上海交通大学:《现代材料科学实验方法前沿》课程教学资源_三维原子探针(3D)Atom probe

(3D)Atom probe Lanting Zhang School of Materials Science and Engineering SJTU lantingzh@sjtu.edu.cn Courtesy:Prof.Dr.Hono (NIMS)
(3D) Atom probe Lanting Zhang School of Materials Science and Engineering, SJTU lantingzh@sjtu.edu.cn Courtesy: Prof. Dr. Hono (NIMS)

Why atom probe? Chemistry at nano/atomic-scale The advantages and disadvantages of other way around?
Why atom probe? • Chemistry at nano/atomic-scale •The advantages and disadvantages of other way around? 2

Spatial resolution and detection limit 100% 10% TEM AES SEM Raman XPS XRD 1% FTIR 0.1% nano- SIMS WDS U-PIXE U-XRF XRF 100 ppm 10 ppm TOF-SIMS 1 ppm ICP-MS/ 100 ppb INAA SIMS LA-ICP-MS 10ppb APT Tppb 100 ppt Nano Micro Bulk 10 ppt Atom probe 0.1nm 1 nm 10 nm 100nm 1μm 10 um 100μm 1mm 1 cm tomography is superior in Elemental composition sensitivity and EDS EELS EBSD CL Structural information spatial resolution. Surface and thin film analysis ED EDS SEM and TEM host multiple techniques 3 http://www.ammrf.org.au/myscope/analysis/introduction/ TEM SEM
Spatial resolution and detection limit 3 http://www.ammrf.org.au/myscope/analysis/introduction/ Atom probe tomography is superior in sensitivity and spatial resolution
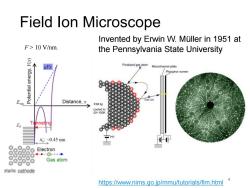
Field lon Microscope Invented by Erwin W.Muller in 1951 at F>10 V/nm. the Pennsylvania State University eFx Poralized gas atom Microchannel plate Phosphor screen Distance,x Gas ion E、w FIMbp cooled to 20-100K Tunnelng xe:-0.45 nm 88 Electron 4◆0--声 Gas atom etallic cathode https://www.nims.go.jp/mmu/tutorials/fim.html
Field Ion Microscope F > 10 V/nm. https://www.nims.go.jp/mmu/tutorials/fim.html Invented by Erwin W. Müller in 1951 at the Pennsylvania State University 4
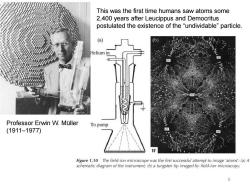
This was the first time humans saw atoms some 2,400 years after Leucippus and Democritus postulated the existence of the "undividable"particle. (a) (b Helium in Professor Erwin W.Muller To pump (1911-1977) W Figure 1.10 The field-ion microscope was the first successful attempt to image'atoms':(a)A schematic diagram of the instrument;(b)a tungsten tip imaged by field-ion microscopy. 5
5 Professor Erwin W. Müller (1911–1977) This was the first time humans saw atoms some 2,400 years after Leucippus and Democritus postulated the existence of the “undividable” particle
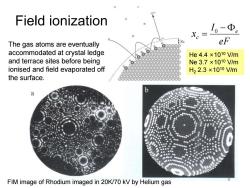
Field ionization 10-Φ。 X。= The gas atoms are eventually Xc eF accommodated at crystal ledge He4.4×1010V/m and terrace sites before being Ne3.7×1010V/m ionised and field evaporated off H22.3×1010V/m the surface. a FIM image of Rhodium imaged in 20K/70 kV by Helium gas
Field ionization eF I x e c − = 0 He 4.4 ×1010 V/m Ne 3.7 ×1010 V/m H2 2.3 ×1010 V/m FIM image of Rhodium imaged in 20K/70 kV by Helium gas 6 The gas atoms are eventually accommodated at crystal ledge and terrace sites before being ionised and field evaporated off the surface
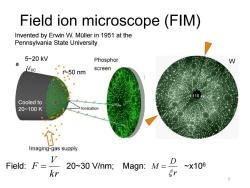
Field ion microscope(FIM) Invented by Erwin W.Muller in 1951 at the Pennsylvania State University 5~20kV Phosphor W a oc screen r~50 nm Cooled to 20~100K lonisation Imaging-gas supply V Field:= 20~30 V/nm; Magn:M=D ~X106 kr r 7
Field ion microscope (FIM) 7 Invented by Erwin W. Müller in 1951 at the Pennsylvania State University W kr V F = r D M = Cooled to 20~100 K 5~20 kV r~50 nm Field: Magn: ~x106 20~30 V/nm; 110
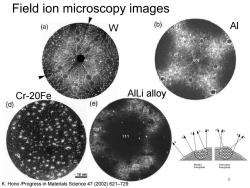
