上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)05 第二相颗粒 Particle strengthening(2/2)
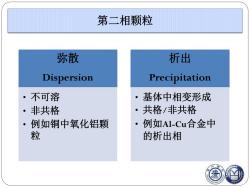
第二相颗粒 弥散 析出 Dispersion Precipitation 不可溶 基体中相变形成 。非共格 ·共格/非共格 例如铜中氧化铝颗 例如Al-Cu合金中 粒 的析出相
第二相颗粒 弥散 Dispersion • 不可溶 • 非共格 • 例如铜中氧化铝颗 粒 析出 Precipitation • 基体中相变形成 • 共格/非共格 • 例如Al-Cu合金中 的析出相
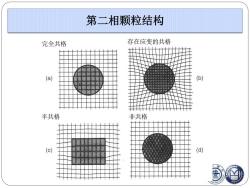
第二相颗粒结构 完全共格 存在应变的共格 (a) (b) 半共格 非共格 (c) (d)
完全共格 存在应变的共格 半共格 非共格 第二相颗粒结构

Summary Dislocations can interact with the stress fields of precipitates. Moving dislocations can: 1.glide through coherent precipitates->shearing the precipitate. 2.bow around incoherent precipitates,leaving loops as they bypass two precipitates which act like pinning centres for the dislocations leading to an increase in the dislocation density). Both these processes need an application of higher stresses (assuming an harder precipitate)lead to the strengthening of the material. ▣ Semi-coherent precipitates have interfacial misfit dislocations which partially relieve the coherency strains.(These dislocations are structural dislocations). 轨
Summary 4 q Dislocations can interact with the stress fields of precipitates. q Moving dislocations can: 1. glide through coherent precipitates → shearing the precipitate. 2. bow around incoherent precipitates, leaving loops as they bypass two precipitates which act like pinning centres for the dislocations (→ leading to an increase in the dislocation density). q Both these processes need an application of higher stresses (assuming an harder precipitate) → lead to the strengthening of the material. q Semi-coherent precipitates have interfacial misfit dislocations which partially relieve the coherency strains. (These dislocations are structural dislocations)

Summary:Precipitate Hardening effect The hardening effect of precipitates can arise in many ways as below: Coherency Strengthening:due to elastic coherency strains surrounding the particle Modulus Hardening:due to difference in elastic moduli of the matrix and particle Lattice Resistance:the dislocation may face an increased lattice friction stress in the precipitate. Chemical Strengthening:arises from additional interface created on shearing Stacking-fault Strengthening:due to difference between stacking-fault energy between particle and matrix when these are both FCC or HCP(when dislocations are split into partials) Order Strengthening:due to additional work required to create an APB in case of dislocations passing through precipitates which have an ordered lattice
Summary: Precipitate Hardening effect 5 The hardening effect of precipitates can arise in many ways as below: q Coherency Strengthening: due to elastic coherency strains surrounding the particle q Modulus Hardening: due to difference in elastic moduli of the matrix and particle q Lattice Resistance: the dislocation may face an increased lattice friction stress in the precipitate. q Chemical Strengthening: arises from additional interface created on shearing q Stacking-fault Strengthening: due to difference between stacking-fault energy between particle and matrix when these are both FCC or HCP (when dislocations are split into partials) q Order Strengthening: due to additional work required to create an APB in case of dislocations passing through precipitates which have an ordered lattice
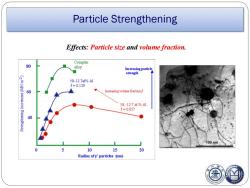
Particle Strengthening Effects:Particle size and volume fraction Complex 80 alloy Increasing particle strength Ni-12.7at%Al f=0139 60 Increasing volume fraction,f i-12.7at%A1 f=0.057 40 100nm 0 10 15 20 Radius ofy'particles (nm)
Particle Strengthening Ef ects: Particle size and volume fraction

经典第二相形貌 ●W-Y2O3 ·Cu-Al2O3 ·Fe-NbC(VC,TiC) ·Ni-gamma ·Al-析出相 国
经典第二相形貌 W-Y2O3 Cu-Al2O3 Fe-NbC (VC,TiC) Ni-gamma ’ Al-析出相
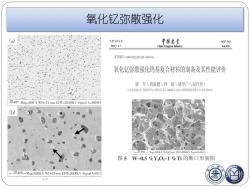
氧化钇你撒强化 第27卷第1期 中國篱菜 Vol.27.No.I 2012年2月 China Tungsten Industry Feh.2012 文章编号:1009-0622201201-0040-04 氧化钇弥散强化钨基复合材料的制备及其性能评价 谈军,周张健,钟铭,骆学广3,屈丹丹 山.北京科技大学材料科学马工学观,北京1003:2北京天是妈相科技有灵公司,北京10111》 20 m Mag=500 X WD=21 mm EHT=20.00kV Signal A=OBSD b T0 gm Mag300KX WD-21mm EHT-2000kV SignalA-SEI 图5W-0.5%Y,03-1%Ti的断口形貌图 10 umMag-300KX WD-21mm EHT-2000kV Signal A-SEI 世当
氧化钇弥散强化

