西安电子科技大学:《现代数字通信与编码理论》课程教学资源(讲义)Polar codes

State Key Laboratory of Integrated Services Networks 国家重点实验室 Polar Codes 西安电子科技大学SN 白宝明 2017.11.13
State Key Laboratory of Integrated Services Networks Polar Codes 西安电子科技大学ISN 白宝明 2017.11.13

N 国家重点实验室 Outline o Introduction o Channel Polarization o Construction Encoding Decoding o Performance o Open Problems 2
Outline Introduction Channel Polarization Construction Encoding & Decoding Performance Open Problems 2

国家重点实验室 Introduction Polar codes,invented by Erdal Arikan in 2008, are the first codes to provably achieve capacity 。特点: >Capacity-achieving for symmetric binary-input memoryless channels(包括Bl-AWGN,BSC,BEC) >Low encoding and decoding complexity:O(Nlog N) >Block error probability is roughly O(2-N) And this performance guarantee is analytical. >For symmetric channels,code construction is deterministic. That is,the above statements are true not only for ensembles of codes,but also for individual polar codes
Introduction Polar codes, invented by Erdal Arikan in 2008, are the first codes to provably achieve capacity. 特点: Capacity-achieving for symmetric binary-input memoryless channels (包括BI-AWGN, BSC, BEC) Low encoding and decoding complexity: Block error probability is roughly And this performance guarantee is analytical. For symmetric channels, code construction is deterministic. That is, the above statements are true not only for ensembles of codes, but also for individual polar codes. 3 ON N ( log ) (2 ) N O −

国家重点实验室 核心思想 o Channel Polarization >Create extreme channels:Either noiseless or useless. o Channel coding problem trivial for these two types of channels >Perfect channels:C(W)=1,the output Y determines the input X Useless channels:C(W)=0,the output Y is independent of the input X o Channel polarization is a technique to convert any binary-input channel into a mixture of binary-input extreme channels 。极化方法 >信道合并与分裂(由编译码共同完成) 4
核心思想 Channel Polarization Create extreme channels: Either noiseless or useless. Channel coding problem trivial for these two types of channels Perfect channels: C(W)=1, the output Y determines the input X Useless channels: C(W)=0, the output Y is independent of the input X Channel polarization is a technique to convert any binary-input channel into a mixture of binary-input extreme channels 极化方法 信道合并与分裂(由编译码共同完成) 4

N The Channel 国家重点实验室 Let w:be a binary-input discrete-memoryless channel X W >Input alphabet:=0,1 >Transition probabilities:W(ylx),x∈X,y∈y o Two independent uses of the channel W xi>w →Y xw→g Nindependent copies of W:WN:XN->YN w')=IIwG,I) 5
The Channel Let be a binary-input discrete-memoryless channel Input alphabet: Transition probabilities: , , Two independent uses of the channel W N independent copies of W: 5 X1 Y1 X2 Y2 W W W : → ={0,1} Wyx ( ) | x∈ y ∈ : NN N WX Y → 1 1 1 ( | ) (|) N N N N i i i W y x Wy x = =∏
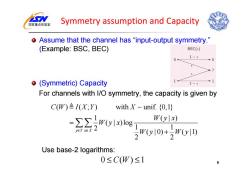
国家重点实验室 Symmetry assumption and Capacity o Assume that the channel has "input-output symmetry. (Example:BSC,BEC) BEC(c) 0 1-9 0 (Symmetric)Capacity 1 1-c For channels with I/O symmetry,the capacity is given by C(W)≌I(X;Y) with X unif.(0,1) =∑∑)W0y川x)log W(yx) eeX2 W(y川0)+,W0y1D) 2 Use base-2 logarithms: 0≤C(W)≤1 6
Symmetry assumption and Capacity Assume that the channel has “input-output symmetry.” (Example: BSC, BEC) (Symmetric) Capacity For channels with I/O symmetry, the capacity is given by Use base-2 logarithms: 6 ( ) ( ; ) with unif. {0,1} 1 (|) ( | )log 2 1 1 ( | 0) ( |1) 2 2 y Yx X CW I X Y X Wyx Wyx W y W y ∈ ∈ = + 0 ()1 ≤ ≤ C W