Field ion microscopy images (a) W () AI Cr-20Fe AlLi alloy (d) (e) Blunted Protruding Precipitate Precipitate -10nm 8 K.Hono /Progress in Materials Science 47(2002)621-729
Field ion microscopy images K. Hono /Progress in Materials Science 47 (2002) 621–729 W Al Cr-20Fe AlLi alloy 8
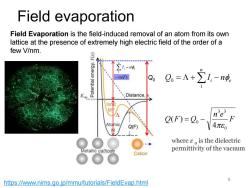
Field evaporation Field Evaporation is the field-induced removal of an atom from its own lattice at the presence of extremely high electric field of the order of a few V/nm. ∑1,-n neFx RQ,=A+2-陵 E Distance, M 33 Q(F)=2- F Atomic Q(F) 4π80 where &o is the dielectric Metallic cathode permittivity of the vacuum Cation 9 https://www.nims.go.jp/mmu/tutorials/FieldEvap.html
L e n i I − n 1 e n i Q = L +I − n 1 Q0 0 Q(F) F n e Q F Q 0 3 3 0 4 ( ) = − https://www.nims.go.jp/mmu/tutorials/FieldEvap.html Field evaporation Field Evaporation is the field-induced removal of an atom from its own lattice at the presence of extremely high electric field of the order of a few V/nm. 9 where ε 0 is the dielectric permittivity of the vacuum
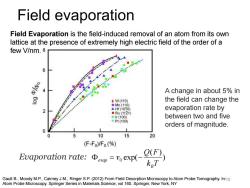
Field evaporation Field Evaporation is the field-induced removal of an atom from its own lattice at the presence of extremely high electric field of the order of a few V/nm.8 6 A change in about 5%in 8 ◆W(110) the field can change the ■M0(110) ▲Hf(1010) evaporation rate by ■Ru(1121) ●r(100) between two and five Pt(100) orders of magnitude. 0 L 5 10 15 20 (F-F)Fo(%) vaporation rate:vexp(- Gault B.,Moody M.P.,Cairney J.M.,Ringer S.P.(2012)From Field Desorption Microscopy to Atom Probe Tomography.In:10 Atom Probe Microscopy.Springer Series in Materials Science,vol 160.Springer,New York,NY
) ( ) exp( 0 k T Q F v B evap = − Field evaporation Gault B., Moody M.P., Cairney J.M., Ringer S.P. (2012) From Field Desorption Microscopy to Atom Probe Tomography. In: Atom Probe Microscopy. Springer Series in Materials Science, vol 160. Springer, New York, NY Evaporation rate: A change in about 5% in the field can change the evaporation rate by between two and five orders of magnitude. 10 Field Evaporation is the field-induced removal of an atom from its own lattice at the presence of extremely high electric field of the order of a few V/nm
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(课堂练习)exam_example4.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(课堂练习)exam_example3.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(课堂练习)exam_example2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》课程教学资源(课堂练习)exam_example1.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Application of Twist Extrusion.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)An investigation of surface nanocrystallization mechanism in Fe induced by surface mechanical attrition treatment.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Making strong nanomaterials ductile with gradients.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Science_Dislocation Mean Free Paths and Strain Hardening of Crystals.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Science_Hardening by Annealing and Softening by Deformation in Nanostructured Metals.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)MICROSTRUCTURES AND DISLOCATION CONFIGURATIONS IN NANOSTRUCTURED Cu PROCESSED BY REPETITIVE.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Aging behavior and tensile properties of 6061A1-0.3 um Al2O3p particle composites produced.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Recent developments in advanced aircraft aluminium alloys.