中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O-pres

Key ingredients to achieve effective 1/O 4 asycop nct caching c/e Key ingredients to achieve effective l/O Sebastien Ponce sebastien.ponce@cern.ch CERN Thematic CERN School of Computing 2018 1/57 S.Ponce-CERN
Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O 1 / 57 S. Ponce - CERN async IOopt struct caching c/c Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O S´ebastien Ponce sebastien.ponce@cern.ch CERN Thematic CERN School of Computing 2018

Key ingredients to achieve effective 1/O 4,yme0op时nct caching c/c In the previous episodes... o We've found out how to store data efficiently o And how to distribute it o We've learnt how to detect data corruptions o And made sure our data was safe and consistent 2/57 S.Ponce-CERN
Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O 2 / 57 S. Ponce - CERN async IOopt struct caching c/c In the previous episodes... We’ve found out how to store data efficiently And how to distribute it We’ve learnt how to detect data corruptions And made sure our data was safe and consistent Today How do we use them ? Efficiently

Key ingredients to achieve effective 1/O syme 0opt snict caching c/e “ In the previous episodes... o We've found out how to store data efficiently o And how to distribute it o We've learnt how to detect data corruptions o And made sure our data was safe and consistent Today How do we use them Efficiently 2/57 S.Ponce-CERN
Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O 2 / 57 S. Ponce - CERN async IOopt struct caching c/c In the previous episodes... We’ve found out how to store data efficiently And how to distribute it We’ve learnt how to detect data corruptions And made sure our data was safe and consistent Today How do we use them ? Efficiently

Key ingredients to achieve effective 1/O ye I(op nct caching c/e Outline ① Asynchronous 1/O Latency Asynchronous l/O interfaces ●Message queues 2 I/O optimizations Optimizing network transfers Optimizing local transfers Influence of data structures on I/O o Measuring I/O efficiency of algorithms Caching o Principles Policies ●Distributed Caches 3 Conclusion 3/57 S.Ponce-CERN
Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O 3 / 57 S. Ponce - CERN async IOopt struct caching c/c Outline 1 Asynchronous I/O Latency Asynchronous I/O interfaces Message queues 2 I/O optimizations Optimizing network transfers Optimizing local transfers 3 Influence of data structures on I/O Measuring I/O efficiency of algorithms 4 Caching Principles Policies Distributed Caches 5 Conclusion

