北京化工大学:《化学反应工程》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chemical reaction engineering(2010)Chapter 17-18

Chapter 17 Heterogeneous Reaction--Introduction Since more than one phase is present,the movement of material from phase to phase must be considered in the rate equation.Thus the rate expression in general will incorporate mass transfer terms in addition to the usual chemical kinetics term.These mass transfer terms are different in type and numbers in the different kinds of heterogeneous systems;hence,no single rate expression has general application. 1
1 Chapter 17 Heterogeneous Reaction--Introduction Since more than one phase is present,the movement of material from phase to phase must be considered in the rate equation. Thus the rate expression in general will incorporate mass transfer terms in addition to the usual chemical kinetics term. These mass transfer terms are different in type and numbers in the different kinds of heterogeneous systems; hence, no single rate expression has general application

EXAMPLE IZ.I THE BURNING OF A CARBON PARTICLE IN AIR Tell how many rate steps are involved.The kinetics is given by C+O2→CO2 and ignore the possible formation of CO. SOLUTION From Fig.E17.1 we see that two steps in series are involved-mass transfer of oxygen to the surface followed by reaction at the surface of the particle. 03 02 Model Air C02 c02 Burning carbon particle Gas film Fig.E17.1 2
2

EXAMPLE 17.2 AEROBIC FERMENTATION Tell how many rate steps are involved when air bubbles through a tank of liquid which contains dispersed microbes and is taken up by the microbes to produce product material. SOLUTION From Fig.E17.2 we see that there are up to seven possible resistance steps,only one involving the reaction.How many you choose to consider depends on you and on the situation. Cell wall Interface Bulk transport Air Microbial bubble 4 cell 5, 3 Liquid film Gas film Liquid film- Fig.E17.2 3
3

To get an overall rate expression,write the individual rate steps on the same basis(unit surface of burning particle,unit volume of fermenter,unit volume of cells,etc.). 1 dNA= -rA=-V dt mol A reacted volume of reactor fluid.time or 1 dN mol A reacted 一ra=一wdt mass of solid.time or 1dNA= -=-s di mol A reacted interfacial surface.time Now put all the mass transfer and reaction steps into the same rate form and then combine.Thus mol Areacted-(-rA)V=(rAw-(A)S time 4
4

or V and if the steps are in series,as in Examples 17.1 and 17.2 roverall =r1=r2=r3 If they are in parallel roverall=r1 +r2 Consider steps in series.In general,if all the steps are linear in concentration, then it is easy to combine them.However,if any of the steps are nonlinear,then you will get a messy overall expression.Therefore,you may try to bypass this nonlinear step in one of various ways.Approximating the ra versus Ca curve by a first-order expression is probably the most useful procedure. Another point:in combining rates we normally do not know the concentration of materials at intermediate conditions,so these are the concentrations that we eliminate in combining rates.Example 17.3 shows this. 5
5
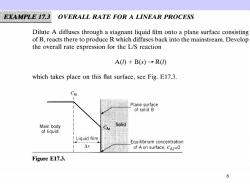
EXAMPLE 17.3 OVERALL RATE FOR A LINEAR PROCESS Dilute A diffuses through a stagnant liquid film onto a plane surface consisting of B,reacts there to produce R which diffuses back into the mainstream.Develop the overall rate expression for the L/S reaction A()+B(S)→R() which takes place on this flat surface,see Fig.E17.3. CAL Plane surface of solid B Main body Solid A of liquid I Liquid film Equilibrium concentration △x of A on surface,CA2=0 Figure E17.3. 6
6

SOLUTION By diffusion,the flux of A to the surface is 4-a0=-是cw-c小=C-C rm=s di () Reaction is first order with respect to A,so based on unit surface 1dNA=k"CA rhe=S di (的 At steady state the flow rate to the surface is equal to the reaction rate at the surface (steps in series).So rAI=TA2 and from Eqs.(i)and (ii) k,(CA-CA)=k”CAs 7
7

from which k CCM () Replacing Eq.(iii)into either Eq.(i)or Eq.(ii)then eliminates CAs which cannot be measured,giving 1 mol rA1=r=rA=-1 -CAl=-koverall CAl, m2.s k,k” Comment This result shows that 1/k and 1/k"are additive resistances.It so happens that the addition of resistances to obtain on overall resistance is permissi- ble only when the rate is a linear function of the driving force and when the processes occur in series. 8
8

