北京化工大学:《化学反应工程》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chemical reaction engineering(2011)Chapter 11-15

Chapter 11 Basics of Non-Ideal Flow So far we have treated two flow patterns,plug flow and mixed flow.Most cases we try to design equipment to approach one or the other.But real equipment always deviates from these ideals. In this chapter,we deals with: RTD state of aggregation earliness and lateness of mixing 1
1 Chapter 11 Basics of Non-Ideal Flow So far we have treated two flow patterns, plug flow and mixed flow. Most cases we try to design equipment to approach one or the other. But real equipment always deviates from these ideals. In this chapter, we deals with: RTD state of aggregation earliness and lateness of mixing

The Residence Time Short-circuiting- Distribution,RTD ·To simplify,.we will only consider Stagnant regions the steady-state flow, Packed bed without reaction and without density Channeling,especially Extreme short-circuiting and bypass serious in countercurrent two-phase operations change,of a single fuid through a vesse Nonidealatems which mayin roce equipment. 2
2 The Residence Time Distribution, RTD • To simplify, we will only consider the steady-state flow, without reaction and without density change, of a single fluid through a vessel
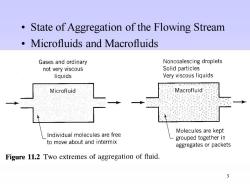
State of Aggregation of the Flowing Stream Microfluids and Macrofluids Gases and ordinary Noncoalescing droplets not very viscous Solid particles liquids Very viscous liquids Microfluid Macrofluid Molecules are kept Individual molecules are free grouped together in to move about and intermix aggregates or packets Figure 11.2 Two extremes of aggregation of fluid. 3
3 • State of Aggregation of the Flowing Stream • Microfluids and Macrofluids

Single-Phase Systems These lie somewhere between the extremes of macro-and microfluids. ·Two-Phase Systems A stream of solids always behaves as a macrofluid,but for gas reacting with liquid, either phase can be a macro-or microfluid depending on the contacting scheme being used. 4
4 • Single-Phase Systems • These lie somewhere between the extremes of macro- and microfluids. • Two-Phase Systems • A stream of solids always behaves as a macrofluid, but for gas reacting with liquid, either phase can be a macro- or microfluid depending on the contacting scheme being used
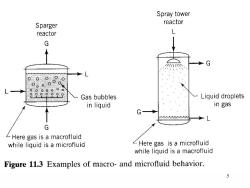
Spray tower Sparger reactor reactor L G G Gas bubbles Liquid droplets in liquid in gas G -Here gas is a macrofluid while liquid is a microfluid -Here gas is a microfluid while liquid is a macrofluid Figure 11.3 Examples of macro-and microfluid behavior. 5
5
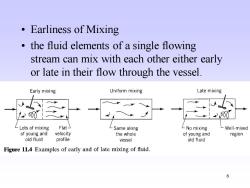
。Earliness of Mixing the fluid elements of a single flowing stream can mix with each other either early or late in their flow through the vessel Early mixing Uniform mixing Late mixing 00 00 Lots of mixing Flat- Same along LNo mixing Well-mixed of young and velocity the whole of young and region old fluid profile vessel old fluid Figure 11.4 Examples of early and of late mixing of fluid. 6
6 • Earliness of Mixing • the fluid elements of a single flowing stream can mix with each other either early or late in their flow through the vessel
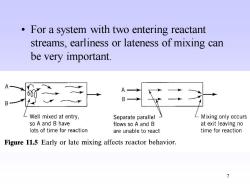
For a system with two entering reactant streams,earliness or lateness of mixing can be very important. A 60 B LWell mixed at entry, Separate parallel LMixing only occurs so A and B have flows so A and B at exit leaving no lots of time for reaction are unable to react time for reaction Figure 11.5 Early or late mixing affects reactor behavior. 7
7 • For a system with two entering reactant streams, earliness or lateness of mixing can be very important