国家重点实验室 Symmetry assumption and Capacity o Bhattacharyya parameter Z(wW)兰∑√W(y10)w(y1西 o The parameters C(W)and Z(W)are used as measures of rate and reliability. Define the decision region for message m,D=yAIf(y)=m For codes with two codewords,the error probability,when message 2 is transmitted,is P.(eI2)=∑Pw(ylx2) yeD For yeD1,Py(ylx)P(ylx2)for ML decoding 。经过简单处理,有P.(2)≤∑VRyx)R) yeD 进而P,(em)≤∑VP(yIx)P(y) known as the Bhattacharyya bound on error probability 7
Symmetry assumption and Capacity Bhattacharyya parameter The parameters C(W) and Z(W) are used as measures of rate and reliability. Define the decision region for message m, For codes with two codewords, the error probability, when message 2 is transmitted, is 经过简单处理,有 进而 7 ( ) ( | 0) ( |1) y Y ZW W y W y ∈ { | () } N m Y =∈ = y y f m 1 2 ( | 2) ( | ) Pe P B N ∈ = y y x For y ∈ 1, for ML decoding 1 2 (| ) (| ) P P N N yx yx ≥ 1 1 2 ( | 2) ( | ) ( | ) Pe P P B NN ∈ ≤ y y x y x 1 2 ( | ) ( | ) ( | ) P em P P B NN ≤ y y x y x known as the Bhattacharyya bound on error probability

