陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 6 Glass Containers 第6课 玻璃容器

Lesson 6 Glass Containers 第6课 玻璃容器 ⚫ Glass Types and General Properties ⚫ Bottle Manufacture ⚫ Bottle Design Features
Lesson 6 Glass Containers 第6课 玻璃容器 ⚫ Glass Types and General Properties ⚫ Bottle Manufacture ⚫ Bottle Design Features

一. Glass Types and General Properties ⚫ Definition and characters- an inorganic substance fused at high temperatures and cooled quickly ⚫ About the principle component -silica (quartz), ⚫ The ingredients of the components and different formulations. ⚫ Other mineral compounds be used to achieve improved properties: decolorizers – to clear; colorants– change the appearance. ⚫ Other glass types used for special packaging purposes. lead compounds, boron compounds, borosilicate glasses. ⚫ The problems of different formulations include soda-lime and regular container glass are mixed when recycling
一. Glass Types and General Properties ⚫ Definition and characters- an inorganic substance fused at high temperatures and cooled quickly ⚫ About the principle component -silica (quartz), ⚫ The ingredients of the components and different formulations. ⚫ Other mineral compounds be used to achieve improved properties: decolorizers – to clear; colorants– change the appearance. ⚫ Other glass types used for special packaging purposes. lead compounds, boron compounds, borosilicate glasses. ⚫ The problems of different formulations include soda-lime and regular container glass are mixed when recycling

一. Glass Types and General Properties Advantages as a packaging material: ⚫ inert to most chemicals ⚫ perfect foods container. ⚫ impermeability ⚫ clarity ⚫ perceived image ⚫ rigidity ⚫ stable at high temperatures Disadvantages : breakability; high weight; high energy costs
一. Glass Types and General Properties Advantages as a packaging material: ⚫ inert to most chemicals ⚫ perfect foods container. ⚫ impermeability ⚫ clarity ⚫ perceived image ⚫ rigidity ⚫ stable at high temperatures Disadvantages : breakability; high weight; high energy costs

二. Bottle Manufacture 1. Blowing the Bottle or Jar ⚫ Process: "blow-and-blow”; "press-and-blow" ⚫ two molds: blank mold forms the neck and the initial shape blow mold produce the final shape ⚫ A blank mold comes in a number of sections: finish section cavity section (made in two halves to allow parison removal) a guide or funnel for inserting the gob a seal for the gob opening once the gob is settled in the mold blowing tubes through the gob and neck openings
二. Bottle Manufacture 1. Blowing the Bottle or Jar ⚫ Process: "blow-and-blow”; "press-and-blow" ⚫ two molds: blank mold forms the neck and the initial shape blow mold produce the final shape ⚫ A blank mold comes in a number of sections: finish section cavity section (made in two halves to allow parison removal) a guide or funnel for inserting the gob a seal for the gob opening once the gob is settled in the mold blowing tubes through the gob and neck openings
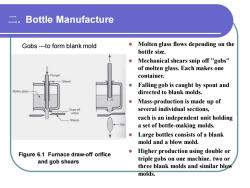
二. Bottle Manufacture Figure 6.1 Furnace draw-off orifice and gob shears ⚫ Molten glass flows depending on the bottle size. ⚫ Mechanical shears snip off "gobs" of molten glass. Each makes one container. ⚫ Falling gob is caught by spout and directed to blank molds. ⚫ Mass-production is made up of several individual sections, each is an independent unit holding a set of bottle-making molds. ⚫ Large bottles consists of a blank mold and a blow mold. ⚫ Higher production using double or triple gobs on one machine. two or three blank molds and similar blow molds. Gobs -to form blank mold
二. Bottle Manufacture Figure 6.1 Furnace draw-off orifice and gob shears ⚫ Molten glass flows depending on the bottle size. ⚫ Mechanical shears snip off "gobs" of molten glass. Each makes one container. ⚫ Falling gob is caught by spout and directed to blank molds. ⚫ Mass-production is made up of several individual sections, each is an independent unit holding a set of bottle-making molds. ⚫ Large bottles consists of a blank mold and a blow mold. ⚫ Higher production using double or triple gobs on one machine. two or three blank molds and similar blow molds. Gobs -to form blank mold