氧化铝你撒强化 2012年8月 材料开发与应用 ·27· 文章编号:1003H545(2012)04002707 弥散强化铜弥散相特征与其性能的关系 王永朝,刘国元,付自来,陈会东,雷竹芳,李文甫 (中国船舶重工集团公司等七二五研究所,河南洛阳471023) (a)BF (b)DF 图9ODSC20横截面上的纳米氧化铝的分布
氧化铝弥散强化
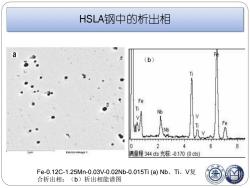
HSLA钢中的析出相 a (b) Ti Fe Ti Nb Ti Fe 0 2 4 6 8 Zum Electron Image 1 满量程344cts光标-0.170(0cts) Fe-0.12C-1.25Mn-0.03V-0.02Nb-0.015Ti(a))Nb、Ti、V复 合析出相; (b)析出相能谱图
HSLA钢中的析出相 Fe-0.12C-1.25Mn-0.03V-0.02Nb-0.015Ti (a) Nb、Ti、V复 合析出相;(b)析出相能谱图 (b)

Ni-gamma 1pm JEOL X10:,000 15.0kV SEI SEM WD 6.4mm
Ni-gamma’
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)04 细晶强化 Grain refinement.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)04 晶界工程与强韧化 More On Grain Boundary Engineering.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)03 位错强化 Dislocation Strengthening(2/2).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)03 位错强化 Dislocation Strengthening(1/2).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)02 固溶强化 Solid Solution(1/2).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)02 固溶强化 Solid Solution(1/2).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)10 复习 Excersices.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)01 Introduction and deformation mechanism(主讲:赵冰冰、万见峰).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《材料工程导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)面向产业的材料工程(动力与能源)航空发动机与燃气轮机.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料工程导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)身边的材料工程.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料工程导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)课程简介、概述.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料工程导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)面向产业的材料工程——航空航天.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料工程导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)面向产业的材料工程——交通运输产业.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料工程导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)面向产业的材料工程——交通运输产业.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料工程导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)材料工程中的创新——TRIZ创新研究方法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料工程导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)材料工程前沿技术(材料基因组、3D打印技术、同步辐射技术).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料工程导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)生物医用材料.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料工程导论》课程教学资源(2016课件)身边的材料工程.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料工程导论》课程教学资源(2016课件)概述.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料工程导论》课程教学资源(2015课件)面向产业的材料工程——高端装备制造(航空发动机与燃气轮机).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)05 第二相颗粒 Particle strengthening(1/2).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)06 强烈塑性变形 Severe Plastic Deformation(SPD).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)07 典型强化案例——超轻超强铝合金 Al.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)08 镁合金 Mg、钛合金 Ti.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)09 汽车轻量化 Steel.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)材料的相变、微观组织与强韧化——复合组织与材料强韧化.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)珠光体组织与材料强韧化(1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)珠光体组织与材料强韧化(2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)贝氏体组织与材料的强韧化(3/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)贝氏体组织与材料的强韧化(1/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)贝氏体组织与材料的强韧化(2/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)马氏体组织与材料强韧化(1/2)马氏体与马氏体相变、马氏体组织的形态.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)马氏体组织与材料强韧化(2/2)马氏体组织的强度、塑性和韧性、基于马氏体强韧化技术路径.ppt
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)NOVEL ULTRA-HIGH STRAINING PROCESS FOR BULK MATERIALSÐDEVELOPMENT OF THE ACCUMULATIVE ROLL-BONDING(ARB)PROCESS.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Performance and applications of nanostructured materials produced by severe plastic deformation.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Applying the texture analysis for optimizing thermomechanical treatment of high manganese twinning-induced plasticity steel.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Mechanisms of Radiation-Induced Viscous Flow:Role of Point Defects.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Averback Point defect movement and annealing in collision cascades.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Constrained groove pressing and its application to grain refinement of aluminum.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Microstructural evolution over a large strain range in aluminium deformed by cyclic-extrusion–compression.pdf