Role of RTD,State of Aggregation,and Earliness of Mixing in Determining Reactor Behavior In some situations one of these three factors can be ignored,in others it can become crucial.Often,much depends on the time for reaction t,the time for mixingtmix,and the time for stay in the vessel tsty.In many casests has a meaning somewhat like but somewhat broader. 8
8 • Role of RTD, State of Aggregation, and Earliness of Mixing in Determining Reactor Behavior • In some situations one of these three factors can be ignored, in others it can become crucial. Often, much depends on the time for reaction , the time for mixing , and the time for stay in the vessel . In many cases has a meaning somewhat like but somewhat broader. trx t mix t stay t stay t mix

11.1 E,The Age Distribution of Fluid,the RTD In this section,we do not consider any reaction It is evident that elements of fluid taking different routs through the reactor may take different lengths of time to pass through the vessel.The distribution of these times for the stream of fluid leaving the vessel is called the exit age distribution E,or the residence time distribution RTD of the fluid. E has the units of time-1. 9
9 11.1 E, The Age Distribution of Fluid, the RTD • It is evident that elements of fluid taking different routs through the reactor may take different lengths of time to pass through the vessel. The distribution of these times for the stream of fluid leaving the vessel is called the exit age distribution E, or the residence time distribution RTD of the fluid. E has the units of time -1 . In this section, we do not consider any reaction

As a beginning,we have a review of ideal flow reactor MFR (CSTR)in which fluid has maximum back-mixing PFR in which there isn't any back-mixing Non-ideal reactor:it's back-mixing between CSTR and PFR back-mixing The mix of fluid with different stay time 10
10 • As a beginning, we have a review of ideal flow reactor • MFR(CSTR) in which fluid has maximum back-mixing • PFR in which there isn’t any back-mixing • Non-ideal reactor: it’s back-mixing between CSTR and PFR • back-mixing The mix of fluid with different stay time
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《化学反应工程》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chemical reaction engineering(2010)Chapter 06-10.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《化学反应工程》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chemical reaction engineering(2010)Chapter 17-18.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《化学反应工程》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chemical reaction engineering(2009)Chapter 01-05.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《化学反应工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)化学反应工程(第二版,共九章,负责人:郭锴).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第12章 过渡元素.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第11章 主族元素.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第05章 酸碱平衡(Acid-Base Equilibria).pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第10章 配位化合物和配位平衡.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第09章 化学键和分子结构.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第08章 原子结构和元素周期率.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第07章 氧化还原反应.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第06章 难溶电解质的沉淀溶解平衡.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第04章 化学反应速率及化学平衡.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第03章 化学热力学基础.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第02章 物质的聚集状态和溶液.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第01章 绪论 Fundamental Chemistry(负责人:李保山).pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2013-2014学年第一学期《基础化学》期中考试试卷及参考答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013学年第一学期国际班《基础化学》期中考试试卷及参考答案.pdf
- 《基础化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Quantum gas goes below absolute zero.doc
- 《基础化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)合成氨进展——科学家开发出氨合成节能技术.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机分析》课程教学资源(实验指导,高职,文字版).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(大纲教材)天然药物化学中英文对照专业词汇(2009版).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(大纲教材)天然药物化学教学大纲(2014版).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(大纲教材)天然药物化学教学大纲(2015版).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(大纲教材)本科天然药物化学教学大纲(2017版).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(大纲教材)天然药物化学中英文对照专业词汇(2018版).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(复习题集)天然药物化学复习题(2014版,无答案).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(复习题集)本科学生专业选修课《有机分析》习题(无解答).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(复习题集)天然药物化学复习题(海洋天然产物,含答案).pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)D.S. Bhakuni&D.S. Rawat《Bioactive marine natural products》.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Deep-sea natural products.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Drugs from the Sea - Opportunities and Obstacles.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Marine-Sourced Anti-Cancer and Cancer Pain Control Agents in Clinical and Late Preclinical Development.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Highlights of marine natural products chemistry(1972–1999).pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Marine Organisms as Potential Supply for Drug Finding-A Review Study.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Marine Natural Products and Related Compounds in Clinical and Advanced Preclinical Trials.pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Marine Pharmaceuticals.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Marketed Marine Natural Products in the Pharmaceutical and Cosmeceutical Industries - Tips for Success.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Biomedicinals from the phytosymbionts of marine invertebrates - A molecular approach.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Lessons from the past and charting the future of marine natural products drug discovery and chemical biology.pdf