国家重点实验室 Main idea for channel polarization Channel coding problem trivial for two types of channels Perfect:C(W)=1 Useless:C(W)=0 Transform ordinary W into such extreme channels >Perfect channels:C(W)=1,the output Y determines the input X Useless channels:C(W)=0,the output Y is independent of the input X o Channel polarization is a technique to convert any binary-input channel into a mixture of binary-input extreme channels
Main idea for channel polarization Perfect channels: C(W)=1, the output Y determines the input X Useless channels: C(W)=0, the output Y is independent of the input X Channel polarization is a technique to convert any binary-input channel into a mixture of binary-input extreme channels 8
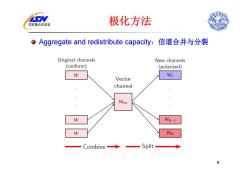
国家重点实验室 极化方法 。Aggregate and redistribute capacity:信道合并与分裂 Original channels New channels (uniform) (polarized) Wi Vector channel Wvec W WN-1 W WN Combine→ Split 9
极化方法 Aggregate and redistribute capacity:信道合并与分裂 9
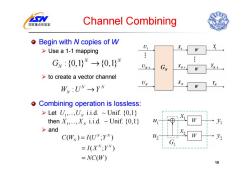
国家重点实验室 Channel Combining 0 Begin with N copies of W >Use a 1-1 mapping Gw:{0,1W→{0,1} UNA IN-1 >to create a vector channel UN W:UN→YW oCombining operation is lossless: >Let U.Uv i.i.d.-Unif.01 then X,.Xy i.i.d.~Unif.(01) >and C(W)=I(UN;YN) =I(XN:YN) =NC(W) 10
Channel Combining Begin with N copies of W Use a 1-1 mapping to create a vector channel Combining operation is lossless: Let then and 10 :{0,1} {0,1 } N N GN → : N N WU Y N → 1,., i.i.d. Unif. {0,1} U UN 1,., i.i.d. Unif. {0,1} X X N () (;) ( ; ) ( ) N N N N N CW IU Y I X Y NC W = = =
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代数字通信与编码理论》课程教学资源(讲义)Chapter 05 Coded-Modulation for Band-Limited AWGN Channels(5.1-5.8).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代数字通信与编码理论》课程教学资源(讲义)Chapter 04 Binary Capacity-Approaching Codes(4.8)Low-Density Parity-Check Codes.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代数字通信与编码理论》课程教学资源(讲义)Chapter 04 Binary Capacity-Approaching Codes(4.6-4.7).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代数字通信与编码理论》课程教学资源(讲义)Chapter 04 Binary Capacity-Approaching Codes(4.1-4.5).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代数字通信与编码理论》课程教学资源(讲义)Chapter 03 Performance Bounds of Coded Communication Systems.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代数字通信与编码理论》课程教学资源(讲义)Chapter 02 Modulation and Coding for Ideal Gaussian channels.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代数字通信与编码理论》课程教学资源(讲义)信息论与编码理论基础 Introduction to Channel Coding.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代数字通信与编码理论》课程教学资源(讲义)Chapter 01 Introduction(主讲:白宝明).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《信息论基础》课程教学资源(学习资料)MIMO信道容量 Channel.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《信息论基础》课程教学资源(学习资料)随机编码错误指数(Gallager bound).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《通信原理》课程教学资源(实验指导)通信原理仿真实验指导.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《通信原理》课程教学大纲 Principles of Communication(负责人:伍忠东).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《通信原理》课程各章作业习题(含参考答案).doc
- 《世界流行单片机技术手册》参考书籍(PDF)世界流行单片机技术手册——日本系列(主编:余永权,2002).pdf
- 《电子材料及元器件》参考教材PDF电子书(共十二章,含六个实验).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电工学》课程实验指导(打印版)电子技术实验指导.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电工学》课程实验指导(打印版)电工技术实验指导.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电工学》课程实验指导(打印版)电工电子实验指导.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电工学》课程授课教案(打印版)电工电子技术教案(二).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电工学》课程授课教案(打印版)电工电子技术教案(一).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代数字通信与编码理论》课程教学资源(讲义)Chapter 05 Coded-Modulation for Band-Limited AWGN Channels(5.9-5.14).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代数字通信与编码理论》课程教学资源(讲义)Chapter 07 Coding and Modulation for Fading Channels.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代数字通信与编码理论》课程教学资源(讲义)Chapter 08 Space-Time Coded-Modulation for Multiple Antenna Systems(for MIMO Channels).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《信息论与编码》课程教学资源(讲义,Information Theory and Coding,共八章,主讲:白宝明).pdf
- 石河子大学:《模拟电子技术》课程教学大纲 Analog electronic technique foundation(负责人:张宁).doc
- 石河子大学:《模拟电子技术》课程授课教案.doc
- 《模拟电子技术》课程教学资源(章节习题)半导体二极管及其应用(无答案).doc
- 《模拟电子技术》课程教学资源(章节习题)半导体三极管及其放大电路(无答案).doc
- 《模拟电子技术》课程教学资源(章节习题)场效应管及其放大电路(无答案).doc
- 《模拟电子技术》课程教学资源(章节习题)集成运算放大器(无答案).doc
- 《模拟电子技术》课程教学资源(习题集)第一章 半导体器件(含答案).doc
- 《模拟电子技术》课程教学资源(习题集)第二章 基本放大电路(含答案).doc
- 《模拟电子技术》课程教学资源(习题集)第三章 负反馈放大电路(含答案).doc
- 《模拟电子技术》课程教学资源(习题集)第四章 集成运算放大器(含答案).doc
- 《模拟电子技术》课程教学资源(习题集)第五章 功率放大电路(含答案).doc
- 《模拟电子技术》课程教学资源(习题集)第六章 直流稳压电源(含答案).doc
- 《模拟电子技术》课程习题课件(PPT)半导体元件.ppt
- 《模拟电子技术》课程习题课件(PPT)差分放大电路.ppt
- 《模拟电子技术》课程习题课件(PPT)负反馈放大电路.ppt
- 《模拟电子技术》课程习题课件(PPT)运算放大电路.ppt