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Rapid hardening induced by electric pulse annealing in nanostructured pure aluminum.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)On mechanical properties and superplasticity of Mg–15Al–1Zn alloys processed by reciprocating extrusion.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Dislocation multi-junctions and strain hardening.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Nanostructured Titanium for Biomedical Applications.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Nanostructured steel for automotive body structures.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)Ultra-Fine Grain Development in an AZ31 Magnesium Alloy during Multi-Directional Forging under Decreasing Temperature Conditions.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)NANOSTRUCTURED METALS Less is more 2006.pdf
- 《金属材料强韧化与组织调控》教学资源(参考文献)EFFECTS OF FRICTION STIR WELDING ON MICROSTRUCTURE OF 7075 ALUMINUM.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《现代材料科学实验方法前沿》课程教学资源_原位透射电子显微技术在材料的研究进展.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《现代材料科学实验方法前沿》课程教学资源_同步辐射原理实验技术讲课 Synchrotron Radiation Properties and Production.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《现代材料科学实验方法前沿》课程教学资源_多尺度关联的组织结构表征方法 Correlative multi-scale characterization(1/2)INTRODUCTION TO ANALYTICAL ELECTRON MICROSCOPY.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《现代材料科学实验方法前沿》课程教学资源_多尺度关联的组织结构表征方法 Correlative multi-scale characterization(2/2)CORRELATIVE MULTI-SCALE CHARACTERIZATION.pdf
- 《现代材料科学实验方法前沿》课程教学资源:热分析简明教程(热分析实验和哲理).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《合成材料 Composite Materials》课程教学资源(讲义,1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《合成材料 Composite Materials》课程教学资源(讲义,2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料应用和实践 Materials Applications and Practices》课程教学资源_Materials applications in nuclear power equipments.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料应用和实践 Materials Applications and Practices》课程教学资源_MT333 Course Introduction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料应用和实践 Materials Applications and Practices》课程教学资源_MT333 Course Project Guideline.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料应用和实践 Materials Applications and Practices》课程教学资源_MT333 Superalloys A-Materials & Applications in Aerospace.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料应用和实践 Materials Applications and Practices》课程教学资源_MT333 Superalloys in Aerospace(Superalloys Additive Manufacturing).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料应用和实践 Materials Applications and Practices》课程教学资源_MT333 Superalloys in Aerospace(Superalloys Subtractive Manufacturing).pdf
- 《材料应用和实践 Materials Applications and Practices》课程教学资源(阅读材料)How to write a paper.pdf
- 《材料应用和实践 Materials Applications and Practices》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Tool Condition Monitoring in?Machining Superalloys.pdf
- 《材料应用和实践 Materials Applications and Practices》课程教学资源(阅读材料)PROCESS DEVELOPMENT AND APPROACH FOR 3D PROFILE GRINDING/POLISHING.pdf
- 《材料应用和实践 Materials Applications and Practices》课程教学资源(阅读材料)ADAPTIVE ROBOTIC SYSTEM FOR 3D PROFILE GRINDING/POLISHING.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料科学与工程前沿》课程教学资源(案例讲座)微电子材料与产业.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料科学与工程前沿》课程教学资源(案例讲座)一代大飞机、一代新材料.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《材料科学与工程前沿》课程教学资源(案例讲座)工程类研究生课《临床医学与材料》(1/2).pdf