二. Bottle Manufacture ⚫ Blow-and-blow process-for narrow-necked bottles ⚫ The two processes differ according to the parison producing. ⚫ Blow-and-blow process: (Figure 6.2): 1. Gob dropped into the blank mold through a funnel-shaped guide (985°C) 2. parison bottomer replaced guide ;air blown into settle mold to force the finish section. At this point the bottle finish is complete. 3. Solid bottom plate replaced parison bottomer ; air is forced to expand the glass upward and form the parison. 4. Parison removed from the blank mold, rotated to a right-side-up orientation for placement into the blow mold. 5. Air forces the glass to conform to the shape of the blow mold. The bottle is cooled to stand without becoming distorted and is then placed on conveyors to the annealing oven
二. Bottle Manufacture ⚫ Blow-and-blow process-for narrow-necked bottles ⚫ The two processes differ according to the parison producing. ⚫ Blow-and-blow process: (Figure 6.2): 1. Gob dropped into the blank mold through a funnel-shaped guide (985°C) 2. parison bottomer replaced guide ;air blown into settle mold to force the finish section. At this point the bottle finish is complete. 3. Solid bottom plate replaced parison bottomer ; air is forced to expand the glass upward and form the parison. 4. Parison removed from the blank mold, rotated to a right-side-up orientation for placement into the blow mold. 5. Air forces the glass to conform to the shape of the blow mold. The bottle is cooled to stand without becoming distorted and is then placed on conveyors to the annealing oven

二. Bottle Manufacture Figure 6.2 Blow-and-blow bottle manufacture
二. Bottle Manufacture Figure 6.2 Blow-and-blow bottle manufacture

二. Bottle Manufacture Figure 6.3 Press and blow forms the parison by mechanical action ⚫ Gob delivery and settle-blow steps are similar to blow-and-blow forming. ⚫ Parison is pressed into shape with a metal plunger rather than blown into shape(Figure 6.3). ⚫ The final blowing step is identical to the blow-and-blow process. ⚫ Used for smaller necked containers. ⚫ Better control of glass distribution press-and-blow process-for wide-mouthed jars
二. Bottle Manufacture Figure 6.3 Press and blow forms the parison by mechanical action ⚫ Gob delivery and settle-blow steps are similar to blow-and-blow forming. ⚫ Parison is pressed into shape with a metal plunger rather than blown into shape(Figure 6.3). ⚫ The final blowing step is identical to the blow-and-blow process. ⚫ Used for smaller necked containers. ⚫ Better control of glass distribution press-and-blow process-for wide-mouthed jars

二. Bottle Manufacture Difference of the two processes ⚫ Blow-and-blow used for narrow-necked bottles. Press-and-blow used to make wide-mouthed jars and for increasingly smaller necked containers. Better control of glass distribution. ⚫ Typical production rates range from 60 to 300 bottles per minute, depending on the number of sections in a machine, the number of gobs being extruded, and the size of the container. ⚫ The blown bottle is removed from the blow mold with takeout tongs and placed on a deadplate to air cool for a few moments before transfer to a conveyor that transports it to the annealing oven
二. Bottle Manufacture Difference of the two processes ⚫ Blow-and-blow used for narrow-necked bottles. Press-and-blow used to make wide-mouthed jars and for increasingly smaller necked containers. Better control of glass distribution. ⚫ Typical production rates range from 60 to 300 bottles per minute, depending on the number of sections in a machine, the number of gobs being extruded, and the size of the container. ⚫ The blown bottle is removed from the blow mold with takeout tongs and placed on a deadplate to air cool for a few moments before transfer to a conveyor that transports it to the annealing oven

