同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Simulink

S 11:Simulink 令a形 Part 1:What is Simulink Part 2:Create a new simulation Part 3:Build a model Part 4:Create subsystems Part 5:Run the simulation ▣Part6:Exercises @日济大学 AW TONGJI UNIVERSITY
11: Simulink Part 1: What is Simulink Part 2: Create a new simulation Part 3: Build a model Part 4: Create subsystems Part 5: Run the simulation Part 6: Exercises

Simulink What is Simulink +形 Simulink is a software used in academia and industries for modeling,simulating and analyzing dynamical systems. It supports linear and non linear systems,modeled in continuous time and/or sampled time. The modeling part is done by using a graphical user interface (GUD)for building models as block diagrams.Simulink includes a block library of sinks,sources,linear and nonlinear components and connectors. @月协大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Simulink What is Simulink ➢ Simulink is a software used in academia and industries for modeling, simulating and analyzing dynamical systems. ➢ It supports linear and non linear systems, modeled in continuous time and/or sampled time. ➢ The modeling part is done by using a graphical user interface (GUI) for building models as block diagrams. Simulink includes a block library of sinks, sources, linear and nonlinear components and connectors

Simulink What is Simulink >After you define a model,you can simulate it using a choice of integration methods from Simulink or by entering commands in MATLAB's command window. Model analysis tools include linearization and trimming tools which can be accessed from the MATLAB command line,plus the tools in MATLAB and its application toolboxes. MATLAB and Simulink are integrated.It is therefore possible to simulate,analyze and revise the models in either environment at any point. 同濟大学 AW TONGJI UNIVERSITY
➢ After you define a model, you can simulate it using a choice of integration methods from Simulink or by entering commands in MATLAB’s command window. ➢ Model analysis tools include linearization and trimming tools which can be accessed from the MATLAB command line, plus the tools in MATLAB and its application toolboxes. ➢ MATLAB and Simulink are integrated. It is therefore possible to simulate, analyze and revise the models in either environment at any point. Simulink What is Simulink
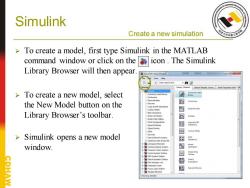
Simulink Create a new simulation To create a model,first type Simulink in the MATLAB command window or click on the icon.The Simulink Library Browser will then appear rary Browser 回x ·约窗 >To create a new model,select y Usedbc the New Model button on the 四 Library Browser's toolbar. 四 Ports Subsystems 国 6o Sinks 回 >Simulink opens a new model 图 e window. DSP System Topbo 回 Embedded Coder Fuzzy Loglc Toob 图 Gauges Blocks
Simulink Create a new simulation ➢ To create a model, first type Simulink in the MATLAB command window or click on the icon . The Simulink Library Browser will then appear. ➢ To create a new model, select the New Model button on the Library Browser’s toolbar. ➢ Simulink opens a new model window

Simulink Build a model:Bloc Library The model is creating by copying blocks into the model from the Simulink block libraries. untitled" -回x Each icon in the main File Edit View Simulation Format Tools Help 03日每¥电自|中→分|22|,■而 Simulink window can be double clicked to bring up the corresponding block library.Blocks in each library can then be dragged into a model R100% ode45 window to build a model 同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Simulink Build a model: Bloc Library ➢ The model is creating by copying blocks into the model from the Simulink block libraries. ➢ Each icon in the main Simulink window can be double clicked to bring up the corresponding block library. Blocks in each library can then be dragged into a model window to build a model
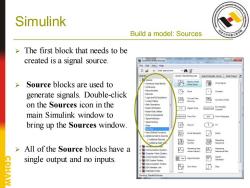
Simulink Build a model:Sources The first block that needs to be created is a signal source. Simulink Lbrary Browser -回 File Edit View Help Enter search term ·封首 Lbeary Sim/iniu/Sources Search Rasuts (none)Most Freque Source blocks are used to ☒e 哑 generate signals.Double-click -Discrete © 回 Logic and Bt Operations -Lookup Tables 四 四 on the Sources icon in the -Math Operations □ main Simulink window to Ports&Subsystems Signal Attribute与 From File -Signal Routing bring up the Sources window. Srts 昏 Ground 1○t 四 Pulse Gonerao ☑ Ramp Addiconal Discrele -Addoonal lath: 四 逊 >All of the Source blocks have a 四 e25 四 aa2sa single output and no inputs 图可 slgnlEuildo SP System loaibax 同 里Data AcqutionToob EDASi-ulator Link 母 Sine Wave 四 Embedded Code wing:Simulnk/Sources
Simulink Build a model: Sources ➢ The first block that needs to be created is a signal source. ➢ Source blocks are used to generate signals. Double-click on the Sources icon in the main Simulink window to bring up the Sources window. ➢ All of the Source blocks have a single output and no inputs