Key ingredients to achieve effective 1/O 4心async0op时anet caching c/e Asynchronous 1/O ①Asynchronous I/O Latency Asynchronous l/O interfaces ·Message queues ②l/0 optimizations Influence of data structures on 1/O Caching Conclusion tancy ac mi名 4/57 S.Ponce-CERN
Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O 4 / 57 S. Ponce - CERN async IOopt struct caching c/c latency async msgQ Asynchronous I/O 1 Asynchronous I/O Latency Asynchronous I/O interfaces Message queues 2 I/O optimizations 3 Influence of data structures on I/O 4 Caching 5 Conclusion
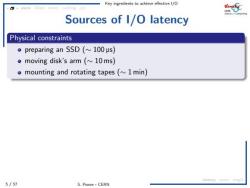
Key ingredients to achieve effective 1/O asyne l0op nact cachincc 花5 Sources of I/O latency Physical constraints preparing an SSD(~100 us) omoving disk's arm (~10ms) omounting and rotating tapes(1 min) latency amc mig 5/57 S.Ponce-CERN
Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O 5 / 57 S. Ponce - CERN async IOopt struct caching c/c latency async msgQ Sources of I/O latency Physical constraints preparing an SSD (∼ 100 ➭s) moving disk’s arm (∼ 10 ms) mounting and rotating tapes (∼ 1 min) Network infrastructure number of switches routers on the way 200 ➭s delay per switch/router “slow” speed of light “speed” of light is slower in a fiber (refractive index 1.47) that gives around 200 m ➭s −1 or 20 cm ns −1 Budapest’s ping time from CERN is ∼21 ms for ∼2500 km
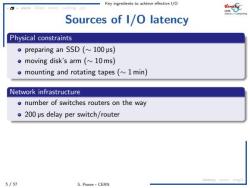
Key ingredients to achieve effective 1/O caching c/c Sources of 1/O latency Physical constraints preparing an SSD(~100 us) omoving disk's arm (~10ms) o mounting and rotating tapes(1 min) Network infrastructure o number of switches routers on the way o 200 us delay per switch/router latency ac mig 5/57 S.Ponce-CERN
Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O 5 / 57 S. Ponce - CERN async IOopt struct caching c/c latency async msgQ Sources of I/O latency Physical constraints preparing an SSD (∼ 100 ➭s) moving disk’s arm (∼ 10 ms) mounting and rotating tapes (∼ 1 min) Network infrastructure number of switches routers on the way 200 ➭s delay per switch/router “slow” speed of light “speed” of light is slower in a fiber (refractive index 1.47) that gives around 200 m ➭s −1 or 20 cm ns −1 Budapest’s ping time from CERN is ∼21 ms for ∼2500 km
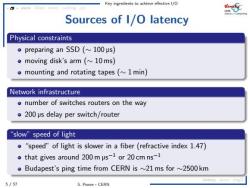
Key ingredients to achieve effective 1/O asyncOop4nut caching c/c Sources of I/O latency Physical constraints preparing an SSD(~100 us) moving disk's arm (10ms) o mounting and rotating tapes(~1 min) Network infrastructure o number of switches routers on the way 200 us delay per switch/router "slow"speed of light "speed"of light is slower in a fiber(refractive index 1.47) ·that gives around200mμs-1or20cmns-1 o Budapest's ping time from CERN is ~21ms for ~2500km latency ac mig 5/57 S.Ponce-CERN
Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O 5 / 57 S. Ponce - CERN async IOopt struct caching c/c latency async msgQ Sources of I/O latency Physical constraints preparing an SSD (∼ 100 ➭s) moving disk’s arm (∼ 10 ms) mounting and rotating tapes (∼ 1 min) Network infrastructure number of switches routers on the way 200 ➭s delay per switch/router “slow” speed of light “speed” of light is slower in a fiber (refractive index 1.47) that gives around 200 m ➭s −1 or 20 cm ns−1 Budapest’s ping time from CERN is ∼21 ms for ∼2500 km
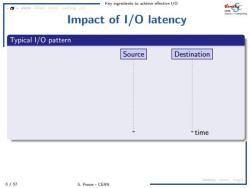
Key ingredients to achieve effective 1/O asyne l0op nact cachinc Impact of I/O latency Typical I/O pattern Source Destination time latency ac mg 6/57 S.Ponce-CERN
Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O 6 / 57 S. Ponce - CERN async IOopt struct caching c/c latency async msgQ Impact of I/O latency Typical I/O pattern send a packet to destination wait for ack go to next block Source Destination time sending time efficiency = sending time sending time + ping time
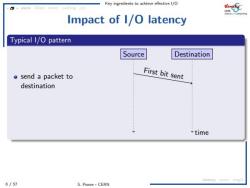
Key ingredients to achieve effective 1/O asyne l0op nact cachinc Impact of I/O latency Typical I/O pattern Source Destination ●send a packet to First bit sent destination time 6/57 latency c mig S.Ponce-CERN
Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O 6 / 57 S. Ponce - CERN async IOopt struct caching c/c latency async msgQ Impact of I/O latency Typical I/O pattern send a packet to destination wait for ack go to next block Source Destination time First bit sent sending time efficiency = sending time sending time + ping time
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Preserving data-booklet.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Optimizing existing large codebase-booklet.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Optimizing existing large codebase-pres.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Preserving data-pres.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Many ways to store data-booklet.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Many ways to store data-pres.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Structuring data for efficient I/O-booklet.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Structuring data for efficient I/O-pres.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Optimizing existing large codebase-booklet.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Optimizing existing large codebase-pres.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Modern programming languages for HEP-booklet.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Modern programming languages for HEP-pres.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Practical vectorization-booklet.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Practical vectorization-pres.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Writing Parallel software(booklet).pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Writing Parallel software(pres).pdf
- 中国科学院高能所计算中心:数据技术上机 Data Technologies – CERN School of Computing 2019.pdf
- 中国科学院高能所计算中心:数据技术课程 CSC 2018 Data Technologies Exercises(CSC DT 2018 Introduction).pdf
- 中国科学院高能所计算中心:高能物理数据的存储和管理(汪璐).pptx
- 南京大学:《数据结构 Data Structures》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第九章 排序.ppt
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Key ingredients to achieve effective I/O-booklet.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Data storage and preservation-pres.pdf
- 中国科学院:CERN专题计算学校《T-CSC数据存储》课程教学资源(讲义)Data storage and preservation-booklet.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(授课教案)第1章 绪论(许录平).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(授课教案)第2章 数字图像处理基础.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(授课教案)第3章 图像变换.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(授课教案)第4章 图像增强.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(授课教案)第5章 图象恢复.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(授课教案)第6章 图像压缩编码.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(授课教案)第7章 图像分割.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(授课教案)第8章 图像描述.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(授课教案)第9章 图像分类识别.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(作业习题)各章要求及必做题参考答案.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(实验指导)数字图像处理与Matlab.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(实验指导)上机辅导讲义 - Matlab简介.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数学图像处理 Digital Image Processing Digital Image Processing》课程教学资源(实验指导)数字图像处理上机实验题.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《计算机应用基础》课程教学大纲 Fundamentals of Computer Application(打印版).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《计算机应用基础》课程授课教案 Fundamentals of Computer Application(打印版).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《现代密码学理论与实践》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第1章 引言 Introduction(主讲:杨寿保).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《现代密码学理论与实践》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第2章 传统加密技术 Classical Encryption Techniques.ppt
