同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 03Top-down and bottom-up design

Chapter 3 Part 1:Top-down Program Design Part 2:Relational and Logical Operators @日济大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Chapter 3 Part 1: Top-down Program Design Part 2: Relational and Logical Operators

Top-down Program Design(1/14) Top-down and bottom-up design Top-down and bottom-up are both strategies o,mostly involving software. Top-down design is the process of starting with a large task and breaking it down into smaller,more easily understandable pieces(subtasks),which perform a portion of the desired task. Bottom-up design is the piecing together of systems to give rise to grander systems,thus making the original systems sub-systems of the emergent system. @月停大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
➢ Top-down and bottom-up design Top-down and bottom-up are both strategies o, mostly involving software. ✓ Top-down design is the process of starting with a large task and breaking it down into smaller, more easily understandable pieces(subtasks), which perform a portion of the desired task. ✓ Bottom-up design is the piecing together of systems to give rise to grander systems, thus making the original systems sub-systems of the emergent system. Top-down Program Design(1/14)

Top-down Program Design(2/14) >The top-down design progress Clearly state the problem that you are trying to solve. Define the inputs required by the program and the outputs to be produced by the program. Design the algorithm that you intend to implement in the program. Turn the algorithm into MATLAB statement. Test the resulting MATLAB program. @日济大学 AW TONGJI UNIVERSITY
➢ The top-down design progress ✓ Clearly state the problem that you are trying to solve. ✓ Define the inputs required by the program and the outputs to be produced by the program. ✓ Design the algorithm that you intend to implement in the program. ✓ Turn the algorithm into MATLAB statement. ✓ Test the resulting MATLAB program. Top-down Program Design(2/14)
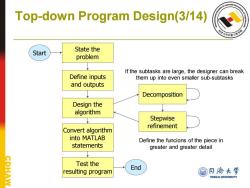
Top-down Program Design(3/14) Start State the problem If the subtasks are large,the designer can break Define inputs them up into even smaller sub-subtasks and outputs Decomposition Design the algorithm Stepwise refinement Convert algorithm into MATLAB Define the funcions of the piece in statements greater and greater detail CDHAW Test the End resulting program @月两大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Start State the problem Define inputs and outputs Design the algorithm Convert algorithm into MATLAB statements Test the resulting program End Decomposition Stepwise refinement If the subtasks are large, the designer can break them up into even smaller sub-subtasks Define the funcions of the piece in greater and greater detail Top-down Program Design(3/14)

Top-down Program Design(4/14) Pseudocode >As a part of the design process,it is necessary to describe the algorithm that you intend to implement. >The description of the algorithm should be in a standard form that is easy for both you and other people to understand, and it should aid you in turning your concept into MATLAB code. Pseudocode @日济大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
➢ As a part of the design process, it is necessary to describe the algorithm that you intend to implement. ➢ The description of the algorithm should be in a standard form that is easy for both you and other people to understand, and it should aid you in turning your concept into MATLAB code. Pseudocode Top-down Program Design(4/14) Pseudocode

Top-down Program Design(5/14) Pseudocode >A hybrid mixture of MATLAB and English for defining algorithms. >Independent of any programming language so it can be easily converted to any programming language Example pseudocode: Prompt user to enter temperature in degrees Fahrenheit Read temperature in degrees Fahrenheit (temp f) temp_k (in Kelvins)<(5/9)*(temp_f-32)+273.15 Write temperature in degree Kelvins @月停大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
➢ A hybrid mixture of MATLAB and English for defining algorithms. ➢ Independent of any programming language so it can be easily converted to any programming language ➢ Example pseudocode: Prompt user to enter temperature in degrees Fahrenheit Read temperature in degrees Fahrenheit (temp_f) temp_k (in Kelvins) (5/9) * (temp_f – 32) + 273.15 Write temperature in degree Kelvins Top-down Program Design(5/14) Pseudocode

