 𝑅 𝐺 𝐵 𝑐 𝑥, 𝑦 = 𝑐𝑅 𝑥, 𝑦 𝑐𝐺 𝑥, 𝑦 𝑐𝐵 𝑥, 𝑦 = 𝑅 𝑥, 𝑦 𝐺 𝑥, 𝑦 𝐵 𝑥, 𝑦
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)彩色图像处理 6.1 彩色基础和彩色模型.pdf
- 电子工业出版社:《数字图像处理》书籍教材PDF电子版(中译第三版)第6章 彩色图像处理.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)图像复原与重建 5.7 逆滤波 5.8 维纳滤波.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)图像复原与重建 5.5 退化函数的估计 5.6 逆滤波.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)图像复原与重建 5.3 空间域滤波方法 5.4 频率域滤波方法.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)图像复原与重建 5.1 图像退化复原过程的模型 5.2 噪声模型.pdf
- 电子工业出版社:《数字图像处理》书籍教材PDF电子版(中译第三版)第5章 图像复原与重建.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)频率域滤波 4.9 使用频率域滤波器锐化图像.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)频率域滤波 4.8 频率域平滑图像(频域平滑滤波器).pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)频率域滤波 4.7 频率域滤波基础.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)频率域滤波 4.6 二维离散傅里叶变换的性质.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)频率域滤波 4.4 单变量的离散傅立叶变换 4.5 两个变量的扩展.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)频率域滤波 4.3 取样和取样函数的傅里叶变换.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)频率域滤波 4.2 基本概念.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)频率域滤波 4.1 背景——傅立叶级数和变换简史.pdf
- 电子工业出版社:《数字图像处理》书籍教材PDF电子版(中译第三版)第4章 频率域滤波.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)灰度变换与空间滤波 3.3 空间滤波 Fundamentals of spatial filtering.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)灰度变换与空间滤波 3.2 直方图 Histogram processing.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)灰度变换与空间滤波 3.1 邻域 邻接、连接 区域、边界 距离.pdf
- 电子工业出版社:《数字图像处理》书籍教材PDF电子版(中译第三版)第3章 灰度变换与空间滤波.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)图像压缩——图像压缩基本概念.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)图像压缩 ——霍夫曼-算术-LZW编码.pdf
- 《数字图像处理》课程教学课件(Digital Image Processing)图像压缩——变换编码.pdf
- 电子工业出版社:《数字图像处理》书籍教材PDF电子版(中译第三版)第9章 形态学图像处理.pdf
- 电子工业出版社:《数字图像处理》书籍教材PDF电子版(中译第三版)第10章 图像分割.pdf
- 电子工业出版社:《数字图像处理》书籍教材PDF电子版(MATLAB版)Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB【美】Richard E.Woods Steven L.Eddins(共十二章).pdf
- 《软件工程》课程教学资源(书籍教材)英文电子版《软件工程——实践者之路》第九版 Software Engineering, A Practitioners Approach(9th Ed, Roger S. Pressman, Ph.D. Bruce R. Maxim, Ph.D., 2019).pdf
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学大纲 Software Engineering.pdf
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第1章 软件工程概述(主讲:杨谊).pptx
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第2章 软件过程.pptx
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第3章 结构化分析 3.1 软件开发计划 3.2 需求分析的内容.pptx
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第3章 结构化分析 3.3 分析建模与规格说明 3.4 实体-关系图 3.5 数据流图 3.6 状态转换图 3.7 数据字典.pptx
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第4章 结构化设计 4.1 什么是软件设计 4.2 设计的概念和原理 4.3 模块独立 4.4 启发规则 4.5 表示软件结构的图形工具 4.6 面向数据流的设计.pptx
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第4章 结构化设计 4.7 人机界面设计 4.8 详细设计的方法和工具 4.8 过程设计的方法和工具 4.10 面向数据结构的设计方法.pptx
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第5章 结构化实现 5.1 编码与程序语言.pptx
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第5章 结构化实现 5.2 算法决策.pptx
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第5章 结构化实现 5.3 测试(原则,方法,技术)5.4 调试.pptx
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第6章 面向对象方法学导论.ppt
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第7章 面向对象分析.ppt
- 南方医科大学:《软件工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第8章 面向对象设计(1/2).ppt