二. Bottle Manufacture 2. Annealing ⚫ Purpose-to reduce internal stresses; in annealing oven ⚫ Reasons- Walls are comparatively thick and cooling will not be even. The inner and outer skins of a glass become rigid The still-contracting inner portion build up internal stresses Uneven cooling develop substantial stresses in the glass. ⚫ Bottle passes through an lehr after removal from the blow mold. ⚫ Steps : glassware is carried on a moving belt temperature is raised to about 565°C gradually cooled to room temperature with all internal stresses reduced to safe levels.(about an hour) ⚫ Improperly annealed bottles are fragile and high breakage ⚫ Hot-filling also produce unacceptable breakage levels
二. Bottle Manufacture 2. Annealing ⚫ Purpose-to reduce internal stresses; in annealing oven ⚫ Reasons- Walls are comparatively thick and cooling will not be even. The inner and outer skins of a glass become rigid The still-contracting inner portion build up internal stresses Uneven cooling develop substantial stresses in the glass. ⚫ Bottle passes through an lehr after removal from the blow mold. ⚫ Steps : glassware is carried on a moving belt temperature is raised to about 565°C gradually cooled to room temperature with all internal stresses reduced to safe levels.(about an hour) ⚫ Improperly annealed bottles are fragile and high breakage ⚫ Hot-filling also produce unacceptable breakage levels
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 5 Metal Containers 第5课 金属容器.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 4 Corrugated Fiberboard Boxes 第4课 瓦楞纸板箱.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 3 Paper and Paperboard 第3课 纸与纸板.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 2 Packaging Functions 第2课 包装的功能.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 20 Filling Systems 第20课 充填灌装系统.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 1 A History of Packaging 第1课 包装发展史.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 19 The Packaging Line 第19课 包装线.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 18 General Overview 第18课 概述.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 17 Computer Aided Packaging System 第17课 计算辅助包装设计系统.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 16 Distribution Packaging 第16课 运输包装.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 15 Seven Steps for Cushioned Package Development 第15课 缓冲包装设计七步法.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 14 Test Method for Product Fragility 第14课 产品脆值试验方法.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 13 Mechanical Shock Theory 第13课 机械冲击理论.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 12 Shock, Vi ation, and Compression 第12课 冲击、振动和受压.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 11 Package Printing 第11课 包装印刷.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 10 Graphic Design in Packaging 第10课 包装中的平面设计.ppt
- 石河子大学:《工业工程基础》课程PPT教学课件(农机专业,2012)第8章 生产率.ppt
- 石河子大学:《工业工程基础》课程PPT教学课件(农机专业,2012)第4章 工作研究概述.ppt
- 石河子大学:《工业工程基础》课程PPT教学课件(农机专业,2012)现场管理.ppt
- 石河子大学:《工业工程基础》课程PPT教学课件(农机专业,2012)第一章 工业工程概述(1.1)工业工程的发展和作用(主讲人:张慧明).ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 7 Plastics in Packaging 第7课 塑料在包装中的应用.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 8 Flexible Packaging Laminates 第8课 软包装复合材料.ppt
- 陕西科技大学:《包装技术基础 Fundamentals of Packaging Technology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lesson 9 Color 第9课 颜色.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流体力学基础 1.1 第一节 空气在管道中流动的基本规律.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流体力学基础 1.2 第二节 流动阻力和能量损失.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流体力学基础 1.3 第三节 管路中的压力、速度和流量的测量.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)风机 2.1 第一节 离心式通风机的构造和工作原理.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)风机 2.2 第二节 离心式通风机的性能参数.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)风机 2.3 第三节 离心式通风机的选择.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)风机 2.4 第四节 离心式通风机的安装与使用.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)通风除尘技术 3.1 第一节 粉尘.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)通风除尘技术 3.2 第二节 含尘浓度、卫生标准和排放标准.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)通风除尘技术 3.3 第三节 粮食厂仓控制粉尘的通风除尘.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)通风除尘技术 3.4 第四节 除尘器.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)通风除尘技术 3.5 第五节 通风除尘网络的设计与计算.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)通风除尘技术 4.1 气力输送技术A.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)通风除尘技术 4.2 气力输送技术B.ppt
- 沈阳师范大学:《通风除尘与物料输送》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)机械输送技术(主讲教师:陈革).ppt
- 《食品工厂设计与环境保护》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)绪论.ppt
- 《食品工厂设计与环境保护》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 基本建设程序和工厂设计的内容.ppt
