《国际金融 International Finance》课程教学资料:National Income Accounting and the Balance of Payments

Chapter 13 Global Editlon National Income Accounting and the Balance of Payments International Economics THEORY POLICY Ninth Edition Paul R.Krugman Maurice Obstfeld Marc J.Melitz PEARSON PEARSON Copyright 2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. Chapter 13 National Income Accounting and the Balance of Payments

Preview National income accounts measures of national income - measures of value of production measures of value of expenditure o National saving,investment,and the current account Balance of payments accounts 13-2 Copyright2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-2 Preview • National income accounts – measures of national income – measures of value of production – measures of value of expenditure • National saving, investment, and the current account • Balance of payments accounts

National Income Accounts Records the value of national income that results from production and expenditure. Producers earn income from buyers who spend money on goods and services. The amount of expenditure by buyers the amount of income for sellers the value of production. National income is often defined to be the income earned by a nation's factors of production. 13-3 Copyright 2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-3 National Income Accounts • Records the value of national income that results from production and expenditure. – Producers earn income from buyers who spend money on goods and services. – The amount of expenditure by buyers = the amount of income for sellers = the value of production. – National income is often defined to be the income earned by a nation’s factors of production

National Income Accounts:GNP Gross national product (GNP)is the value of all final goods and services produced by a nation's factors of production in a given time period. What are factors of production?Factors that are used to produce goods and services:workers (labor services), physical capital (like buildings and equipment),natural resources and others. The value of final goods and services produced by US- owned factors of production are counted as US GNP. 13-4 Copyright2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-4 National Income Accounts: GNP • Gross national product (GNP) is the value of all final goods and services produced by a nation’s factors of production in a given time period. – What are factors of production? Factors that are used to produce goods and services: workers (labor services), physical capital (like buildings and equipment), natural resources and others. – The value of final goods and services produced by US- owned factors of production are counted as US GNP

National Income Accounts:GNP(cont.) GNP is calculated by adding the value of expenditure on final goods and services produced: 1.Consumption:expenditure by domestic consumers 2.Investment:expenditure by firms on buildings equipment 3.Government purchases:expenditure by governments on goods and services 4.Current account balance (exports minus imports):net expenditure by foreigners on domestic goods and services Copyright2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved. 13-5
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-5 National Income Accounts: GNP (cont.) • GNP is calculated by adding the value of expenditure on final goods and services produced: 1. Consumption: expenditure by domestic consumers 2. Investment: expenditure by firms on buildings & equipment 3. Government purchases: expenditure by governments on goods and services 4. Current account balance (exports minus imports): net expenditure by foreigners on domestic goods and services
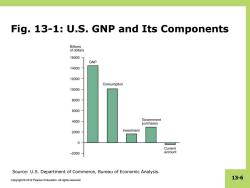
Fig.13-1:U.S.GNP and Its Components Billions of dollars 16000 GNP 14000 12000 Consumption 10000 8000 6000 4000 Government purchases 2000 Investment 0 Current -2000 account Source:U.S.Department of Commerce,Bureau of Economic Analysis. 13-6 Copyright 2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-6 Fig. 13-1: U.S. GNP and Its Components Source: U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Economic Analysis

National Income Accounts GNP is one measure of national income, but a more precise measure of national income is GNP adjusted for following: 1.Depreciation of physical capital results in a loss of income to capital owners,so the amount of depreciation is subtracted from GNP. 2.Unilateral transfers to and from other countries can change national income: payments of expatriate workers sent to their home countries,foreign aid and pension payments sent to expatriate retirees. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved. 13-7
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-7 National Income Accounts • GNP is one measure of national income, but a more precise measure of national income is GNP adjusted for following: 1. Depreciation of physical capital results in a loss of income to capital owners, so the amount of depreciation is subtracted from GNP. 2. Unilateral transfers to and from other countries can change national income: payments of expatriate workers sent to their home countries, foreign aid and pension payments sent to expatriate retirees

National Income Accounts (cont.) Another approximate measure of national income is gross domestic product (GDP): Gross domestic product measures the final value of all goods and services that are produced within a country in a given time period. - GDP GNP-payments from foreign countries for factors of production payments to foreign countries for factors of production 13-8 Copyright2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-8 National Income Accounts (cont.) • Another approximate measure of national income is gross domestic product (GDP): – Gross domestic product measures the final value of all goods and services that are produced within a country in a given time period. – GDP = GNP – payments from foreign countries for factors of production + payments to foreign countries for factors of production

GNP Expenditure on a Country's Goods and Services The national income identity for an open economy is Y-C+I+G+EX-IM C+I+G +CA Expenditure by domestic Net expenditure by foreign individuals and institutions individuals and institutions 13-9 Copyright2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-9 GNP = Expenditure on a Country’s Goods and Services • The national income identity for an open economy is Y = C + I + G + EX – IM = C + I + G + CA Expenditure by domestic individuals and institutions Net expenditure by foreign individuals and institutions

