《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Permutation test

Bootstrap,Jackknife and other resampling methods Part V:Permutation tests Rozenn Dahyot Room 128,Department of Statistics Trinity College Dublin,Ireland dahyot mee.tcd.ie 2005 R.Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 20051/22
Bootstrap, Jackknife and other resampling methods Part V: Permutation tests Rozenn Dahyot Room 128, Department of Statistics Trinity College Dublin, Ireland dahyot@mee.tcd.ie 2005 R. Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 2005 1 / 22

So far The resampling methods are: o Bootstrap resampling:generate samples with the same size n as x with replacement. Jackknife subsampling generate samples with a smaller size than x without replacement. Used for: Compute accuracy measures (standard error,bias,etc.)of a statistic 0 from one set x (x1,...,xn). oCompare two sets of observations:the example of the mouse data R.Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 20052/22
So far The resampling methods are: Bootstrap resampling: generate samples with the same size n as x with replacement. Jackknife subsampling : generate samples with a smaller size than x without replacement. Used for: Compute accuracy measures (standard error, bias, etc.) of a statistic θˆ from one set x = (x1, · · · , xn). Compare two sets of observations: the example of the mouse data R. Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 2005 2 / 22
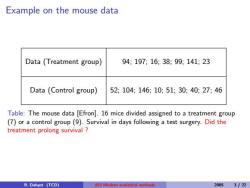
Example on the mouse data Data (Treatment group) 94;197:16;38;99:141;23 Data(Control group) 52;104;146;10:51;30:40;27:46 Table:The mouse data [Efron].16 mice divided assigned to a treatment group (7)or a control group(9).Survival in days following a test surgery.Did the treatment prolong survival R.Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modem statistical methods 20053/22
Example on the mouse data Data (Treatment group) 94; 197; 16; 38; 99; 141; 23 Data (Control group) 52; 104; 146; 10; 51; 30; 40; 27; 46 Table: The mouse data [Efron]. 16 mice divided assigned to a treatment group (7) or a control group (9). Survival in days following a test surgery. Did the treatment prolong survival ? R. Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 2005 3 / 22

Example on the mouse data Compute B bootstrap samples for each group ·x8=(x81…,x8) *(b) x=(…,温g) B bootstrap replications are computed:(= you can approximate the p.d.f.of the replications by a histogram. R.Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 20054/22
Example on the mouse data 1 Compute B bootstrap samples for each group I x ∗(b) Treat = (x ∗(b) Treat 1 , · · · , x ∗(b) Treat 7 ) I x ∗(b) Cont = (x ∗(b) Cont 1 , · · · , x ∗(b) Cont 9 ) 2 B bootstrap replications are computed: θˆ∗ (b) = x ∗(b) Treat − x ∗(b) Cont 3 you can approximate the p.d.f. of the replications by a histogram. R. Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 2005 4 / 22
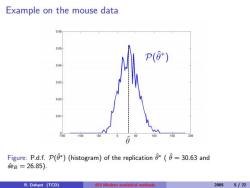
Example on the mouse data 003 0.05 P(0*) 0.04 0.03 0.02 0,01 -100 00 150 200 Figure:P.d.f.P()(histogram)of the replication (=30.63 and 5seB=26.85). R.Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modem statistical methods 2005 5/22
Example on the mouse data Figure: P.d.f. P(θˆ∗ ) (histogram) of the replication θˆ∗ ( θˆ = 30.63 and seˆ B = 26.85). R. Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 2005 5 / 22

Introduction oTwo sample problem definitions Parametric solution Non parametric solution: permutation test randomization test bootstrap test R.Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 20056/22
Introduction Two sample problem : definitions Parametric solution Non parametric solution: I permutation test I randomization test I bootstrap test R. Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 2005 6 / 22
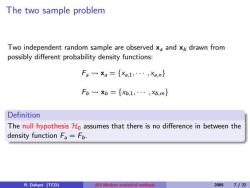
The two sample problem Two independent random sample are observed xa and xb drawn from possibly different probability density functions: Fgxa={x,1,…,X,n} Fbxb={xb,1,…,b,m} Definition The null hypothesis Hto assumes that there is no difference in between the density function Fa=Fb. R.Dahyot (TCD) 453 Moder statistical methods 20057/22
The two sample problem Two independent random sample are observed xa and xb drawn from possibly different probability density functions: Fa xa = {xa,1, · · · , xa,n} Fb xb = {xb,1, · · · , xb,m} Definition The null hypothesis H0 assumes that there is no difference in between the density function Fa = Fb. R. Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 2005 7 / 22