E17.4 OVERALL RATE FOR A NONLINEAR PROCESS Repeat Example 17.3 with just one change:let the reaction step be second order with respect to A,or rh2=-k"Ch SOLUTION Combining the reaction steps to eliminate CAs,as was done in Example 17.3,is now not so simple,and gives -店=-r=元=会2rC+-网+xC, m2.s 9
9

Contacting Patterns for Two-Phase Systems There are many ways that two phases can be contacted,and for each the design equation will be unique. When real flow deviates considerably from ideal flow patterns,we can do one of the two things:we may develop models to mirror actual flow closely,or we may calculate performance with ideal patterns which bracket actual flow. Five flow patterns: 10
10 • Contacting Patterns for Two-Phase Systems There are many ways that two phases can be contacted,and for each the design equation will be unique. • When real flow deviates considerably from ideal flow patterns, we can do one of the two things: we may develop models to mirror actual flow closely, or we may calculate performance with ideal patterns which bracket actual flow. • Five flow patterns:
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《化学反应工程》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chemical reaction engineering(2009)Chapter 01-05.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《化学反应工程》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)化学反应工程(第二版,共九章,负责人:郭锴).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第12章 过渡元素.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第11章 主族元素.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第05章 酸碱平衡(Acid-Base Equilibria).pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第10章 配位化合物和配位平衡.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第09章 化学键和分子结构.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第08章 原子结构和元素周期率.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第07章 氧化还原反应.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第06章 难溶电解质的沉淀溶解平衡.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第04章 化学反应速率及化学平衡.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第03章 化学热力学基础.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第02章 物质的聚集状态和溶液.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第01章 绪论 Fundamental Chemistry(负责人:李保山).pptx
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2013-2014学年第一学期《基础化学》期中考试试卷及参考答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《基础化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013学年第一学期国际班《基础化学》期中考试试卷及参考答案.pdf
- 《基础化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Quantum gas goes below absolute zero.doc
- 《基础化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)合成氨进展——科学家开发出氨合成节能技术.pdf
- 《基础化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)碘与指纹破案.pdf
- 《基础化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)诺贝尔化学奖全书(1901-2001)2/2.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《化学反应工程》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chemical reaction engineering(2010)Chapter 06-10.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《化学反应工程》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Chemical reaction engineering(2011)Chapter 11-15.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《有机分析》课程教学资源(实验指导,高职,文字版).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(大纲教材)天然药物化学中英文对照专业词汇(2009版).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(大纲教材)天然药物化学教学大纲(2014版).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(大纲教材)天然药物化学教学大纲(2015版).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(大纲教材)本科天然药物化学教学大纲(2017版).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(大纲教材)天然药物化学中英文对照专业词汇(2018版).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(复习题集)天然药物化学复习题(2014版,无答案).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(复习题集)本科学生专业选修课《有机分析》习题(无解答).pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程教学资源(复习题集)天然药物化学复习题(海洋天然产物,含答案).pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)D.S. Bhakuni&D.S. Rawat《Bioactive marine natural products》.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Deep-sea natural products.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Drugs from the Sea - Opportunities and Obstacles.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Marine-Sourced Anti-Cancer and Cancer Pain Control Agents in Clinical and Late Preclinical Development.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Highlights of marine natural products chemistry(1972–1999).pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Marine Organisms as Potential Supply for Drug Finding-A Review Study.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Marine Natural Products and Related Compounds in Clinical and Advanced Preclinical Trials.pdf
- 河北医科大学:《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Marine Pharmaceuticals.pdf
- 《天然药物化学》课程参考文献(海洋天然产物)Marketed Marine Natural Products in the Pharmaceutical and Cosmeceutical Industries - Tips for Success.pdf