Expenditure and Production in an Open Economy CA=EX-IM Y-(C+I+G) When production domestic expenditure,exports imports: current account 0 and trade balance 0 when a country exports more than it imports,it earns more income from exports than it spends on imports net foreign wealth is increasing When production domestic expenditure,exports imports: current account 0 and trade balance 0 - when a country exports less than it imports,it earns less income from exports than it spends on imports net foreign wealth is decreasing Copyright2012 Pearson Education.All rights reserved. 13-10
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 13-10 Expenditure and Production in an Open Economy CA = EX – IM = Y – (C + I + G ) • When production > domestic expenditure, exports > imports: current account > 0 and trade balance > 0 – when a country exports more than it imports, it earns more income from exports than it spends on imports – net foreign wealth is increasing • When production < domestic expenditure, exports < imports: current account < 0 and trade balance < 0 – when a country exports less than it imports, it earns less income from exports than it spends on imports – net foreign wealth is decreasing
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第四讲 投资方案经济效果评价指标(一).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第十讲 工程项目投资的盈利性和清偿能力分析(1).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第十四讲 不确定分析与风险分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第十五讲 价值工程.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第十二讲 设备更新与租赁决策.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第十三讲 公共项目的经济分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第十一讲 工程项目投资的盈利性和清偿能力分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第六讲 互斥方案的比选方法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第八讲 折旧、利润与所得税(1).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第五讲 投资方案经济效果评价指标(二).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第二讲 工程项目投资现金流量识别与估算.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第九讲 折旧、利润与所得税(2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第三讲 货币的时间价值与利息公式.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第七讲 独立方案的排序方法及服务寿命不等的方案比较.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源_第一讲 工程经济学的基本概念(胡昊).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源(讲义课件)第九章 不确定性分析与风险分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源(讲义课件)第八章 公共项目的经济分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源(讲义课件)第七章 设备更新的经济分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源(讲义课件)第六章 工程项目投资的盈利性和清偿能力分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程经济学 Engineering Economics》课程教学资源(讲义课件)第五章 折旧、利润与所得税.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《宏观经济学(通选)》课程教学资源_一般均衡存在性证明.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《宏观经济学(通选)》课程教学资源_第23章 衡量一国收入 Measuring a Nation’s Income.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《宏观经济学(通选)》课程教学资源_第24章 衡量生活成本 Measuring the Cost of Living.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《宏观经济学(通选)》课程教学资源_第9篇 长期中的实际经济 第25章 生产与经济增长 Production and Growth.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《宏观经济学(通选)》课程教学资源_第9篇 长期中的实际经济 第26章 储蓄、投资与金融体系 Saving, Investment, and the Financial System.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《宏观经济学(通选)》课程教学资源_第9篇 长期中的实际经济 第27章 基本金融工具 The Basic Tools of Finance.pdf
- 《政府与市场》课程教学资源(阅读材料)亚当·斯密《国富论》(国民财富的性质和原因的研究).pdf
- 《政府与市场》课程教学资源(阅读材料)政府为什么干预经济——政府在市场经济中的角色.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《计量经济学》教学资源_教学资料_Econometrics Introduction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《计量经济学》教学资源_教学资料_Regression Analysis.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《计量经济学》教学资源_教学资料_Multiple Regression Analysis.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《计量经济学》教学资源_教学资料_syllabus.pdf
- 《中国医疗保险制度的转型发展与创新》课程教学资源(讲稿)上海市民众“看病难、看病贵”程度评估、内在机理分析和对策.pdf
- 《中国医疗保险制度的转型发展与创新》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)上海市民众“看病难、看病贵”程度评估、内在机理分析和对策.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《中国医疗保险制度的转型发展与创新》课程教学资源(讲稿)分级诊疗建设案例分享.pdf
- 《中国医疗保险制度的转型发展与创新》课程教学资源(参考资料)世界银行:Deepening Health Reform In China Building High-Quality And Value-Based Service Delivery.pdf
- 《中国医疗保险制度的转型发展与创新》课程教学资源(参考资料)我所经历的三明医改.pdf
- 《中国医疗保险制度的转型发展与创新》课程教学资源(参考资料)深化中国医药卫生体制改革(建设基于价值的优质服务提供体系——政策总论)deepening health reform in china in Chinese version.pdf
- 《中国医疗保险制度的转型发展与创新》课程教学资源(参考资料)People-centred integrated care in urban China.pdf
- 《中国医疗保险制度的转型发展与创新》课程教学资源(参考资料)The Luohu Model:A Template for Integrated Urban Healthcare Systems in China.pdf