Simulink Build a model:Sources The proprieties of the source can be modified in the Source Block Parameters window by double clicking on the block. Source Block Parameters:Sine Wave Parameters For example,for a Sine Wave Sine type:Time based signal,the common parameters Time(t):Use simulation time Amplitude: to set consist in the Amplitude Bias: and the Frequency 0 Frequency(rad/sec): untitled' -回X mulation Format Phase(rad): Tools Help 0 Sample time: 0 Interpret vector parameters as 1-D HAW 100% OK Cancel Help
Simulink Build a model: Sources ➢ The proprieties of the source can be modified in the Source Block Parameters window by double clicking on the block. ➢ For example, for a Sine Wave signal, the common parameters to set consist in the Amplitude and the Frequency

Simulink Build a model:Block categories > Copy the rest of the blocks in a similar manner from their respective libraries into the model window. Each block's behavior can be modified by double clicking on it and by modifying its properties or its behavior's equations. The Continuous Blocks are elements of continuous-time dynamic systems.For example,Derivate makes the output equal to the derivative of the input. @月停大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
➢ Copy the rest of the blocks in a similar manner from their respective libraries into the model window. ➢ Each block’s behavior can be modified by double clicking on it and by modifying its properties or its behavior’s equations. ➢ The Continuous Blocks are elements of continuous-time dynamic systems. For example, Derivate makes the output equal to the derivative of the input. Simulink Build a model: Block categories
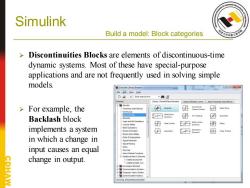
Simulink Build a model:Block categories > Discontinuities Blocks are elements of discontinuous-time dynamic systems.Most of these have special-purpose applications and are not frequently used in solving simple models. Simulink Library Brower Eile Edit View Help D ·刺百 Search Resuts:(none)Most Frequentty Used Blacks For example,the Comronly Used Blocks 诏sata 田 asaon 出 Backlash block m 好 Crng 超 -Lookup Tables 招 Rate Limiter 围 Relay implements a system Wath Operatons satuaton 回 Wrap Te Zeo in which a change in 0r&3u3ys input causes an equal er-er change in output. AW
Simulink Build a model: Block categories ➢ Discontinuities Blocks are elements of discontinuous-time dynamic systems. Most of these have special-purpose applications and are not frequently used in solving simple models. ➢ For example, the Backlash block implements a system in which a change in input causes an equal change in output

Simulink Build a model:Block categories Discrete Blocks are elements of discrete time dynamic systems. Simulink Library Browser 口回x Eile Edit yewe > Enter sea As an example,the Difference block outputs 常 8w7ao the current input value L9 kup ae minus the previous input 哥 包 何 母 value. 侧 Unit Delsy -Sources User-Detned Functions 四 2-0d 2 Control System Toolbo @月停大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Simulink Build a model: Block categories ➢ Discrete Blocks are elements of discrete time dynamic systems. ➢ As an example, the Difference block outputs the current input value minus the previous input value
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Graphical User Interface.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 09 Probability and statistics.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 08 Advanced Mathematics.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 07 Sparse Arrays, Cell Arrays, and Structures.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 06 User-defined Functions.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 05 Plotting.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 04 Branches and Loops.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 03Top-down and bottom-up design.ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 02 MATLAB Basics(负责人:陈明).ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 01 MATLAB Programming for Mechanical Engineering(Introduction to MATLAB).ppt
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Final Examination(B)The First Semester(2013-2014).pdf
- 同济大学:《Matlab在机械设计中的应用》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Final Examination(A)The First Semester(2013-2014).pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 齿轮.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 平面机构的结构分析.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 其他常见机构.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第9章 机械中的摩擦与效率.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 凸轮机构.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第10章 机械的平衡.pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 轮系(Gear Train).pdf
- 运城学院:《机械原理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 平面机构的运动分析(Kinematic Analysis).pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第一章 内燃机工作原理及总体构造 The Working Principles and Overall Structure of Internal Combustion Engines.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第二章 机体组及曲柄连杆机构 Engine Block, Crank and Connecting Rod Mechanism.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第三章 配气机构 Valve Trains(负责人:李理光).pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第四章 汽油机燃油供给系统 Fuel Supply System For Gasoline Engine.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第六章 进气、排气及增压系统 Intake, Exhaust and Boost Systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第五章 柴油机燃油供给系统 Fuel Supply System for Diesel Engines.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第七章 发动机冷却系 Cooling System.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第九章 起动系统 Starting System.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第八章 发动机润滑系 Lubrication System for Automotive Engines.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十章 发动机点火系统 Engine Ignition System.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十二章 发动机有害排放物的控制系统 Control System of Harmful Emissions in Engine Exhaust.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Automobile structure(Types of modern automobiles).pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 13 传动系统 Overview of automobile drivetrain.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 14 离合器 Clutch.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 15 变速箱 Transmission and transfer case.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 16 自动变速器 Vehicle Automatic transmission.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 17 传动装置 Universal Gearing.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 18 驱动桥 Driving Axle.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 传动装置 Running Gear.pdf
- 同济大学:《汽车构造》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 20 车架和车身 Frame and Monocoque Body.pdf