Top-down Program Design(6/14) Testing In a large programming project,the time actually spent programming is surprisingly small. In the book The Mythical Man-Month,Frederick P.Brooks,ir suggests that in a typical large software project: 1/6 of the time is spent writing the program 1/3 of the time is spent planning what to do 1/2 of the time is spent testing @日济大学 AW TONGJI UNIVERSITY
➢ In a large programming project, the time actually spent programming is surprisingly small. ➢ In the book The Mythical Man-Month,Frederick P.Brooks,jr suggests that in a typical large software project: ✓ 1/6 of the time is spent writing the program ✓ 1/3 of the time is spent planning what to do ✓ 1/2 of the time is spent testing Top-down Program Design(6/14) Testing

Top-down Program Design(7/14) Testing >A typical testing process for large program Test individual subtasks:unit testing Add tested components one by one and test them together: build √Alpha release Beta release n√Finished program @凡两大学 AW TONGJI UNIVERSITY
➢ A typical testing process for large program ✓ Test individual subtasks: unit testing ✓ Add tested components one by one and test them together: build ✓ Alpha release ✓ Beta release ✓ Finished program Top-down Program Design(7/14) Testing

Top-down Program Design(8/14) Testing When we have written a program and it is not working, how do we debugging? >Three types of errors are found in MATLAB programs. √Syntax error Caused by the spelling errors or punctuation errors. >x=(y+3)/2) ?x=(y+3)/2) Error:Unbalanced or misused parentheses or brackets. Solution:Check spelling and punctuation 同濟大学 AW TONGJI UNIVERSITY
When we have written a program and it is not working, how do we debugging? ➢ Three types of errors are found in MATLAB programs. ✓ Syntax error Caused by the spelling errors or punctuation errors. Solution: Check spelling and punctuation Top-down Program Design(8/14) Testing

Top-down Program Design(9/14) Testing √Run-time error It occurs when an illegal mathematical operation is attempted during program execution.(For example attempting to divide by 0) >>x=pi/log(1) Warning:Divide by zero. X= Inf Solution: 2 ·Check input data Can remove“,”or add“disp'statements @月停大学 AW TONGJI UNIVERSITY
✓ Run-time error It occurs when an illegal mathematical operation is attempted during program execution. (For example , attempting to divide by 0) Solution: • Check input data • Can remove “;” or add “disp” statements Top-down Program Design(9/14) Testing
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 02 MATLAB Basics(负责人:陈明).ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 01 MATLAB Programming for Mechanical Engineering(Introduction to MATLAB).ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Final Examination(B)The First Semester(2013-2014).pdf
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Final Examination(A)The First Semester(2013-2014).pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 齿轮.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 平面机构的结构分析.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 其他常见机构.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第9章 机械中的摩擦与效率.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 凸轮机构.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第10章 机械的平衡.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 轮系(Gear Train).pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 平面机构的运动分析(Kinematic Analysis).pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 平面四杆机构.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 绪论(负责人:倪娟).pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第1章 绪论(打印版).pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第9章 机械中的摩擦和效率.doc
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第8章 其他常用机构.doc
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第11章 机械系统运动方案的设计.doc
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第10章 机械的平衡.doc
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第6章 齿轮机构.doc
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 04 Branches and Loops.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 05 Plotting.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 06 User-defined Functions.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 07 Sparse Arrays, Cell Arrays, and Structures.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 08 Advanced Mathematics.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 09 Probability and statistics.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Graphical User Interface.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Simulink.pptx
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第一章 内燃机工作原理及总体构造 The Working Principles and Overall Structure of Internal Combustion Engines.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第二章 机体组及曲柄连杆机构 Engine Block, Crank and Connecting Rod Mechanism.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第三章 配气机构 Valve Trains(负责人:李理光).pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第四章 汽油机燃油供给系统 Fuel Supply System For Gasoline Engine.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第六章 进气、排气及增压系统 Intake, Exhaust and Boost Systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第五章 柴油机燃油供给系统 Fuel Supply System for Diesel Engines.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第七章 发动机冷却系 Cooling System.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第九章 起动系统 Starting System.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第八章 发动机润滑系 Lubrication System for Automotive Engines.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十章 发动机点火系统 Engine Ignition System.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十二章 发动机有害排放物的控制系统 Control System of Harmful Emissions in Engine Exhaust.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Automobile structure(Types of modern automobiles).pdf