Hypothesis test and Achieved significance level (ASL) Definition A hypothesis test is a way of deciding whether or not the data decisively reject the hypothesis Ho. Definition The achieved significance level of the test (ASL)is defined as: AsL=P(0*≥Ho) =6P(1to)d0 The smaller ASL,the stronger is the evidence of Ho false.The notation star differentiates between an hypothetical value generated according to Ho,and the actual observation 0. R.Dahyot (TCD)】 453 Modem statistical methods 2005 8/22
Hypothesis test and Achieved significance level (ASL) Definition A hypothesis test is a way of deciding whether or not the data decisively reject the hypothesis H0. Definition The achieved significance level of the test (ASL) is defined as: ASL = P(θ ˆ∗ ≥ θ ˆ|H0) = R +∞ θˆ P(θˆ∗ |H0) dθˆ∗ The smaller ASL, the stronger is the evidence of H0 false. The notation star differentiates between an hypothetical value θˆ∗ generated according to H0, and the actual observation θˆ. R. Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 2005 8 / 22

Parametric test o A tradionnal way is to consider some hypotheses:Fa~N(ua,2) and F~N(ub,2),and the null hypothesis becomes ua =ub. Under Ho,the statistic =Xa-can be modelled as a normal distribution with mean 0 and variance2(). o The ASL is then computed: -(*-2 ∫+心e2 ASL= d0* √2π0a R.Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 20059/22
Parametric test A tradionnal way is to consider some hypotheses: Fa ∼ N (µa, σ2 ) and Fb ∼ N (µb, σ2 ), and the null hypothesis becomes µa = µb. Under H0, the statistic θˆ = xa − xb can be modelled as a normal distribution with mean 0 and variance σ 2 θˆ = σ 2 ( 1 m + 1 n ). The ASL is then computed: ASL = Z +∞ θˆ e −(θˆ∗−θˆ) 2 2σ2 θˆ √ 2πσθˆ dθˆ∗ R. Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 2005 9 / 22

Parametric test oo is unknown and has to be estimated from the data: a2=∑1=(xai-x,)2+∑1(xb1-xb2 m+n-2 For the mouse data ASL =.131 the null hypothesis cannot be rejected. o However,this(parametric)method relies on the hypotheses made while calculating the ASL. R.Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 2005 10/22
Parametric test σ is unknown and has to be estimated from the data: σ 2 = Pn i=1(xai − xa) 2 + Pm i=1(xbi − xb) 2 m + n − 2 For the mouse data ASL = .131 : the null hypothesis cannot be rejected. However, this (parametric) method relies on the hypotheses made while calculating the ASL. R. Dahyot (TCD) 453 Modern statistical methods 2005 10 / 22
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)一些理论 Bootstrap and Jackknife Estimation of Sampling Distributions.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Bootstrap and Jackknife.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)A Review on Empirical Likelihood Methods for Regression.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Empirical Likelihood notes.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Statistical functionals and delta method.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Asymtotic relative efficiency of two tests.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)回归与方差分析 Practical Regression and Anova using R(共16章)Faraway-PRA.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)A Comparative Study of Tests for Homogeneity of Variances, with Applications to the Outer Continental Shelf Bidding Data.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Chi square test with both margins fixed.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Conditonal versus unconditional exact tests for comparing two binomials.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Fisher's Exact Test , When to use Fisher's exact test.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Association Between Variables.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)with Implementation in S-PLUS.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Binomial Distribution - Hypothesis Testing, Confidence Intervals(CI), and Reliability.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Introduction Review of R.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第一讲 参数统计与非参数统计——回顾与简介.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Matrix Cook Book.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)北师大矩阵代数讲稿.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)附录——矩阵代数(主讲:张伟平).pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Types of Sums of Squares.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Density Estimation.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)W.J.Braun's Nonparametric regression notes.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Patrick Breheny's Spline and penalized regression note.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)简介:Why Probability and Statistics - some examples.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第一章 事件与概率 1.1 事件及其运算、概率及其性质.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第一章 事件与概率 1.2 古典概型和几何概率.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第一章 事件与概率 1.3 条件概率与独立性.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第一章 随机事件与概率(主讲:张伟平)样本空间与概率.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第二章 随机变量及其分布.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第二章 随机变量及其分布 2.1 离散型随机变量.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第二章 随机变量及其分布 2.2 连续型随机变量.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第二章 随机变量及其分布 2.3 多维随机变量.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第二章 随机变量及其分布 2.4 条件分布与独立性.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第二章 随机变量及其分布 2.5 随机变量的函数的分布.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第三章 随机变量的数字特征.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第三章 随机变量的数字特征 3.1 中心位置数字特征.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第三章 随机变量的数字特征 3.2 方差、相关系数以及其他数字特征.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第四章 大数律与中心极限定理.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第四章 大数律与中心极限定理 4.1 大数律与中心极限定理.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第五章 数理统计的基本概念与抽样分布.pdf
